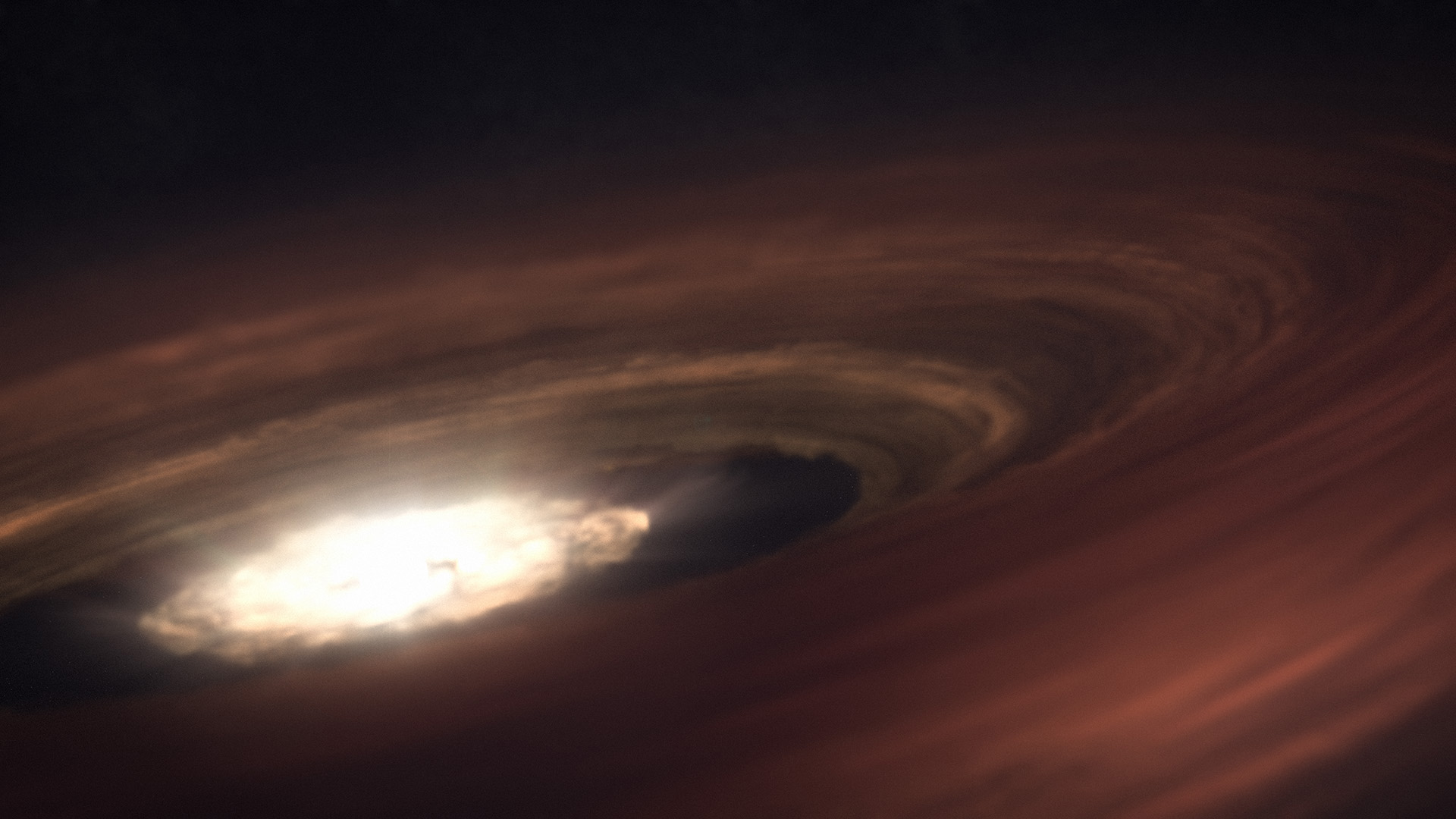
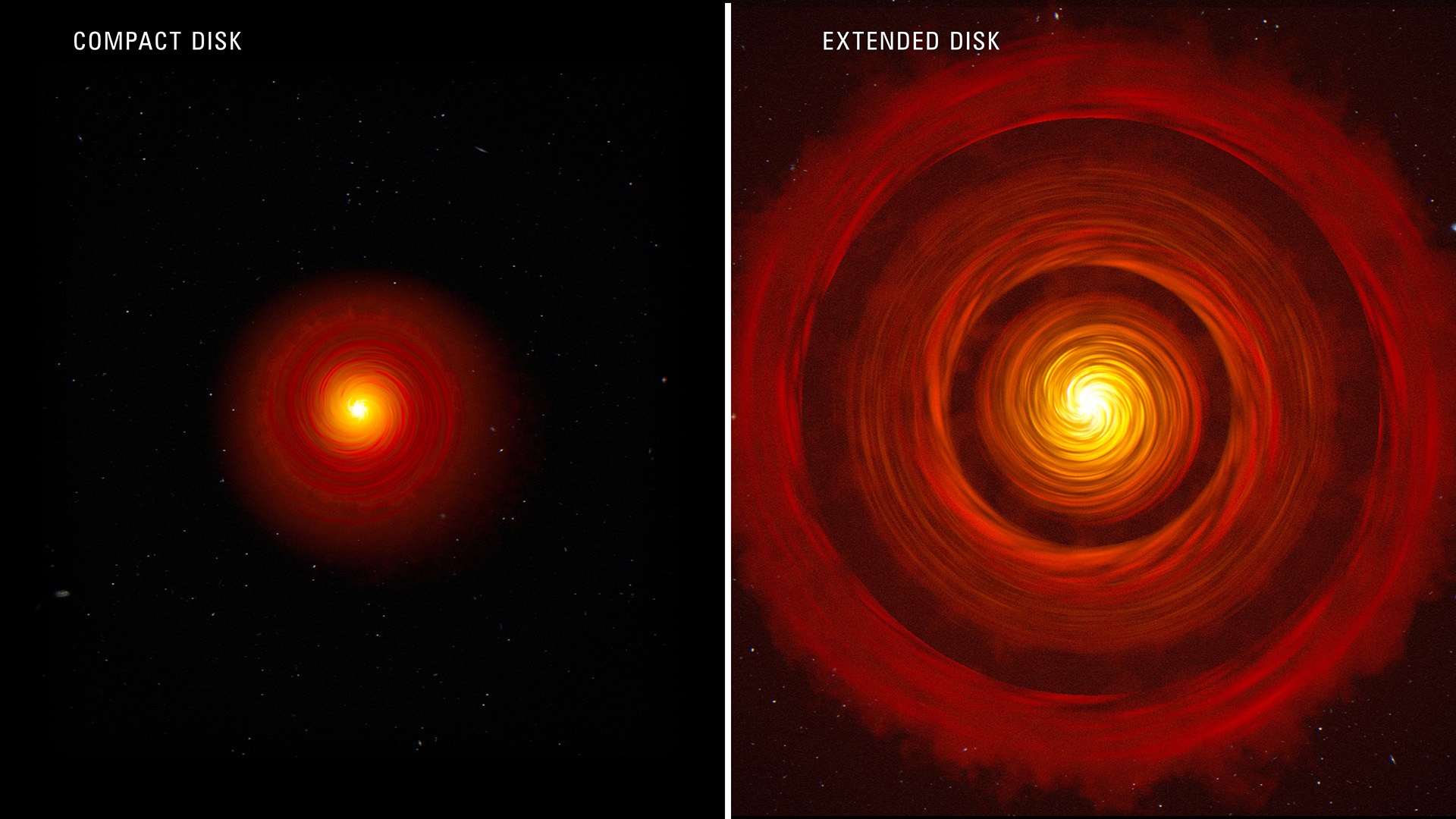
Everyone knows that the James Webb Space Telescope is a ground-breaking infrared space telescope that’s helping us better understand the cosmos. The JWST’s discerning infrared eyes are deepening our understanding of everything from exoplanets to primitive galaxies to the birth of stars.
But it’s not the first ground-breaking infrared space telescope we’ve launched. There was IRAS, then ISO, then the Spitzer Space Telescope. The Spitzer is the JWST’s most recent infrared predecessor, and the JWST is observing one of the same targets that the Spitzer did, taking note of some puzzling changes.
Continue reading “JWST Follows Neon Signs Toward New Thinking on Planet Formation”