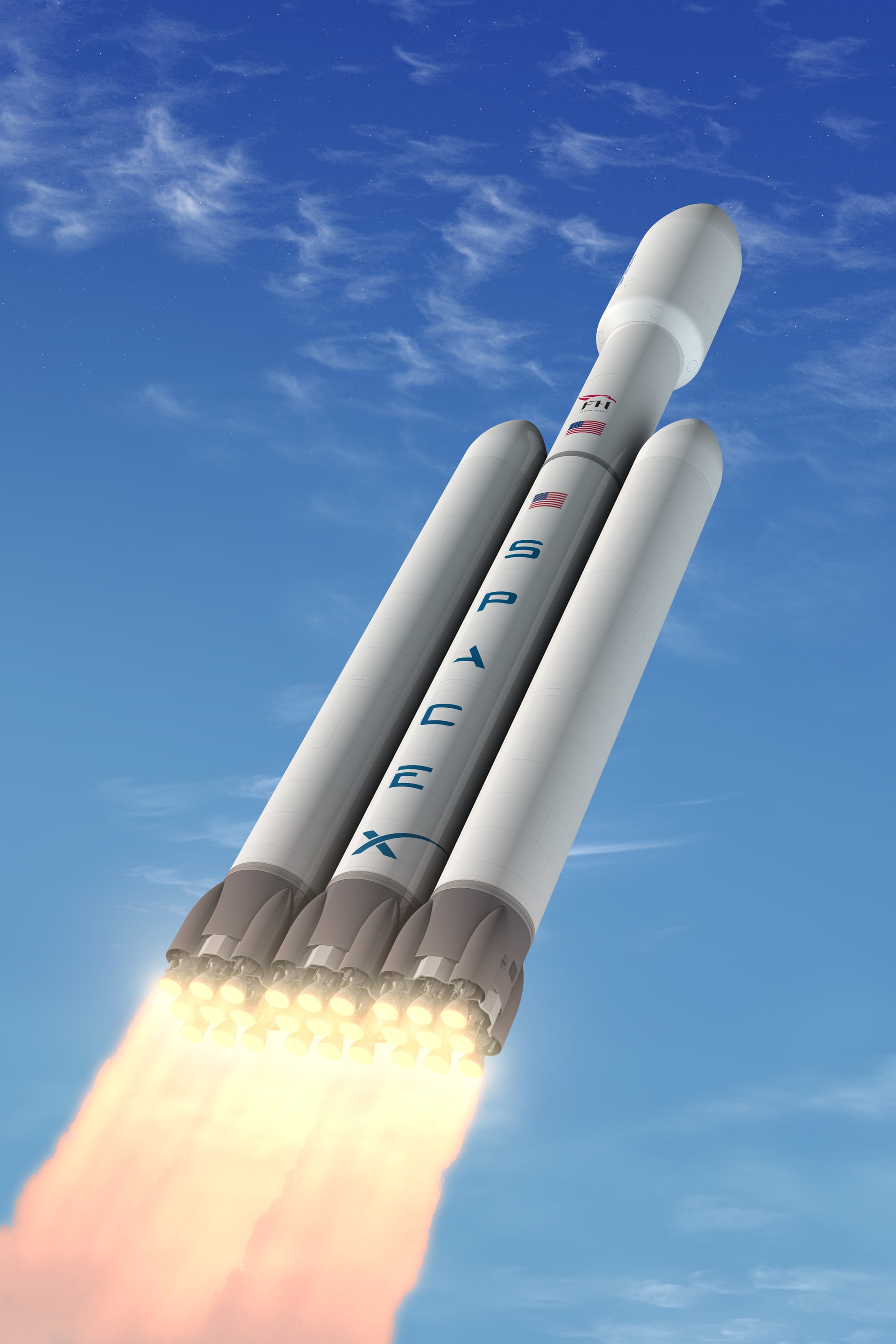
[/caption]Elon Musk, the CEO and chief rocket designer of Space Exploration Technologies (SpaceX) announced today (April 5) that SpaceX will build and launch the world's most
powerful rocket
- dubbed the Falcon Heavy - within two years.
Musk said that he expects SpaceX will
launch
the first Falcon Heavy by late 2012 or early 2013 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California.
"We are excited to announce the Falcon Heavy and only recently completed the design," said Musk.
"Falcon Heavy will carry more payload to
orbit
or escape velocity than any
vehicle
in history, apart from the Saturn V
moon
rocket, which was decommissioned after the Apollo program. This opens a new world of capability for both
government
and commercial
space
missions."
Musk unveiled the design plans for the privately developed, 227 foot tall
heavy lift rocket
at a briefing for reporters at the National Press Club in Washington, DC.
"This is a
rocket
of truly huge scale."
Falcon Heavy would
lift
from 100,000 to 120,000 pounds to orbit, about three times the
performance
of the Falcon 9. It is comprised of three nine- engine Falcon 9 first stage booster cores and would utilize upgraded Merlin 1D engines currently being tested at the SpaceX rocket development facility in McGregor, Texas. The Falcon booster cores would be the first to have cross feed propellant capability enabling significant enhancements in payload
performance
, Musk explained.
"We expect to launch a lot, maybe 20 launches per year," said Musk. He thinks that the launches would be spilt about equally between the current Falcon 9 and the new Falcon Heavy allowing SpaceX to compete in the full gamut of opportunities for commercial rocket providers. The Falcon Heavy could even be used for
interplanetary
science
missions to
Mars
and elsewhere in the
Solar System
(watch for follow up article).
[caption id="attachment_84641" align="aligncenter" width="580" caption="With over 3.8 million pounds of thrust at liftoff, Falcon Heavy will be the most capable rocket flying. By comparison, the liftoff thrust of the Falcon Heavy equals fifteen Boeing 747 aircraft at full power. Credit: SpaceX"]
[/caption]
The Falcon Heavy would also be launched from
Cape Canaveral
after upgrading the existing Falcon 9 pad at the Cape. Indeed a majority of launches is expected from Florida vs. California.
SpaceX is in discussions with NASA to also possibly use one of the
shuttle pads at Launch Complex 39
at the
Kennedy Space Center
. Both launch pads will be vacant
after the shuttle stops flying
later this year.
"First launch from our Cape Canaveral launch complex is planned for late 2013 or 2014," Musk said.
The new heavy lift booster will have twice the performance capability of
NASA's retiring Space shuttle fleet
or the
Delta IV Heavy
according to Musk.
"The Falcon Heavy will have more payload capability than any rocket since the Saturn V moon rocket."
Musk said the Falcon Heavy will be dramatically cheaper and more cost effective compared to current
rockets
and set new world records in affordability and cost per pound. "The cost will be about $1000 per pound to orbit." That price is a long sought and near mythical goal. It is also a critical selling point during these times of flat, very tight and declining budgets.
SpaceX says they are offering the Falcon 9 for some $50-60M and the Falcon Heavy for $80-$125M per launch. They say this compares to the projected
Air Force
average cost of $435M per launch for the 2012 budget year.
"The Falcon Heavy will be about one third the cost of the
Delta IV
Heavy and with twice the performance. That's about 6 times more cost effective," Musk stated. "That's a pretty huge leap in capability."
SpaceX will finance the cost of the first demonstration launch. The rocket will only loft several small payloads unless some organization is willing to take a gamble for a reduced cost. Without being specific, Musk added that SpaceX has had "strong interest from
U.S. government
agencies and commercial entities" for the second launch and beyond. "No one wants to be first." [caption id="attachment_84643" align="aligncenter" width="580" caption="Comparison of Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy offerd by SpaceX. Credit: SpaceX"]
[/caption]
Ensuring reliability is key to SpaceX future. Musk explained that the Falcon Heavy is also designed to meet
NASA human rating
standards, unlike other satellite launch vehicles. The rocket is designed to meet higher structural safety margins of 40% above flight loads, rather than the 25% level of other rockets, and triple redundant avionics.
To date, SpaceX has launched two Falcon 9 rockets. NASA has awarded SpaceX with a $1.6 billion contract to conduct a minimum of twelve Falcon 9 flights with the Dragon spacecraft to deliver at least 20,000 kg of cargo to resupply the International Space Station (ISS) after the Space Shuttle is retired.
Musk said that there is a lot to be learned and applied from using high volume production techniques used in the automotive industry while maintaining stringent quality control.
The date of the frist Falcon Heavy launch is expected to depend greatly on regulatory requirements, just like the maiden launch of the Falcon 9.
[caption id="attachment_84646" align="aligncenter" width="580" caption="The Falcon Heavy is SpaceX's entry into the heavy lift launch vehicle category. Capable of lifting over 32,000 kg to Low Earth Orbit (LEO), and over 19,500 kg to Geostationary Transfer Orbit (GTO), the Falcon Heavy will compete with the largest commercial launchers now available. It consists of a standard Falcon 9 with two additional Falcon 9 first stages acting as liquid strap-on boosters. With the Falcon 9 first stage already designed to support the additional loads of this configuration and with common tanking and engines across both vehicles, development and operation of the Falcon Heavy will be highly cost-effective. Credit: SpaceX"]
[/caption]
Watch a SpaceX YouTube video about Falcon Heavy here:
 Universe Today
Universe Today