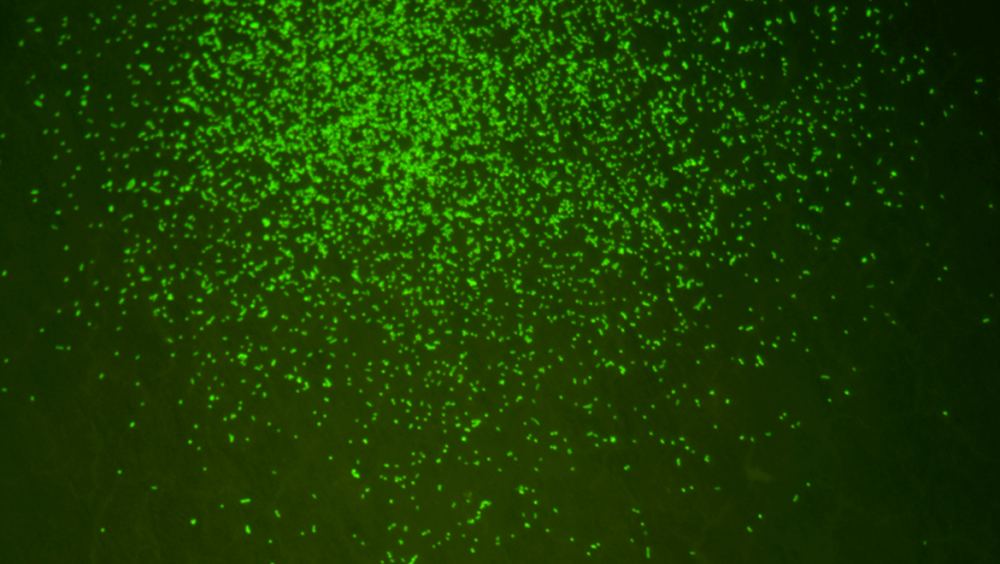
At the bottom of the ocean in the South Pacific Gyre, there’s a sediment layer that is among the most nutrient-starved environments on Earth. Because of conditions in that area, there’s almost no “marine snow”—the shower of organic debris common in the ocean—that falls to the ocean floor. Without all that organic debris falling to the floor, there’s a severe lack of nutrients there, and that makes this one of the least hospitable places on Earth.
A team of researchers took sediment samples from that area, and extracted 101.5 million year old microbes. When they “fed” those microbes, they sprang back to life.
The results are expanding our knowledge of microbial life and how long it can be dormant when conditions force it to be.
Continue reading “Microbes Were Dormant for Over 100 Million Years, But They Were Able to Spring Back to Life”