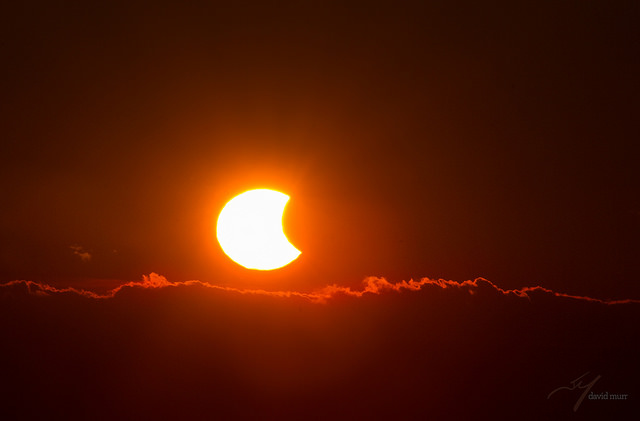
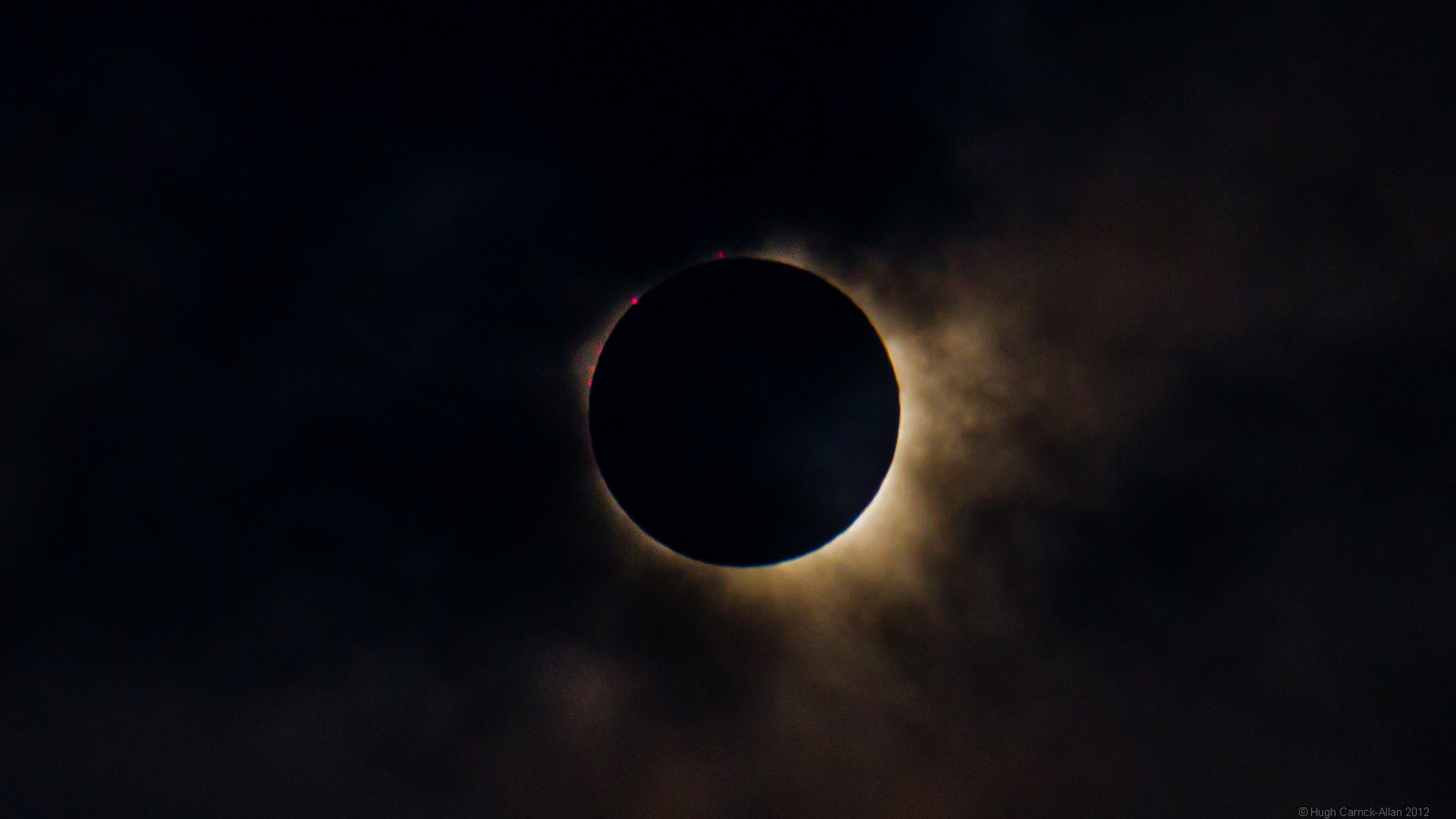
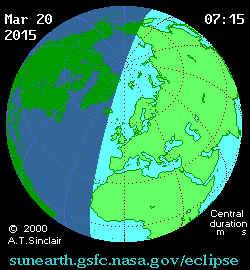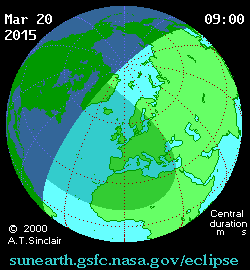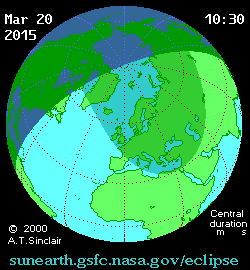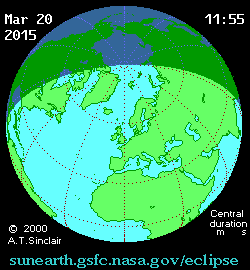
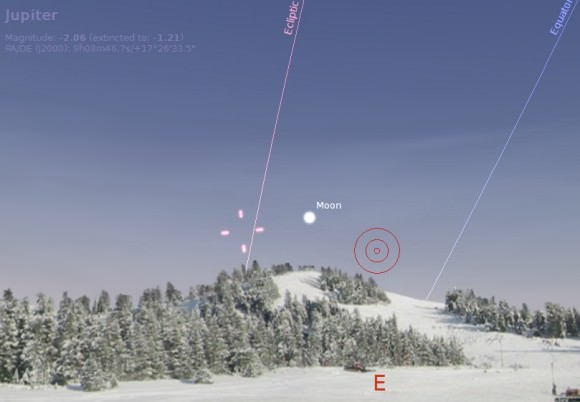
The first eclipse of 2015 is coming right up on Friday, March 20th, and may provide a unique challenge for solar energy production across Europe.
Sure, we’ve been skeptical about many of the websites touting a ‘blackout’ and Y2K-like doom pertaining to the March 20th total solar eclipse as of late. And while it’s true that comets and eclipses really do bring out the ‘End of the World of the Week’ -types across ye ole web, there’s actually a fascinating story of science at the core of next week’s eclipse and the challenge it poses to energy production.
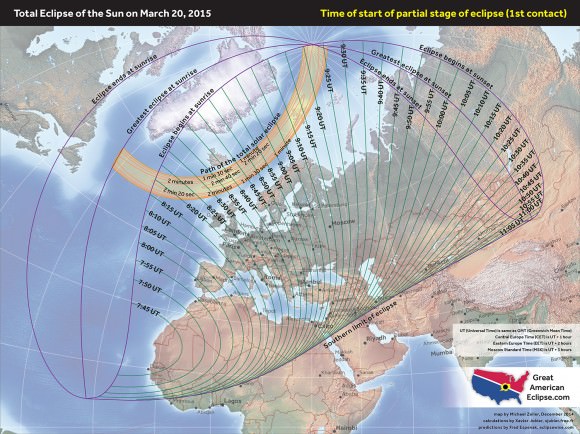
But first, a brief recap of the eclipse itself. Dubbed the “Equinox Eclipse,” totality only occurs over a swath of the North Atlantic and passes over distant Faroe and Svalbard Islands. Germany and central Europe can expect an approximately 80% partially obscured Sun at the eclipse’s maximum.
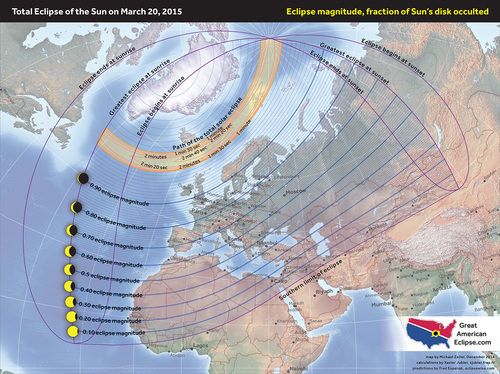
We wrote a full guide with the specifics for observing this eclipse yesterday. But is there a cause for concern when it comes to energy production?
A power grid is a huge balancing act. As power production decreases from one source, other sources must be brought online to compensate. This is a major challenge — especially in terms of solar energy production.
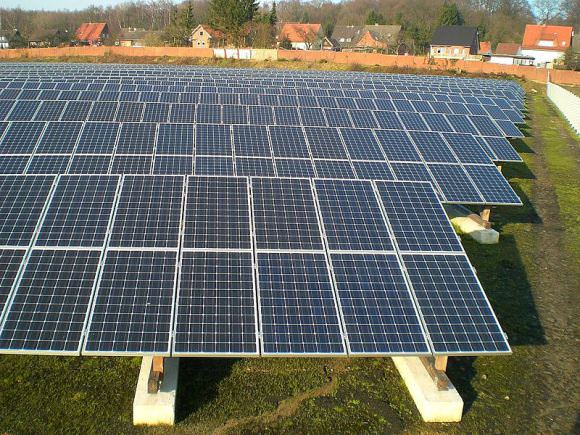

Germany currently stands at the forefront of solar energy technology, representing a whopping quarter of all solar energy capacity installed worldwide. Germany now relies of solar power for almost 7% of its annual electricity production, and during the sunniest hours, has used solar panels to satisfy up to 50% of the country’s power demand.
We recently caught up with Barry Fischer to discuss the issue. Fischer is the Head Writer at Opower, a software company that uses data to help electric and gas utilities improve their customer experience. Based on Opower’s partnerships with nearly 100 utilities worldwide, the company has amassed the world’s largest energy dataset of its kind which documents energy consumption patterns across more than 55 million households around the globe.
A study published last week by Opower highlights data from the partial solar eclipse last October over the western United States. There’s little historical precedent for the impact that an eclipse could have on the solar energy grid. For example, during the August 11th, 1999 total solar eclipse which crossed directly over Europe, less than 0.1% of utility electricity was generated using solar power.
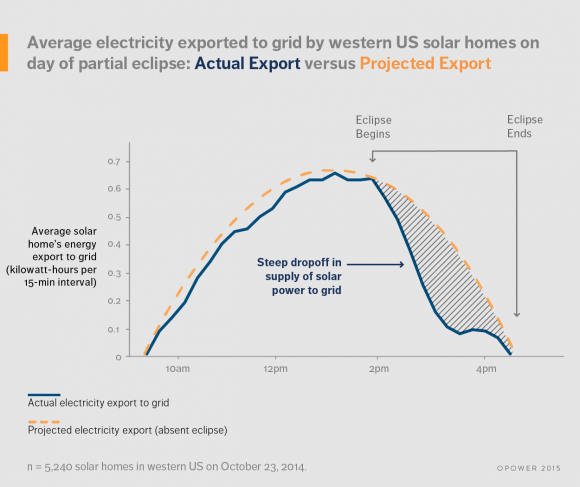
What they found was intriguing. Although the 2014 partial solar eclipse only obscured 30 to 50% of the Sun, solar electric production dropped over an afternoon span of nearly three hours before returning to a normal pattern.
Examining data from 5,000 solar-powered homes in the western United States, Opower found that during the eclipse those homes sent 41% less electricity back to the grid than normal. Along with a nearly 1,000 megawatt decline in utility-scale solar power production, these drop-offs were compensated for by grid operators ramping up traditional thermal power plants that were most likely fueled by natural gas.
No serious problems were experienced during the October 23rd, 2014 partial solar eclipse in terms of solar electricity production in the southwestern United States, though it is interesting to note that the impact of the eclipse on solar energy production could be readily detected and measured.
How does the drop and surge in solar power output anticipated for the March 20th eclipse differ from, say, the kind presented by the onset of night, or a cloudy day? “The impact of an eclipse can register broadly – and unusually rapidly – across an entire region,” Fischer told Universe Today. On a small scale, one area many be cloudy, while on a larger regional scale, other areas of clear or partly sunny skies can compensate. An eclipse — even a partial one — is fundamentally different, because the sudden onset and the conclusion are relatively uniform over a large region.
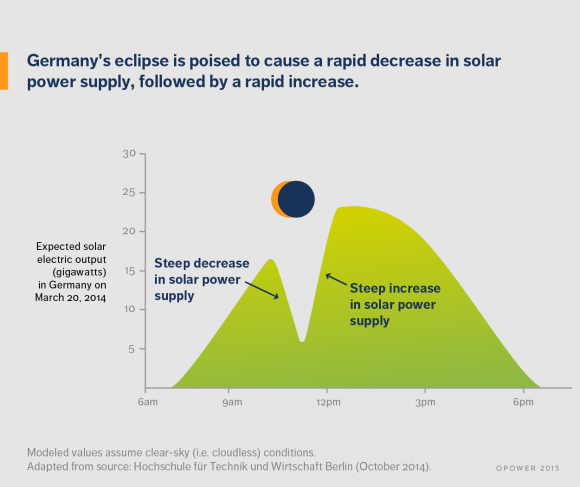
The March 20th event offers an unprecedented chance to study the effects of an eclipse on large-scale solar production up close. A study (in German) by the University of Applied Sciences in Berlin suggests that solar power production will fall at a rate 2.7 times faster than usual as the eclipse progresses over a span of 75 minutes. This is the equivalent of switching off one medium-sized power plant per minute.
The anticipated slingshot might be just as challenging, as 18 gigawatts of power comes back online at the conclusion of the eclipse in just over an hour. And as opposed to the 2014 eclipse over the U.S. which ended towards sunset, the key rebound period for the March 20th eclipse will be around local noon and during a peak production time.
Fischer also noted that “the second half of the partial solar eclipse will also pose a notable challenge” for the grid, as it is flooded with solar power production 3.5 times faster than normal. This phenomenon could also serve as a great model for what could occur daily on a grid that’s increasingly solar power reliant in the future, as energy production ramps up daily at sunrise. Such a reality may be only 15 years away, as Germany projects installed solar capacity to top 66 gigawatts by 2030.

What’s the anticipated impact projected for a future eclipse such as, say, the 2017 and 2024 total solar eclipses over the U.S.?
This eclipse may serve as a great dry run for modeling what could occur as reliance on solar energy production grows.
Such is the modern technical society we live in. It’s fascinating to think that eclipses aren’t only a marvelous celestial spectacle, but their effects on power production may actually serve as a model for the smart grids of tomorrow.