It’s easy to imagine the excitement NASA personnel must have felt when an amateur astronomer contacted NASA to tell them that he might have found their missing IMAGE satellite. After all, the satellite had been missing for 10 years.
IMAGE, which stands for Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration, was launched on March 25th, 2000. In Dec. 2005 the satellite failed to make routine contact, and in 2007 it failed to reboot. After that, the mission was declared over.

It’s astonishing that after 10 years, the satellite has been found. It’s even more astonishing that it was an amateur who found it. As if the story couldn’t get any more interesting, the amateur astronomer who found it—Scott Tilly of British Columbia, Canada—was actually looking for a different missing satellite: the secret ZUMA spy satellite launched by the US government on January 7, 2018. (If you’re prone to wearing a tin foil hat, now might be a good time to reach for one.)

After Tilly contacted NASA, they hurried to confirm that it was indeed IMAGE that had been found. To do that, NASA employed 5 separate antennae to seek out any radio signals from the satellite. As of Monday, Jan. 29, signals received from all five sites were consistent with the radio frequency characteristics expected of IMAGE.
In a press release, NASA said, “Specifically, the radio frequency showed a spike at the expected center frequency, as well as side bands where they should be for IMAGE. Oscillation of the signal was also consistent with the last known spin rate for IMAGE.”
“…the radio frequency showed a spike at the expected center frequency…” – NASA Press Release confirming the discovery of IMAGE
Then, on January 30, the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Lab (JHUAPL) reported that they had successfully collected telemetry data from the satellite. In that signal was the ID code 166, the code for IMAGE. There were probably some pretty happy people at NASA.
So, now what?
NASA’s next step is to confirm without a doubt that this is indeed IMAGE. That means capturing and analyzing the data in the signal. That will be a technical challenge, because the types of hardware and operating systems used in the IMAGE Mission Operations Center no longer exist. According to NASA, “other systems have been updated several versions beyond what they were at the time, requiring significant reverse-engineering.” But that should be no problem for NASA. After all, they got Apollo 13 home safely, didn’t they?
If NASA is successful at decoding the data in the signal, the next step is to attempt to turn on IMAGE’s science payload. NASA has yet to decide how to proceed if they’re successful.
IMAGE was the first spacecraft designed to “see the invisible,” as they put it back then. Prior to IMAGE, spacecraft examined Earth’s magnetosphere by detecting particles and fields they encountered as they passed through them. But this method had limited success. The magnetosphere is enormous, and simply sampling a small path—while better than nothing—did not give us an accurate understanding of it.
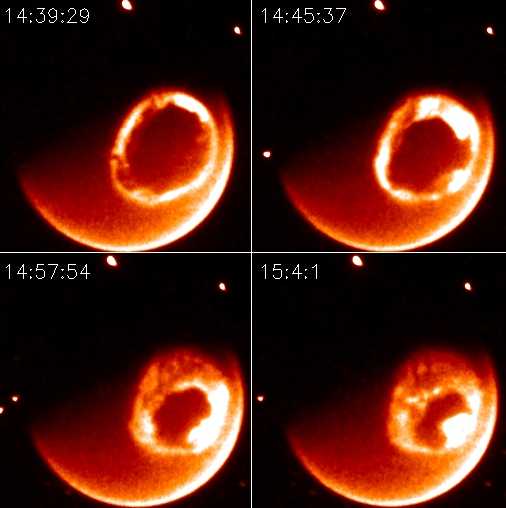
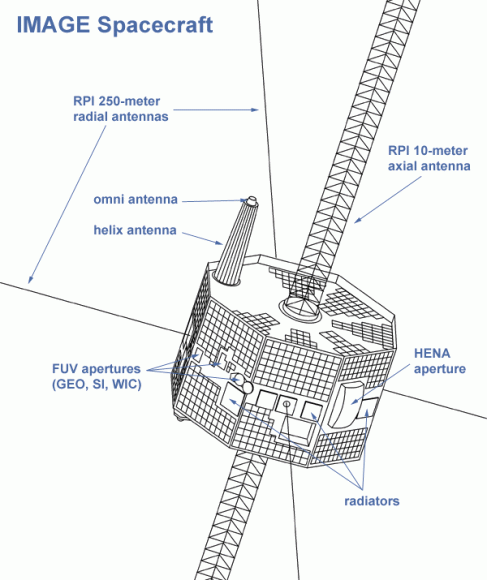
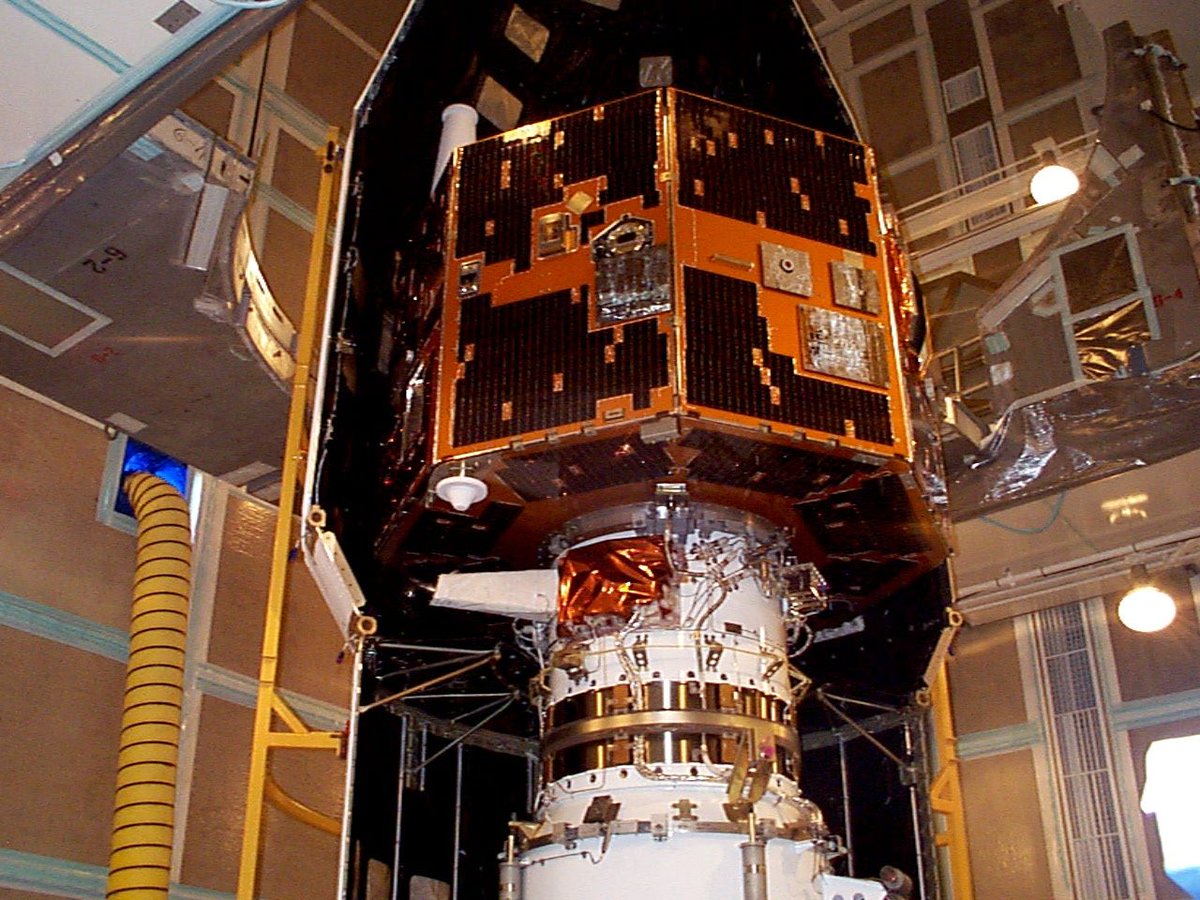
IMAGE was going to do things differently. It used 3-dimensional imaging techniques to measure simultaneously the densities, energies and masses of charged particles throughout the inner magnetosphere. To do this, IMAGE carried a payload of 7 instruments:
- High Energy Neutral Atom (HENA) imager
- Medium Energy Neutral Atom (MENA) imager
- Low Energy Neutral Atom (LENA) imager
- Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) imager
- Far Ultraviolet (FUV) imager
- Radio Plasma Imager (RPI)
- Central Instrument Data Processor (CIDP)
These instruments allowed IMAGE to not only do great science, and to capture great images, but also to create some stunning never-seen-before movies of auroral activity.
This is a fascinating story, and it’ll be interesting to see if NASA can establish meaningful contact with IMAGE. Will it have a treasure trove of unexplored data on-board? Can it be re-booted and brought back into service? We’ll have to wait and see.
This story is also interesting culturally. IMAGE was in service at a time when the internet wasn’t as refined as it is currently. NASA has mastered the internet and public communications now, but back then? Not so much. For example, to build up interest around the mission, NASA gave IMAGE its own theme song, titled “To See The Invisible.” Yes, seriously.
But that’s just a side-note. IMAGE was all about great science, and it accomplished a lot. You can read all about IMAGE’s science achievements here.





















![The Viking 2 lander captured this image of itself on the Martian surface. The Viking Landers were the last missions to directly look for life on Mars. By NASA - NASA website; description,[1] high resolution image.[2], Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=17624](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/608px-Viking2lander1-580x458.jpg)