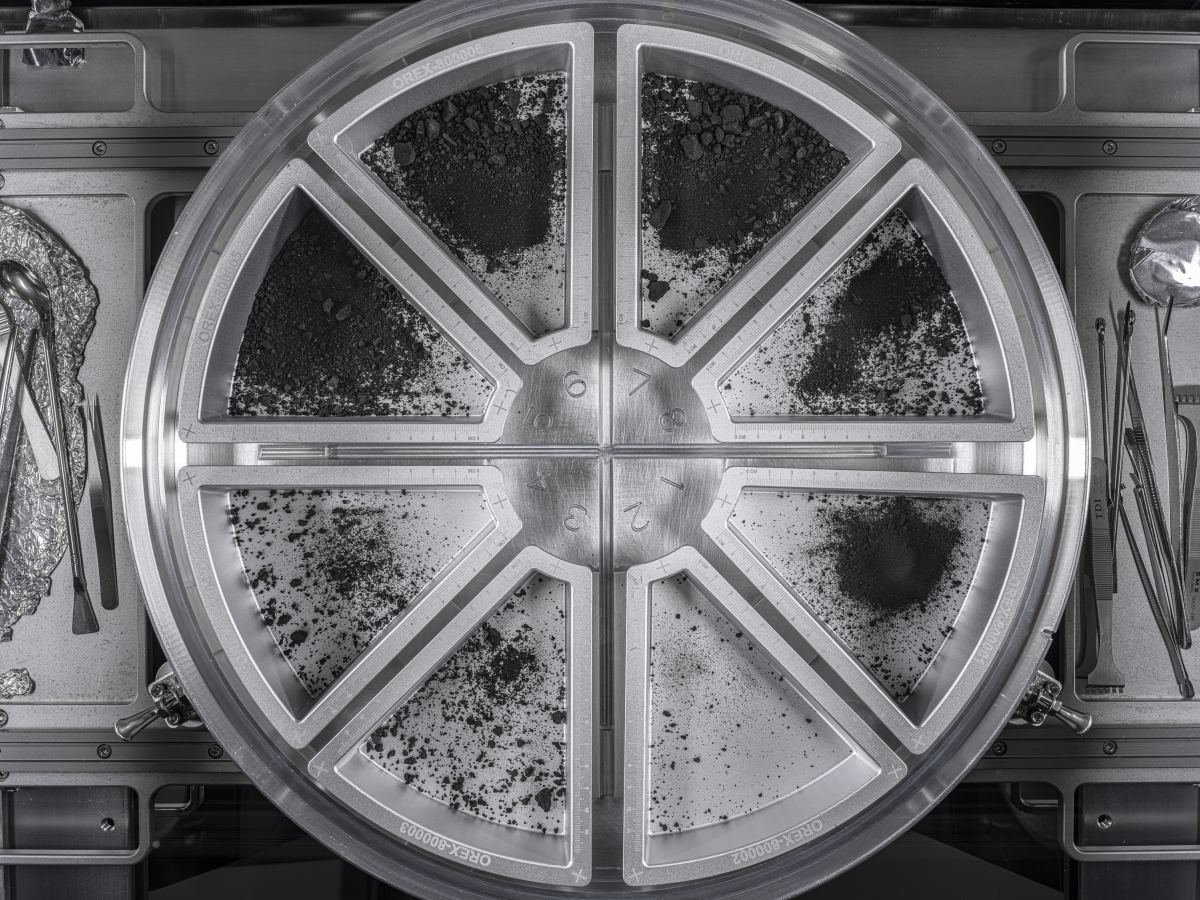
After several months of meticulous, careful work, NASA has the final total for their haul of asteroidal material from the OSIRIS-REx mission to Bennu. The highly successful mission successfully collected 121.6 grams, or almost 4.3 ounces, of rock and dust. It won’t be long before scientists get their hands on these samples and start analyzing them.
Continue reading “OSIRIS-REx’s Final Haul: 121.6 Grams from Asteroid Bennu”OSIRIS-REx’s Final Haul: 121.6 Grams from Asteroid Bennu