What if someone were to tell you that at any given moment, you were traveling at speeds well in excess of the speed of sound? You might think they were crazy, given that - as best as you could tell - you were standing on solid ground, and not in the cockpit of a supersonic jet. Nevertheless, the statement is correct. At any given moment, we are all moving at a speed of about 1,674 kilometers an hour, thanks to the Earth's rotation,
By definition, the Earth's rotation is the amount of time that it takes to rotate once on its axis. This is, apparently, accomplished once a day - i.e. every 24 hours. However, there are actually two different kinds of rotation that need to be considered here. For one, there's the amount of time it take for the Earth to turn once on its axis so that it returns to the same orientation compared to the rest of the Universe. Then there's how long it takes for the Earth to turn so that the Sun returns to the same spot in the sky.
Solar vs. Sidereal Day:
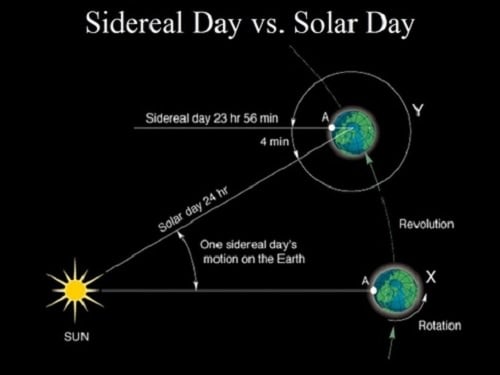
As we all know, it takes exactly 24 hours for the Sun to return to the same spot in the sky, which would seem obvious. 24 hours is what we think of as being a complete day, and the time it takes to transition from day to night and back again. But in truth, it actually takes the Earth 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.09 seconds to turn rotate once on its axis compared to the background stars.
Why the difference? Well, that would be because the Earth is orbiting around the Sun, completing one orbit in just over 365 days. If you divide 24 hours by 365 days, you'll see that you're left with about 4 minutes per day. In other words, the Earth rotates on its axis, but it's also orbiting around the Sun, so the Sun's position in the sky catches up by 4 minutes each day.
[caption id="attachment_11875" align="aligncenter" width="800"]
The night sky, showing 6 hours of rotation captured by long-exposure. Credit: Chris Schur
[/caption]
The amount of time it takes for the Earth to rotate once on its axis is known as a
sidereal day
- which is 23.9344696 hours. Because this type of day-measurement is based on the Earth's position relative to the stars, astronomers use it as a time-keeping system to keep track of where stars will appear in the night sky, mainly so they will know which direction to point their telescopes in.
The amount of time it takes for the Sun to return to the same spot in the sky is called a solar day, which is 24 hours. However, this varies through the year, and the accumulated effect produces seasonal deviations of up to 16 minutes from the average. This is caused by two factors, which include the Earth's elliptical orbit around the Sun and it's axial tilt.
Orbit and Axial Tilt:
As
Johannes Kepler
stated in his
(1609), the Earth and Solar planets do not rotate about the Sun in perfect circles. This is known as
Kepler's First Law
, which states that "the orbit of a planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun's center of mass at one focus". At perihelion (i.e. its closest) it is 147,095,000 km (91,401,000 mi) from the Sun; whereas at aphelion, it is 152,100,000 km (94,500,000 mi).
This change in distance means that the Earth's orbital speed increases when it is closest to the Sun. While its speed averages out to about 29.8 km/s (18.5 mps) or 107,000 km/h (66487 mph), it actually ranges by a full km per second during the course of the year - between 30.29 km/s and 29.29 km/s (109,044 - 105,444 km/h; 67,756.8 - 65,519.864 mph).
[caption id="attachment_117033" align="aligncenter" width="580"]
Earth's axial tilt (or obliquity) and its relation to the rotation axis and plane of orbit as viewed from the Sun during the Northward equinox. Credit: NASA
[/caption]
At this rate, it takes the Sun the equivalent of 24 hours - i.e. one solar day - to complete a full rotation about the Earth's axis and return to the meridian (a point on the globe that runs from north to south through the poles). Viewed from the vantage point above the north poles of both the Sun and Earth, Earth orbits in a counterclockwise direction about the Sun.
This Earth's rotation around the Sun, or the precession of the Sun through the equinoxes, is the reason a year lasts approximately 365.2 days. It is also for this reason that every four years, an extra day is required (a February 29th during every Leap Year). Also, Earth's rotation about the Sun is subject to a slight eccentricity of (0.0167°), which means that it is periodically closer or farther from the Sun at certain times of the year.
Earth's axis is also inclined at approximately 23.439° towards the ecliptic. This means that when the Sun crosses the equator at both equinoxes, it's daily shift relative to the background stars is at an angle to the equator. In June and December, when the Sun is farthest from the celestial equator, a given shift along the ecliptic corresponds to a large shift at the equator.
So apparent solar days are shorter in March and September than in June or December. In northern temperate latitudes, the Sun rises north of true east during the summer solstice, and sets north of true west, reversing in the winter. The Sun rises south of true east in the summer for the southern temperate zone, and sets south of true west.
Rotational Velocity:
As stated earlier, the Earth's is spinning rather rapidly. In fact, scientists have determined that Earth's rotational velocity at the equator is 1,674.4 km/h. This means that just by standing on the equator, a person would already be traveling at a speed in excess of the speed of sound in a circle. But much like measuring a day, the Earth's rotation can be measured in one of two different ways.
Earth's rotation period relative to the fixed stars is known as a "stellar day", which is
86,164.098903691 seconds
of mean solar time (or
23 hours, 56 minutes and 4.0989 seconds).
Earth's rotation period relative to the precessing or moving mean vernal equinox, meanwhile, is
23 hours 56 minutes and 4.0905 seconds of mean solar time. Not a major difference, but a difference nonetheless.
However, the planet is slowing slightly with the passage of time, due to the tidal effects the Moon has on Earth's rotation. Atomic clocks show that a modern day is longer by about 1.7 milliseconds than a century ago, slowly increasing the rate at which UTC is adjusted by leap seconds. The Earth's rotation also goes from the west towards east, which is why the Sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
[caption id="attachment_127109" align="aligncenter" width="500"]
Visualization of a sidereal day vs a solar day. Credit: quora.com
[/caption]
Earth's Formation:
Another interesting thing about the Earth's rotation is how it all got started. Basically, the planet's rotation is due to the angular momentum of all the particles that came together to create our planet 4.6 billion years ago. Before that, the Earth, the Sun and the rest of the Solar System were part of a giant molecular cloud of hydrogen, helium, and other heavier elements.
As the cloud collapsed down, the momentum of all the particles set the cloud spinning. The current rotation period of the Earth is the result of this initial rotation and other factors, including tidal friction and the hypothetical impact of
Theia
- a collision with a Mars-sized object that is thought to have taken place approx. 4.5 billion years ago and formed the Moon.
This rapid rotation is also what gives the Earth it's shape, flattening it out into an oblate spheroid (or what looks like a squished ball). This special shape of our planet means that points along the equator are actually further from the center of the Earth than at the poles.
[caption id="attachment_52841" align="aligncenter" width="580"]
Artist's impression what the Solar System looked like in the early stages of formation, as a dust cloud circling a star. Credit: JPL/NASA
[/caption]
History of Study:
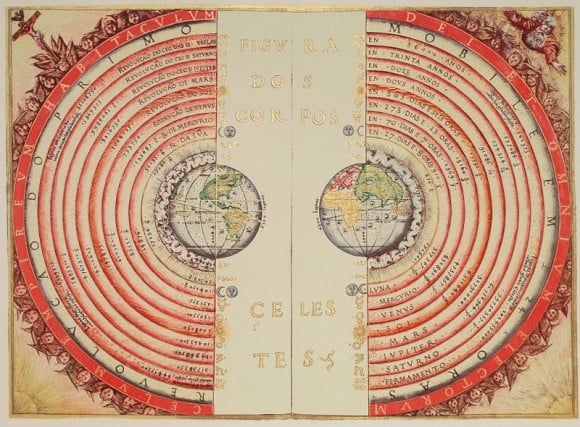
In ancient times, astronomers naturally believed that the Earth was a fixed body in the cosmos, and that the Sun, the Moon, the planets and stars all rotating around it. By classical antiquity, this became formalized into cosmological systems by philosophers and astronomers like Aristotle and Ptolemy - which later came to be known as the Ptolemaic Model (or
Geocentric Model
) of the universe.
However, there were those during Antiquity that questioned this convention. One point of contention was the fact that the Earth was not only fixed in place, but that it did not rotate. For instance, Aristarchus of Samos (ca. 310 – 230 BCE) published writings on the subject that were cited by his contemporaries (such as Archimedes). According to Archimedes, Aristarchus espoused that the Earth revolved around the Sun and that the universe was many times greater than previously thought.
And then there was Seleucis of Seleucia (ca. 190 – 150 BCE), a Hellenistic astronomer who lived in the Near-Eastern Seleucid empire. Seleucus was a proponent of the heliocentric system of Aristarchus, and may have even proven it to be true by accurately computing planetary positions and the revolution of the Earth around the Earth-Moon 'center of mass'.
[caption id="attachment_18098" align="aligncenter" width="580"]
An illustration of the Ptolemaic geocentric system by Portuguese cosmographer and cartographer Bartolomeu Velho, 1568. Credit: Bibliothèque Nationale, Paris
[/caption]
The geocentric model of the universe would also be challenged by medieval Islamic and Indian scholars. For instance, In 499 CE, Indian astronomer Aaryabhata published his magnum opus
Aryabhatiya
, in which he proposed a model where the Earth was spinning on its axis and the periods of the planets were given with respect to the Sun.
The 10th-century Iranian astronomer Abu Sa'id al-Sijzi contradicted the Ptolemaic model by asserting that the Earth revolved on its axis, thus explaining the apparent diurnal cycle and the rotation of the stars relative to Earth. At about the same time, Abu Rayhan Biruni 973 – 1048) discussed the possibility of Earth rotating about its own axis and around the Sun – though he considered this a philosophical issue and not a mathematical one.
At the Maragha and the Ulugh Beg (aka. Samarkand) Observatory, the Earth's rotation was discussed by several generations of astronomers between the 13th and 15th centuries, and many of the arguments and evidence put forward resembled those used by Copernicus. It was also at this time that Nilakantha Somayaji published the
Aryabhatiyabhasya
(a commentary on the
Aryabhatiya
)
in which he advocated a partially heliocentric planetary model. This was followed in 1500 by the
in which Somayaji incorporated the Earth's rotation on its axis.
In the 14th century, aspects of heliocentricism and a moving Earth began to emerge in Europe. For example, French philosopher Bishop Nicole Oresme (ca. 1320-1325 to 1382 CE) discussed the possibility that the Earth rotated on its axis. However, it was Polish astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus who had the greatest impact on modern astronomy when, in 1514, he published his ideas about a heliocentric universe in a short treatise titled
Commentariolus
("Little Commentary").
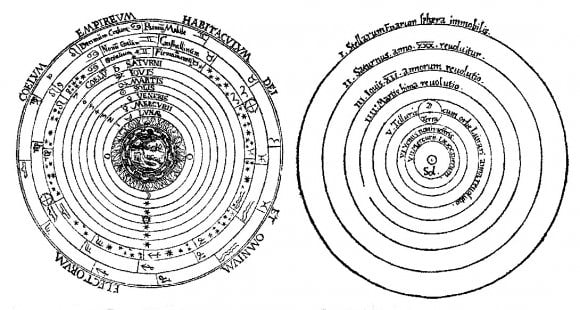
[caption id="attachment_121160" align="aligncenter" width="580"]
A comparison of the geocentric and heliocentric models of the universe. Credit: history.ucsb.edu
[/caption]
Like others before him, Copernicus built on the work of Greek astronomer Atistarchus, as well as paying homage to the Maragha school and several notable philosophers from the Islamic world (see below). Intrinsic to his model was the fact that the Earth, and all the other planets, rolved around the Sun, but also that the Earth revolved on its axis and was orbited by the Moon.
In time, and thanks to scientists such as Galileo and
Sir Isaac Newton
, the motion and revolution of our planet would become an accepted scientific convention. With the advent of the Space Age, the deployment of satellites and atomic clocks, we have not only confirmed that it is in constant motion, but have been able to measure the its orbit and rotation with incredibly accuracy.
In short, the world has been spinning since its inception. And, contrary to what some might say, it actually
is
slowing down, albeit at an incredibly slow rate. But of course, by the time it slows significantly, we will have likely ceased to exist, or slipped its "surly bonds" and become an interplanetary species.
We have written many interesting articles about the motions of the Earth here at Universe Today. Here's
How Fast Does The Earth Rotate?
,
Earth's Orbit Around The Sun
,
How Fast Does The Earth Rotate?
,
Why Does The Earth Spin?
,
What Would Happen If The Earth Stopped Spinning?
, and
What Is The Difference Between the Heliocentric and Geocentric Models Of The Solar System?
If you'd like more information on the Earth's rotation, check out
NASA's Solar System Exploration Guide on Earth
. And here's a link to
NASA's Earth Observatory
.
We've also recorded an episode of Astronomy Cast
all about Earth
. Listen here,
Episode 51: Earth
.
 Universe Today
Universe Today