In 1974, Steven Hawking proposed a seemingly ridiculous hypothesis. Black holes, the gravitational monsters from which nothing escapes, evaporate. To justify this, he proposed that pairs of virtual particles in which one strayed too close to the event horizon, could be split, causing one particle to escape and become an actual particle that could escape. This carrying off of mass would take energy and mass away from the black hole and deplete it. Due to the difficulty of observing astronomical black holes, this emission has gone undetected. But recently, a team of Italian physicists, led by Francesco Belgiorno, claims to have observed Hawking radiation in the lab. Well, sort of. It depends on your definition.
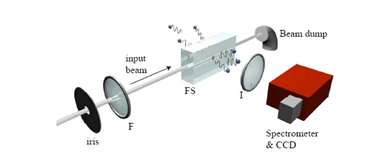
The experiment worked by sending powerful laser pulses through a block of ultra-pure glass. The intensity of the laser would change the optical properties of the glass increasing the refractive index to the point that light could not pass. In essence, this created an artificial event horizon. But instead of being a black hole which particles could pass but never return, this created a "white hole" in which particles could never pass in the first place. If a virtual pair were created near this barrier, one member could be trapped on one side while the other member could escape and be detected creating a situation analogous to that predicted by Hawking radiation.
Readers with some background in quantum physics may be scratching their heads at this point. The experiment uses a barrier to impede the photons, but quantum tunneling has demonstrated that there's no such thing as a perfect barrier. Some photons should tunnel through. To avoid detecting these photons, the team simply moved the detector. While some photons will undoubtedly tunnel through, they would continue on the same path with which they were set. The detector was moved 90º to avoid detecting such photons.
The change in position also helped to minimize other sources of false detections such as scattering. At 90º, scattering only occurs for vertically polarized light and the experiment used horizontally polarized light. As a check to make sure none of the light became mispolarized, the team checked to ensure no photons of the emitted wavelength were observed. The team also had to guard against false detections from absorption and re-emission from the molecules in the glass (fluorescence). This was achieved through experimentation to gain an understanding of how much of this to expect so the effects could be subtracted out. Additionally, the group chose a wavelength in which fluorescence was minimized.
After all the removal of sources of error for which the team could account, they still reported a strong signal which they interpreted as coming from separated virtual particles and call a detection of Hawking radiation. Other scientists disagree in the definition. While they do not question the interpretation, others note that Hawking radiation, by definition, only occurs at gravitational event horizons. While this detection is interesting, it does not help to shed light on the more interesting effects that come with such gravitational event horizons such as quantum gravity or the paradox provided by the
Trans-Planckian problem
. In other words, while this may help to establish that virtual particles like this exist, it says nothing of whether or not they could truly escape from near a black hole, which is a requirement for "true" Hawking radiation.
Meanwhile, other teams continue to explore similar effects with other artificial barriers and event horizons to explore the effects of these virtual particles. Similar effects have been reported in other such systems including ones with
water waves
to form the barrier.
 Universe Today
Universe Today