In a recent study submitted to the Journal of the British Interplanetary Society for the 8th Interstellar Symposium special issue, which is due for publication sometime in 2024, Dr. Jacob Haqq-Misra, who is a senior research investigator and the Chief Operating Officer and co-founder at the Blue Marble Space Institute of Science, examines how future space exploration governing laws could evolve, either crewed or uncrewed and in the solar system or beyond. He views this study as an expansion of interplanetary governance models he previously discussed in his book, Sovereign Mars, to explore potential limits on space governance at interstellar distances.
Continue reading “The Outer Space Treaty was Signed in 1967. Can it Handle the Future of Space Exploration?”Record Setting Italian Female Astronaut and ISS Crewmates Land in Sunny Kazakhstan
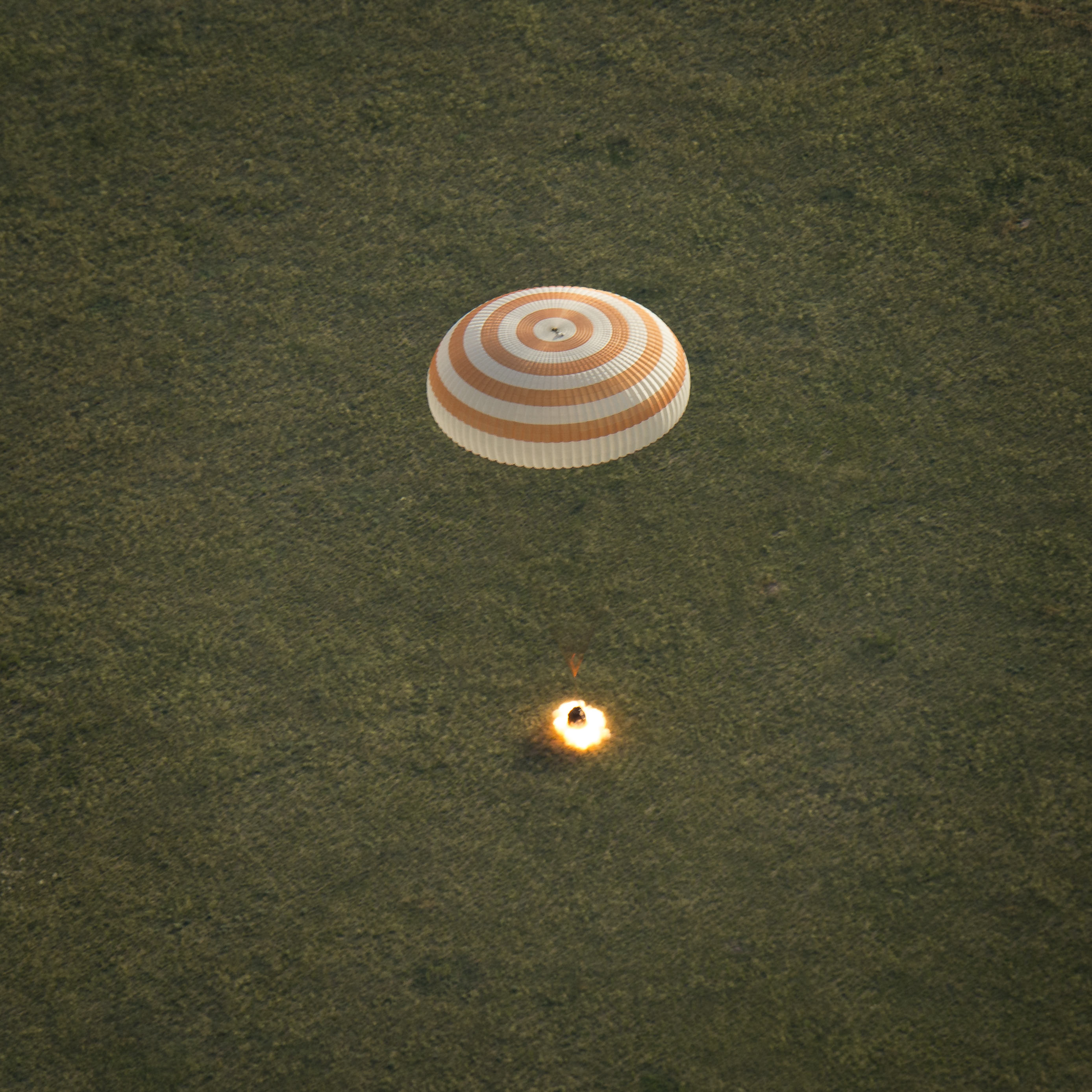

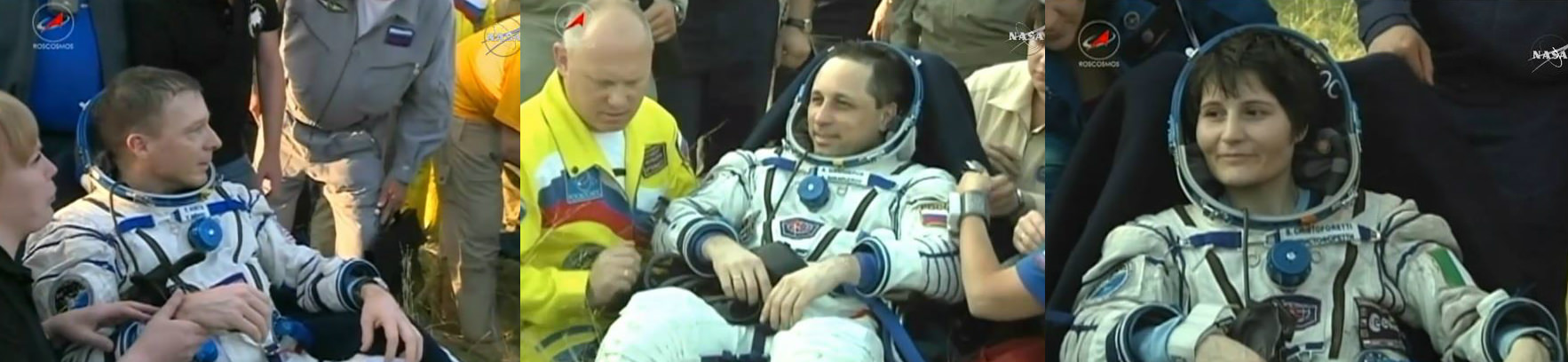
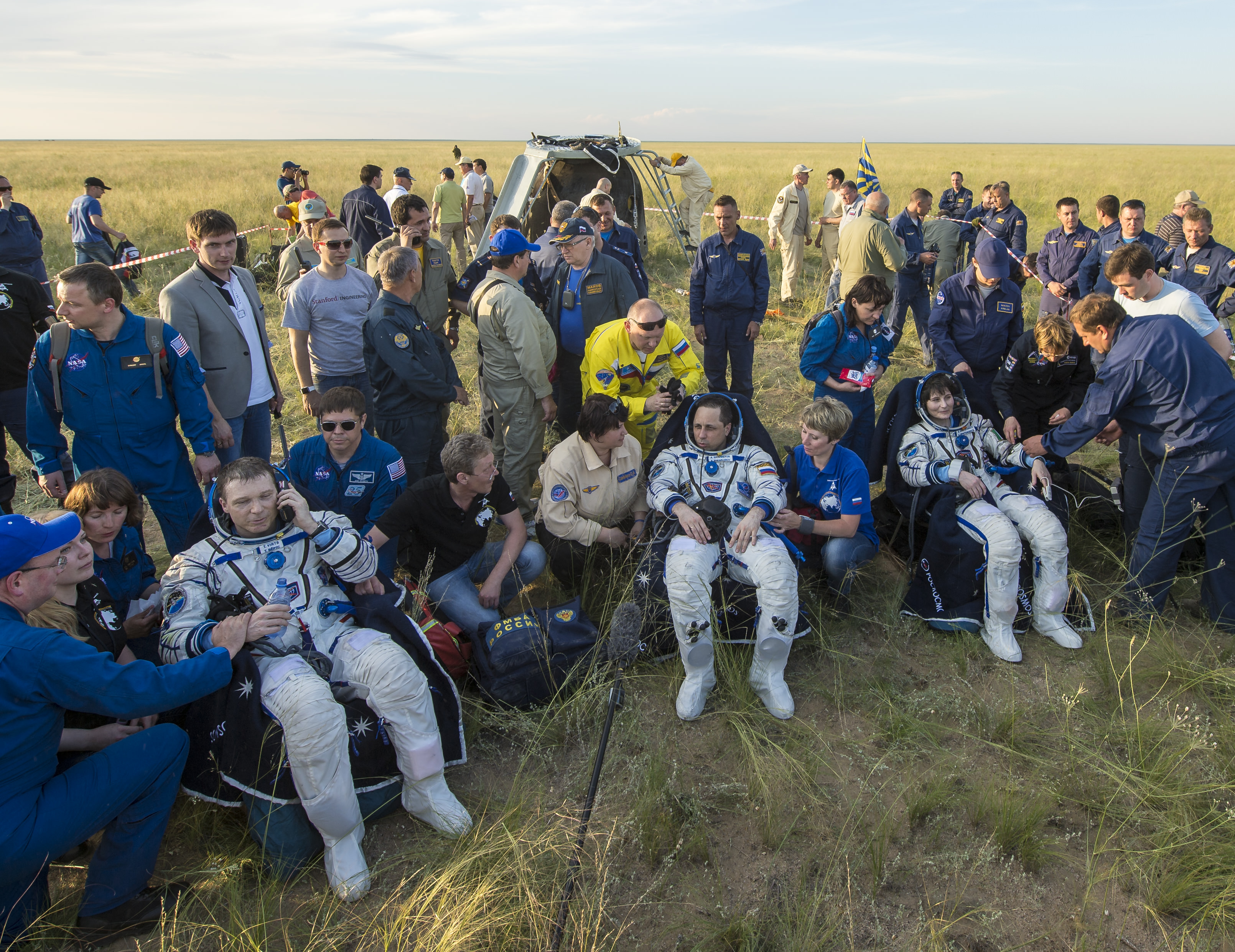
An international crew comprising a Russian cosmonaut, a US astronaut and an Italian astronaut who accomplished a record setting flight for time in space by a female, departed the International Space Station (ISS) earlier today, June 11, and safely landed in sunny and warm Kazakhstan tucked inside their Russia Soyuz ferry ship after a successful and extended 199-day mission devoted to science and station upgrades.
The multinational trio comprising Expedition 43 Commander Terry Virts of NASA, Flight Engineers Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) and Samantha Cristoforetti of ESA (European Space Agency) undocked from the orbiting outposts Russian Rassvet module as scheduled in the Soyuz TMA-15M spaceship at 6:20 a.m. EDT while soaring some 250 miles (400 kilometers) above Mongolia.
A four-minute 40-second deorbit burn at 8:51 a.m EDT slowed the craft for the fiery reentry into the Earth’s atmosphere.
The crew touched down just a few hours after undocking at 9:44 a.m. EDT (7:44 p.m., Kazakh time), southeast of the remote town of Dzhezkazgan on the steppes of Kazakhstan, about an hour and a half before sundown in delightfully summer weather. Temperatures today were in the 80s, but they are ‘bone chilling’ in the winter months.
The Expedition 43 flight was extended at the last minute due to the surprise launch failure of a Russian rocket carrying a station bound Progress resupply ship in late April.
The Progress 59 cargo vessel, also known as Progress M-27M, spun wildly out of control as it separated from the Soyuz-2.1A carrier rocket. The freighter and all its 2.5 tons of contents fpr the crew were destroyed during an uncontrolled plummet as its crashed back to Earth on May 8.
The Soyuz/Progress 59 failure had far reaching consequences and resulted in a postponement of virtually all Russian crew and cargo flights to the ISS for the remainder of 2015, as announced this week by Roscosmos, the Russian Federal Space Agency.
One result is that Cristoforetti now holds the single mission record for a female astronaut, of nearly 200 days.
Expedition 43 was extended by about a month in the wake of the launch failure of the Progress 59 cargo vessel, which quickly cascaded into an extended mission from its originally planned length of about 170 days to 199+ days.
The Soyuz is only certified to stay on orbit for 200 days. So the return home delayed as much as possible to minimize the time when the ISS reverts to only a three person crew – and consequently reduced time for research.
This past weekend on June 6, Cristoforetti surpassed the female astronaut record of 194 days, 18 hours and 2 minutes established by NASA astronaut Sunita Williams on a prior station flight back in 2007.
Cristoforetti, of the European Space Agency (ESA), is on her first ever space flight also counts as she also counts as Italy’s first female astronaut.
The station departure and parachute assisted soft landing was shown during a live webcast on NASA TV.
“The landing was on time and on target after over 199 days in space,” said NASA commentator Rob Navius.
“Everything went by the book for an on target touchdown. The crew is safely back on Earth!”

In the final stages of the return to Earth, the Soyuz descent module glided down safely using a single mammoth orange and white parachute, aided by braking rockets in the final moments just a few feet above ground.
The Soyuz landed upright, which eased the extraction of the crew. Russian recovery team members hoisted all three up and out from the cramped capsule.
Soyuz commander Anton Shkaplerov was hauled up first, followed by Samantha Cristoforetti and finally Terry Virts.
All three crewmembers were healthy and happy, each signaling their elation with a joyous ‘thumbs up.’
After preliminary medical checks, the crew were flown by helicopter to a staging base at Karaganda. From there they split up. Shkaplerov heads back to Moscow and Star City. Cristoforetti and Virts fly to Mission Control in Houston.
During their time aloft, the crew completed several critical spacewalks, technology demonstrations, and hundreds of scientific experiments spanning multiple disciplines, including human and plant biology,” according to NASA.
Among the research experiments conducted were “participation in the demonstration of new, cutting-edge technologies such as the Synthetic Muscle experiment, a test of a new polymer that contracts and expands similar to real muscle. This technology has the potential for future use on robots, enabling them to perform tasks that require considerable dexterity but are too dangerous to be performed by humans in space.”
“The crew engaged in a number of biological studies, including one investigation to better understand the risks of in-flight infections and another studying the effects microgravity has on bone health during long-duration spaceflight. The Micro-5 study used a small roundworm and a microbe that causes food poisoning in humans to study the risk of infectious diseases in space, which is critical for ensuring crew health, safety and performance during long-duration missions. The Osteo-4 study investigated bone loss in space, which has applications not only for astronauts on long-duration missions, but also for people on Earth affected by osteoporosis and other bone disorders.”
Three cargo flights also arrived at the ISS carrying many tons of essential supplies, research equipment, science experiments, gear, spare parts, food, water, clothing.
The resupply freighters included the Russian Progress in February 2015 as well as two SpaceX Dragon cargo ships on the CRS-5 and CRS-6 flights in January and April.

With the return of Virts crew, the new Expedition 44 begins and comprises NASA astronaut Scott Kelly and Russian cosmonauts Mikhail Kornienko, the two members of the first “ISS 1 Year Mission” as well as cosmonaut Gennady Padalka.
Padalka now assumes command of the station for a record setting fourth time. And he’ll soon be setting another record. In late June, he will break the all time record for cumulative time in space currently held by cosmonaut Sergei Krikalev of 803 days on six space flights.
When Padalka returns to Earth around September 10 in the Soyuz TMA-16M ship, that brought the 1 Year crew to the ISS, he will have been in space for a grand total of over 877 days over five flights.
The next cargo ferry flight involves NASA’s next contracted unmanned Dragon cargo mission by commercial provider SpaceX on the CRS-7 flight.
Dragon CRS-7 is now slated for liftoff on June 26. Watch for my onsite reports from KSC.
The Dragon will be carrying critical US equipment, known as the International Docking Adapter (IDA), enabling docking by the SpaceX Crew Dragon and Boeing CST-100 astronaut transporters – due for first crewed launches in 2017.
The most recent unmanned Dragon cargo CRS-6 mission concluded with a Pacific Ocean splashdown on May 21.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
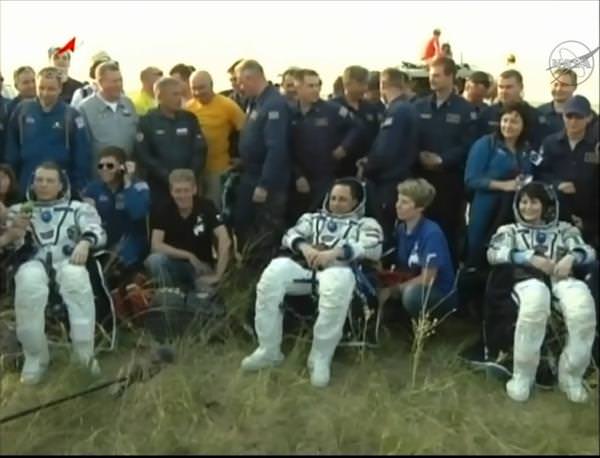

Return of the SpaceX-3 Dragon to Earth Caps Super Science Mission for NASA

SpaceX-3 Dragon commercial cargo freighter was detached from the ISS at 8 AM EDT on May 18, 2014 and released by station crew at 9:26 AM for splashdown in the Pacific Ocean with science samples and cargo. Credit: NASA
Story updated[/caption]
The 30 day flight of the SpaceX-3 Dragon commercial cargo freighter loaded with a huge cache of precious NASA science experiments including a freezer packed with research samples ended today with a spectacular departure from the orbiting lab complex soaring some 266 miles (428 km) above Earth.
Update 3:05 PM EDT May 18: SpaceX confirms successful splashdown at 3:05 p.m. EDT today.
“Splashdown is confirmed!! Welcome home, Dragon!”
Robotics officers at Mission Control at NASA’s Johnson Space Center detached Dragon from the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module at 8 a.m. EDT (1300 GMT) this morning, Sunday, May 18, 2014 using the stations Canadian-built robotic arm.
Engineers had earlier unbolted all 16 hooks and latches firmly connecting the vehicle to the station in preparation.
NASA astronaut Steve Swanson then commanded the gum dropped shaped Dragon capsule’s release from Canadarm2 as planned at 9:26 a.m. EDT (1326 GMT) while the pair were flying majestically over southern Australia.
The undocking operation was shown live on NASA TV.
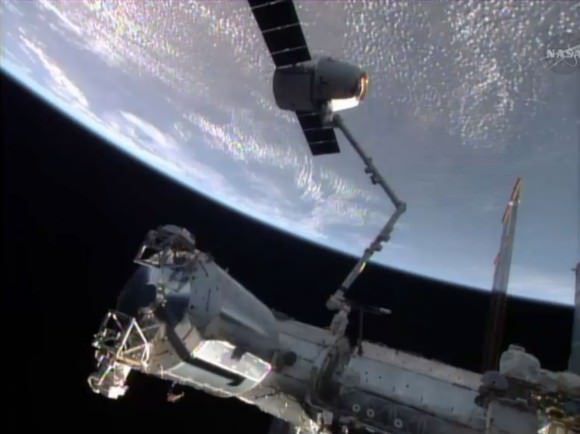

Swanson was assisted by Russian cosmonaut Alexander Skvortsov as the US- Russian team were working together inside the domed Cupola module.
Following the cargo ships release by the 57 foot long arms grappling snares, Swanson carefully maneuvered the arm back and away from Dragon as it moved ever so slowly in free drift mode.
It was already four feet distant within three minutes of release.
Three departure burns by the Dragon’s Draco maneuvering thrusters followed quickly in succession and occurred precisely on time at 9:29, 9:30 and 9:38 a.m. EST.
Dragon exited the 200 meter wide keep out zone – an imaginary bubble around the station with highly restricted access – at the conclusion of the 3rd departure burn.
“The Dragon mission went very well. It was very nice to have a vehicle take science equipment to the station, and maybe some day even humans,” Swanson radioed after the safe and successful departure was completed.
“Thanks to everyone who worked on the Dragon mission.”
The private SpaceX Dragon spent a total of 28 days attached to the ISS.
The six person international crew from Russia, the US and Japan on Expeditions 39 and 40 unloaded some 2.5 tons of supplies aboard and then repacked it for the voyage home.
The SpaceX resupply capsule is carrying back about 3500 pounds of spacewalk equipment, vehicle hardware, science samples from human research, biology and biotechnology studies, physical science investigations and education activities, as well as no longer needed trash.
“The space station is our springboard to deep space and the science samples returned to Earth are critical to improving our knowledge of how space affects humans who live and work there for long durations,” said William Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for human exploration and operations.
“Now that Dragon has returned, scientists can complete their analyses, so we can see how results may impact future human space exploration or provide direct benefits to people on Earth.”
Among the research investigations conducted that returned samples in the cargo hold were an examination of the decreased effectives of antibiotics in space, better growth of plants in space, T-Cell activation in aging and causes of human immune system depression in the microgravity environment.
The 10 minute long deorbit burn took place as scheduled at 2:10 p.m. EDT (1810 GMT) today.
Dragon returned to Earth for a triple parachute assisted splash down today at around 3:02 p.m. EDT (19:02 GMT) in the Pacific Ocean – some 300 miles west of Baja California.

It will be retrieved by recovery boats commissioned by SpaceX. The science cargo will be extracted and then delivered to NASA’s Johnson Space Center within 48 hours.
Dragon thundered to orbit atop SpaceX’s powerful new Falcon 9 v1.1 rocket on April 18, from Cape Canaveral, Fla.
This unmanned Dragon delivered about 4600 pounds of cargo to the ISS including over 150 science experiments, a pair of hi tech legs for Robonaut 2, a high definition Earth observing imaging camera suite (HDEV), the laser optical communications experiment (OPALS), the VEGGIE lettuce growing experiment as well as essential gear, spare parts, crew provisions, food, clothing and supplies to the six person crews living and working aboard in low Earth orbit.

It reached the ISS on April 20 for berthing.
Dragon is the only unmanned resupply vessel supply that also returns cargo back to Earth.
The SpaceX-3 mission marks the company’s third resupply mission to the ISS under the $1.6 Billion Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract with NASA to deliver 20,000 kg (44,000 pounds) of cargo to the ISS during a dozen Dragon cargo spacecraft flights through 2016.
The SpaceX Dragon is among a trio of American vehicles, including the Boeing CST-100 and Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser vying to restore America’s capability to fly humans to Earth orbit and the space station by late 2017, using seed money from NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) in a public/private partnership. The next round of contracts will be awarded by NASA about late summer 2014.
Another significant milestone was the apparently successful attempt by SpaceX to accomplish a controlled soft landing of the Falcon 9 boosters first stage in the Atlantic Ocean for eventual recovery and reuse. It was a first step in a guided 1st stage soft landing back at the Cape.
The next unmanned US cargo mission to the ISS is set for early morning on June 10 with the launch of the Orbital Sciences Cygnus freighter atop an Antares booster from a launch pad at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility on the eastern shore of Virginia.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, Boeing, commercial space, Orion, Chang’e-3, LADEE, Curiosity, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more planetary and human spaceflight news.
………
Ken’s upcoming presentation: Mercy College, NY, May 19: “Curiosity and the Search for Life on Mars” and “NASA’s Future Crewed Spaceships.”

