The Sun's magnetic field will likely reverse sometime in the next three to four months. No, this is not the next doomsday prediction scenario. It really will happen. But there's nothing to fear because in reality the Sun's magnetic field changes regularly, about every 11 years.
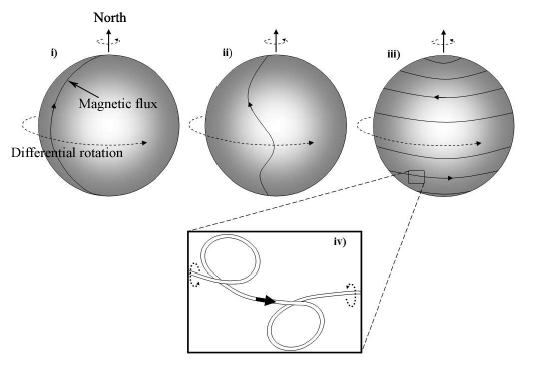
The flip-flopping of the Sun's magnetic field takes place at the peak of each solar activity cycle when the Sun's internal magnetic dynamo reorients itself. When the field reversal happens, the magnetic field weakens, then dies down to zero before emerging again with a reversed polarity.
While this is not a catastrophic event, the reversal will have effects, said solar physicist Todd Hoeksema, the director of Stanford University's Wilcox Solar Observatory, who monitors the Sun's polar magnetic fields. "This change will have ripple effects throughout the Solar System," he said.
When solar physicists talk about solar field reversals, their conversation often centers on the "current sheet." The current sheet is a sprawling surface jutting outward from the sun's equator where the Sun's slowly-rotating magnetic field induces an electrical current. The current itself is small, only one ten-billionth of an amp per square meter (0.0000000001 amps/m2), but there's a lot of it: the amperage flows through a region 10,000 km thick and billions of kilometers wide. Electrically speaking, the entire heliosphere is organized around this enormous sheet.
During field reversals, the current sheet becomes very wavy, and as Earth orbits the Sun, we dip in and out of the current sheet. This means we can see an uptick in space weather, with any solar storms affecting Earth more. So, there may be more auroras in our near future.
Cosmic rays are also affected. These are high-energy particles accelerated to nearly light speed by supernova explosions and other violent events in the galaxy. Cosmic rays are a danger to astronauts and space probes, and some researchers say they might affect the cloudiness and climate of Earth. The current sheet acts as a barrier to cosmic rays, deflecting them as they attempt to penetrate the inner solar system. The good news is that a wavy sheet acts as a better shield against these energetic particles from deep space.
Scientists say the Sun's north pole is already quite far along losing its polarity, with the south pole coming along behind.
"The sun's north pole has already changed sign, while the south pole is racing to catch up," said Phil Scherrer, another solar physicst at Standford. "Soon, however, both poles will be reversed, and the second half of Solar Max will be underway."
Meaning that activity in this
already weak solar cycle
will start to abate.
Source:
NASA
 Universe Today
Universe Today