Could the famed "Big Bang" theory need a revision? A group of theoretical physicists suppose the birth of the universe could have happened after a four-dimensional star collapsed into a black hole and ejected debris.
Before getting into their findings, let's just preface this by saying nobody knows anything for sure. Humans obviously weren't around at the time the universe began. The standard theory is that the
universe grew from an infinitely dense point or singularity
, but who knows what was there before?
"For all physicists know, dragons could have come flying out of the singularity," stated Niayesh Afshordi, an astrophysicist with the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics in Canada who co-authored the new study.
So what are the limitations of the Big Bang theory? The singularity is one of them. Also, it's hard to predict why it would have produced a universe that has an almost uniform temperature, because the age of our universe (about 13.8 billion years) does not give enough time -- as far as we can tell -- to reach a temperature equilibrium.
Most cosmologists say the universe must have been expanding faster than the speed of light for this to happen, but Ashford says even that theory has problems: "The Big Bang was so chaotic, it's not clear there would have been even a small homogenous patch for inflation to start working on."
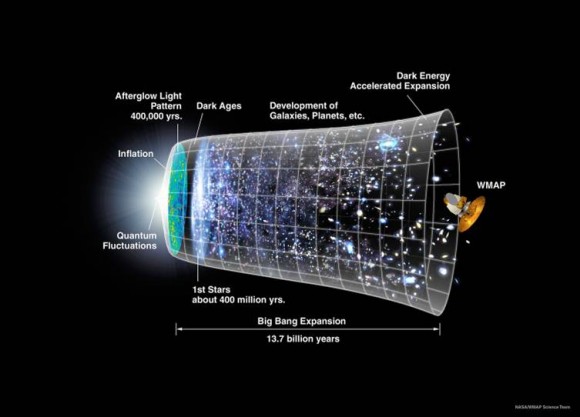
[caption id="attachment_82232" align="alignnone" width="580"]
Representation of the timeline of the universe over 13.7 billion years, from the Big Bang, through the cosmic dark ages and formation of the first stars, to the expansion in the universe that followed. Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team.[/caption]
This is what the physicists propose:
- The model they constructed has the three-dimensional universe floating as a membrane (or brane) in a "bulk universe" that has four dimensions. (Yes, this is making our heads hurt as well, so it might be easier to temporarily think of the brane as two-dimensional and the "bulk universe" as three-dimensional when trying to picture it.) You can read the more technical details in this 2000 paper on which the new theory is based.
- So if this "bulk universe" has four-dimensional stars, these stars could go through the same life cycles as the three-dimensional ones we are familiar with. The most massive ones would explode as supernovae, shed their skin and have the innermost parts collapse as a black hole.
- The 4-D black hole would have an "event horizon" just like the 3-D ones we are familiar with. The event horizon is the boundary between the inside and the outside of a black hole. There are a lot of theories of what goes on inside a black hole, although nothing has ever been observed.
- In a 3-D universe, the event horizon appears as a two-dimensional surface. So in a 4-D universe, the event horizon would be a 3-D object called a hypersphere.
- So basically, what the model says is when the 4-D star blows apart, the leftover material would create a 3-D brane surrounding a 3-D event horizon, and then expand.
The long and the short of it? To bring this back to things that we can see, it is clear from observations
that the universe is expanding
(and indeed is getting faster as it expands, possibly due to the
mysterious dark energy
). The new theory says that the expansion comes from this 3-D brane's growth. But there is at least one limitation.
[caption id="attachment_103050" align="alignnone" width="580"]
This artist's impression shows the surroundings of the supermassive black hole at the heart of the active galaxy NGC 3783 in the southern constellation of Centaurus (The Centaur). New observations using the Very Large Telescope Interferometer at ESO's Paranal Observatory in Chile have revealed not only the torus of hot dust around the black hole but also a wind of cool material in the polar regions. Credit: ESO/M. Kornmesser[/caption]
While the model does explain why the universe has nearly uniform temperature (the 4-D universe preceding it would have existed it for much longer), a European Space Agency telescope called Planck recently
mapped small temperature variations in the cosmic microwave background
, which is believed to be leftovers of the universe's beginnings. (
Read more about the CMB here.
)
The new model differs from these CMB readings by about four percent, so the researchers are looking to refine the model. They still feel the model has worth, however. Planck shows that inflation is happening, but doesn't show
why
the inflation is happening.
"The study could help to show how inflation is triggered by the motion of the universe through a higher-dimensional reality," the researchers stated.
You can read more about their research
on this prepublished Arxiv paper
. The Arxiv entry does not specify if the paper has been submitted to any peer-reviewed scientific journals for publication.
Source:
Nature
 Universe Today
Universe Today