Welcome back to our series on Settling the Solar System! Today, we take a look at the largest asteroid/planetoid in the Main Belt – Ceres!
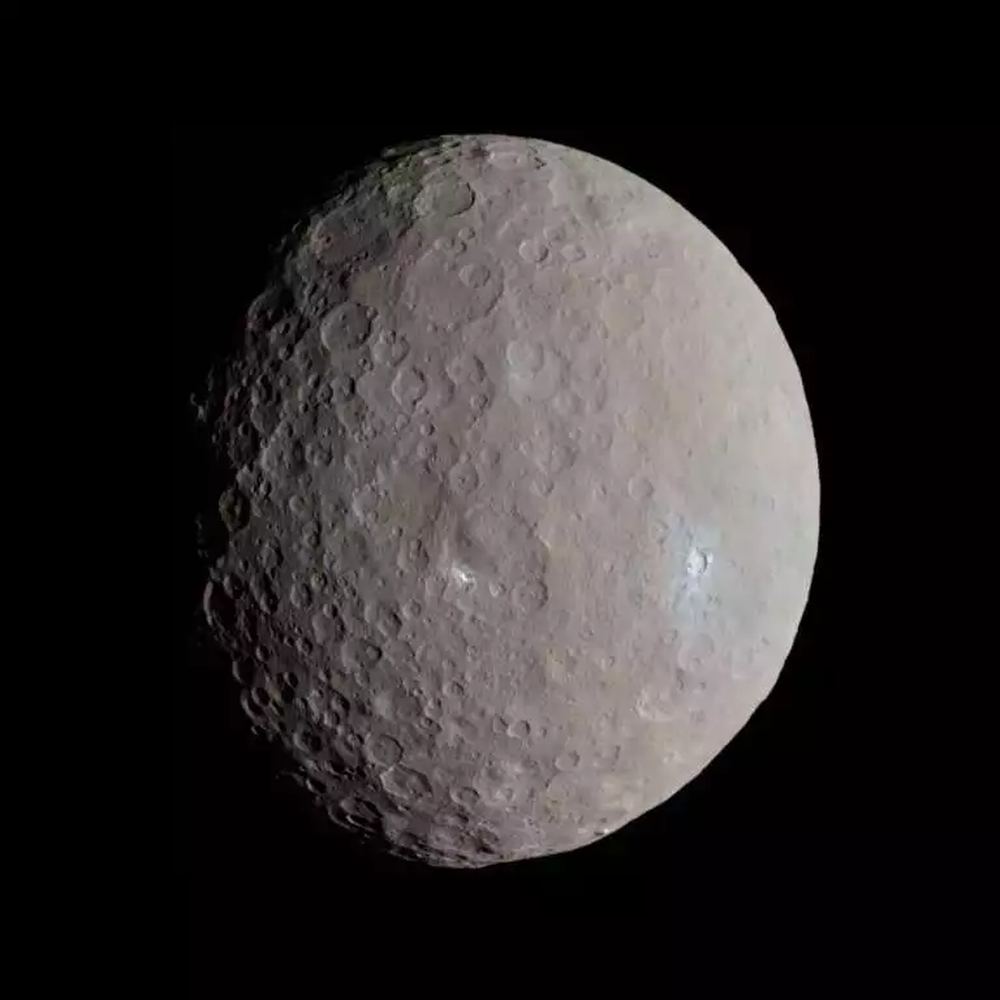
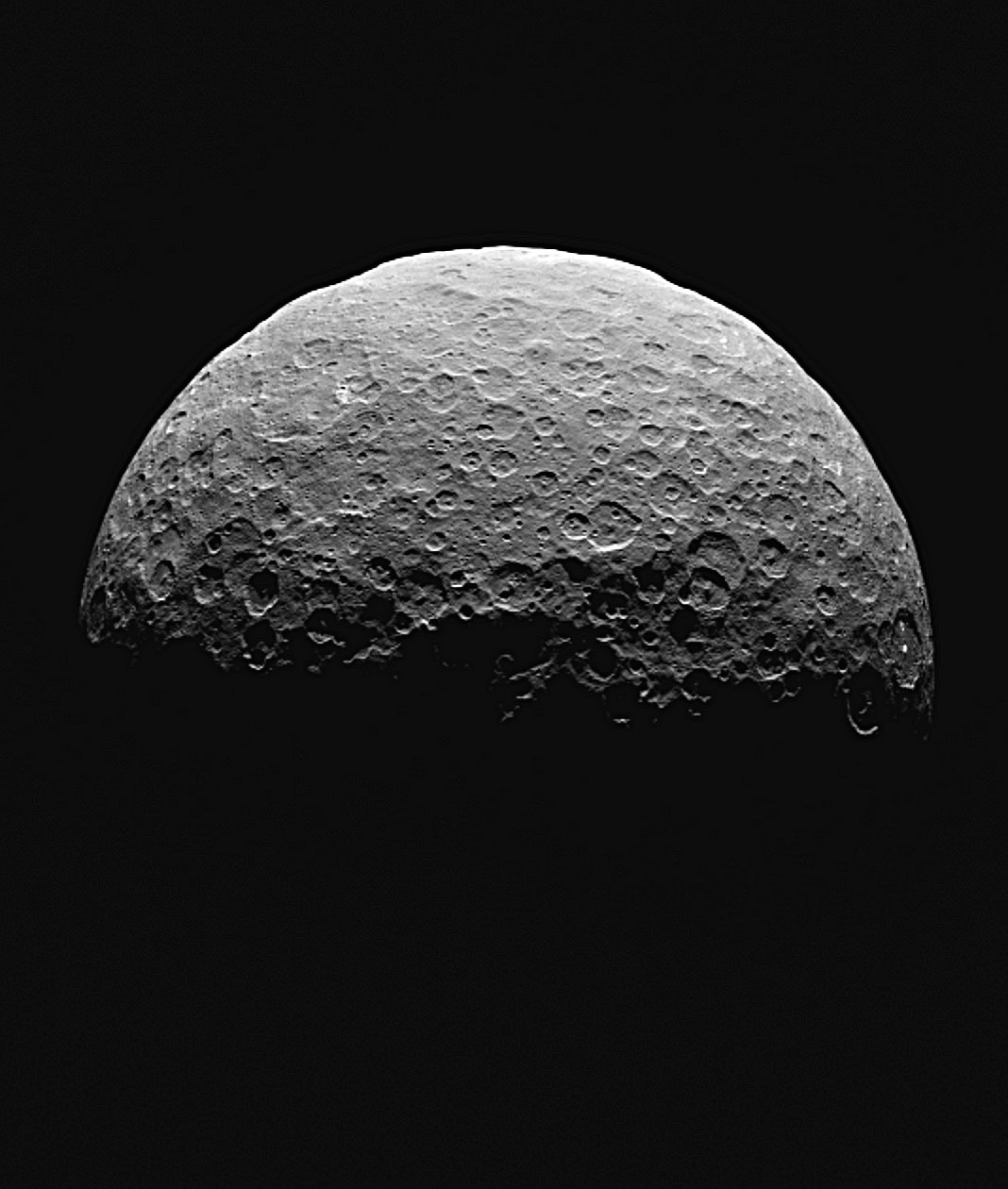
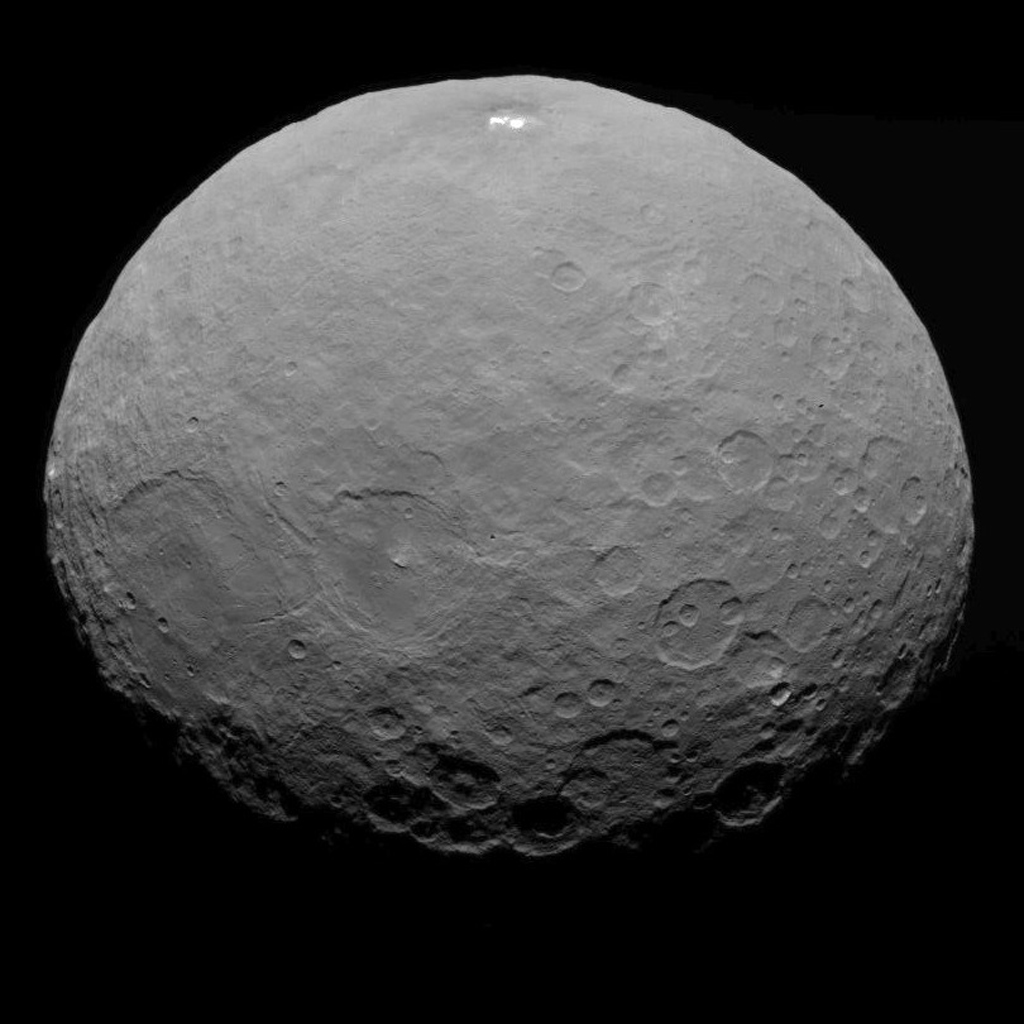
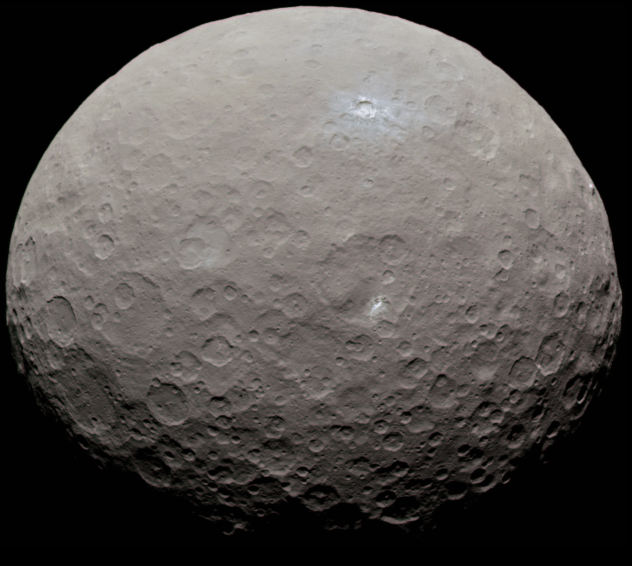
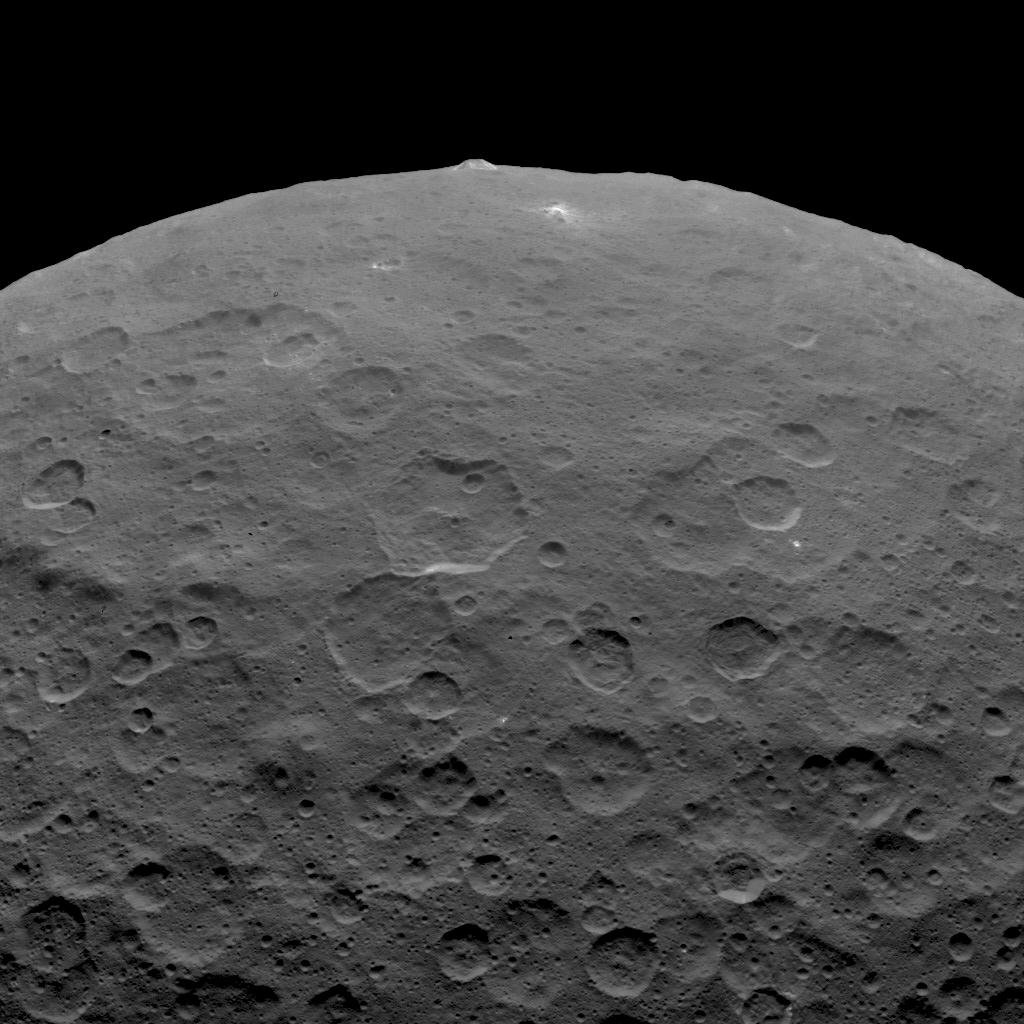
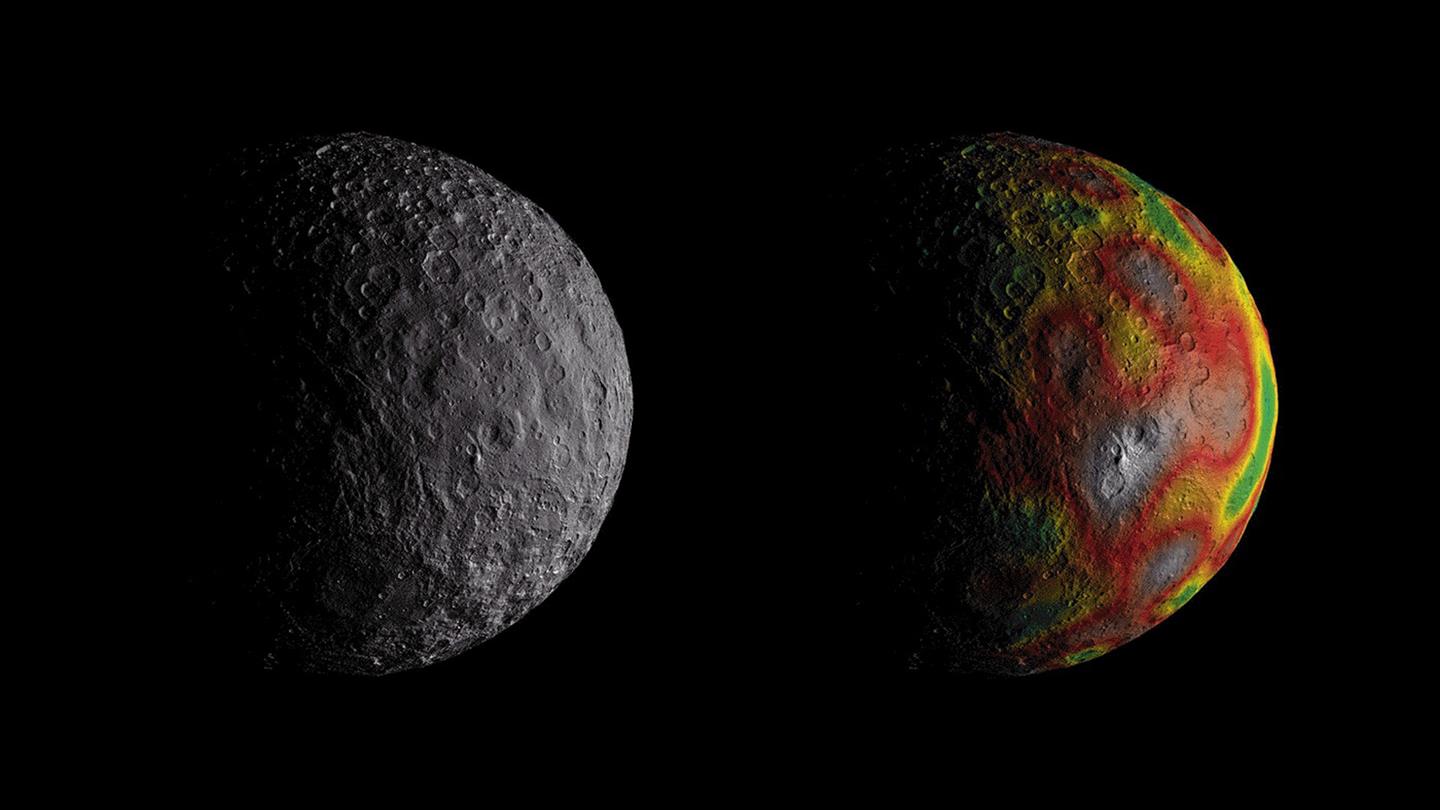
Between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter lies the Solar System’s Main Asteroid Belt. Within this region, it is estimated that there are over 150 million objects that measure 100 meters (330 ft) or more in diameter. The largest of these is the dwarf planet Ceres (aka. 1 Ceres), the only body in the Main Belt that is large enough – 940 km (585 mi) in diameter – to have undergone hydrostatic equilibrium (become spherical).
Because of its important location and the amenities this dwarf planet itself possesses, there are those who have proposed that we establish a colony on Ceres (and even some who’ve explored the idea of terraforming it). This could serve as a base for asteroid mining ventures as well as an outpost of human civilization, one which could facilitate the expansion of humanity farther out into the Solar System.
Continue reading “How Do We Settle on Ceres?”