When Elon Musk of SpaceX tweets something interesting, it generates a wave of excitement. So when he tweeted recently that SpaceX might be working on a way to retrieve upper stages of their rockets, it set off a chain of intrigued responses.
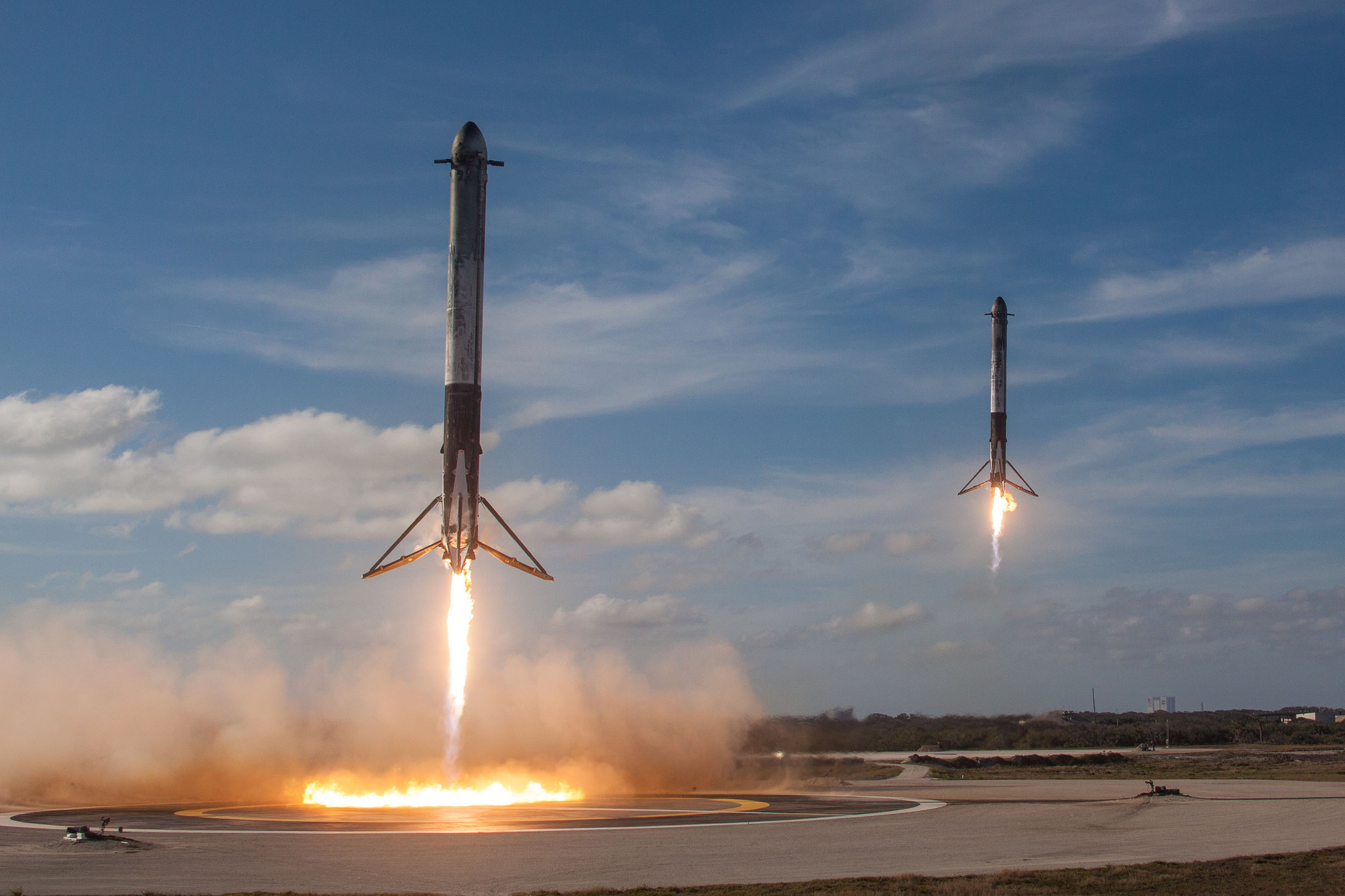
SpaceX has been retrieving and reusing their lower stages for some time now, and it’s lowered the cost of launching payloads into space. But this is the first hint that they may try to do the same with upper stages.
Twitter responders wanted to know exactly what SpaceX has in mind, and what a “giant party balloon” might be. Musk hasn’t elaborated yet, but one of his Twitter followers had something interesting to add.
Quinn Kupec, a student at the University of Maryland’s James Clark School of Engineering tweeted to Musk:
Universe Today contacted Mr. Kupec to see if he could help us understand what Musk may have been getting at. But first, a little background.
An “ultra low ballistic entry coefficient decelerator” is a bit of a mouthful. The ballistic coefficient measures how well a vehicle can overcome air resistance in flight. A high ballistic coefficient means a re-entry vehicle would not lose velocity quickly, and would reach Earth at high speeds. An ultra low ballistic entry coefficient decelerator would lose speed quickly, meaning that a vehicle would be travelling at low, subsonic speeds before reaching the ground.
To recover an upper stage booster, low speeds are desirable, since they generate less heat. But according to Kupec, there’s another problem that must be overcome.
“What happens when these things slow down to landing velocities? If your center of gravity is offset significantly behind your center of drag, as would be the case with a returning upper stage, it can get unstable. If the center of gravity of the re-entry vehicle is too high, it can become inverted, which is obviously not desirable.”
So the trick is to lower the speed of the re-entry vehicle to the point where the heat generated by reentry isn’t damaging the booster, and to do it without causing the vehicle to invert or otherwise become unstable. This isn’t a problem for the main stage boosters that SpaceX now routinely recovers; they have their own retro-rockets to guide their descent and landing. But for the upper stage boosters, which reach orbital velocities, it’s an obstacle that has to be overcome.
“My research is specifically focused on how high you can push the center of gravity and still maintain the proper flight configuration,” said Kupec.
But what about the “giant party balloon” that Musk tweeted about?
Musk could be referring, in colorful terms, to what’s called a ballute. The word is a combination of the words balloon and parachute. They were invented in the 1950’s by Goodyear Aerospace. They can arrest the descent of entry vehicles and provide stability during the descent.
“…the balloon would have to be 120 ft. in diameter, and made of a high-temperature fabric…” – Professor Dave Akin, University of Maryland
Universe Today contacted Professor Dave Akin of the University of Maryland for some insight into Musk’s tweet. Professor Akin has been working on reentry systems for over 2 decades.
In an e-mail exchange, Professor Akin told us, “There have been concepts proposed for deploying a large balloon on a cable that is towed behind you on entry. The balloon lowers your ballistic coefficient, which means you decelerate higher in the atmosphere and the heat load is less.” So the key is to scrub your speed before you get closer to Earth, where the atmosphere is thicker and generates more heat.
But according to Professor Akin, this won’t necessarily be easy to do. “To get the two orders of magnitude reduction in ballistic coefficient that Elon has been talking about the balloon would have to be 120 ft. in diameter, and made of a high-temperature fabric, so it’s not going to be all that easy.”
But Musk’s track record shows he doesn’t shy away from things that aren’t easy.
Retrieving upper rocket stages isn’t all about lowering launch costs, it’s also about space junk. The European Space Agency estimates that there are over 29,000 pieces of space junk orbiting Earth, and some of that junk is spent upper stage boosters. There have been some collisions and accidents already, with some satellites being pushed into different orbits. In 2009, the Iridium 33 communications satellite and the defunct Russian Cosmos 2251 communications satellite collided with each other, destroying both. If SpaceX can develop a way to retrieve its upper stage boosters, that means less space junk, and fewer potential collisions.
There’s a clear precedent for using balloons to manage reentry. With people like Professor Akin and Quinn Kupec working on it, SpaceX won’t have to reinvent the wheel. But they’ll still have a lot of work to do.
Musk tweeted one other thing shortly after his “giant party balloon” tweet:
No word yet on what that might mean.
Elon Musk’s “giant party balloon” tweet: https://twitter.com/elonmusk/status/985655249745592320
Quinn Kupec’s tweet: https://twitter.com/QuinnKupec/status/985736260827471872