Mark Thompson
Science broadcaster and author. Mark is known for his tireless enthusiasm for making science accessible, through numerous tv, radio, podcast and theatre appearances, and books. He was a part of the award-nominated BBC Stargazing LIVE TV Show in the UK and his Spectacular Science theatre show has received 5 star reviews across UK theatres. In 2025 he is launching his new podcast Cosmic Commerce and is working on a new book 101 Facts You Didn't Know About Deep Space In 2018, Mark received an Honorary Doctorate from the University of East Anglia.
You can email Mark here
Recent Articles
-

-

A Laser Ruler for Sharper Black Hole Images
January 30, 2026Researchers at KAIST have developed a breakthrough technology that could dramatically improve our ability to image black holes and other distant objects. The team created an ultra precise reference signal system using optical frequency comb lasers to synchronise multiple radio telescopes with unprecedented accuracy. This laser based approach solves long standing problems with phase calibration that have plagued traditional electronic methods, particularly at higher observation frequencies.
-

The Star That Wasn't Dying After All
January 29, 2026Astronomers have solved a bit of a mystery that had them questioning whether one of the most extreme stars ever observed was about to explode. WOH G64, a massive red supergiant in the Large Magellanic Cloud, began behaving so strangely that researchers suspected it had evolved into a rare yellow hypergiant on the brink of supernova. But new observations from the Southern African Large Telescope reveal the star is still very much a red supergiant, yet still exhibiting strange behaviour.
-

NASA Fires Up Nuclear Future for Deep Space Travel
January 29, 2026NASA has completed its first major testing of nuclear reactor hardware for spacecraft propulsion in over 50 years, marking a crucial step toward faster, more capable deep space missions. Engineers at Marshall Space Flight Center conducted more than 100 ‘cold flow’ tests on a full scale reactor engineering development unit throughout 2025, gathering vital data on how propellant flows through the system under various conditions.
-
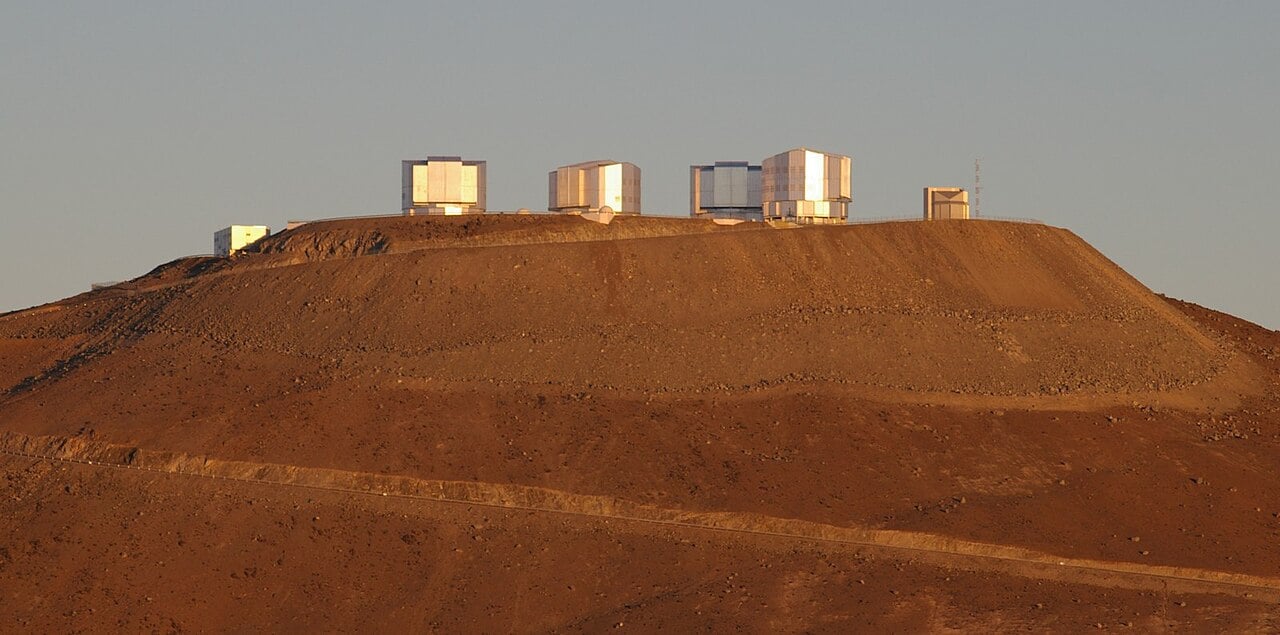

Chile's Paranal Observatory Saved from Industrial Development
January 28, 2026After months of protests led by Nobel laureate Reinhard Genzel, the American energy company AES Andes has abandoned plans to build a massive solar and wind facility just kilometres from one of the world's premier telescope sites. The decision preserves the pristine night skies above Chile's Paranal Observatory, where the European Southern Observatory operates some of humanity's most powerful eyes on the universe.
-
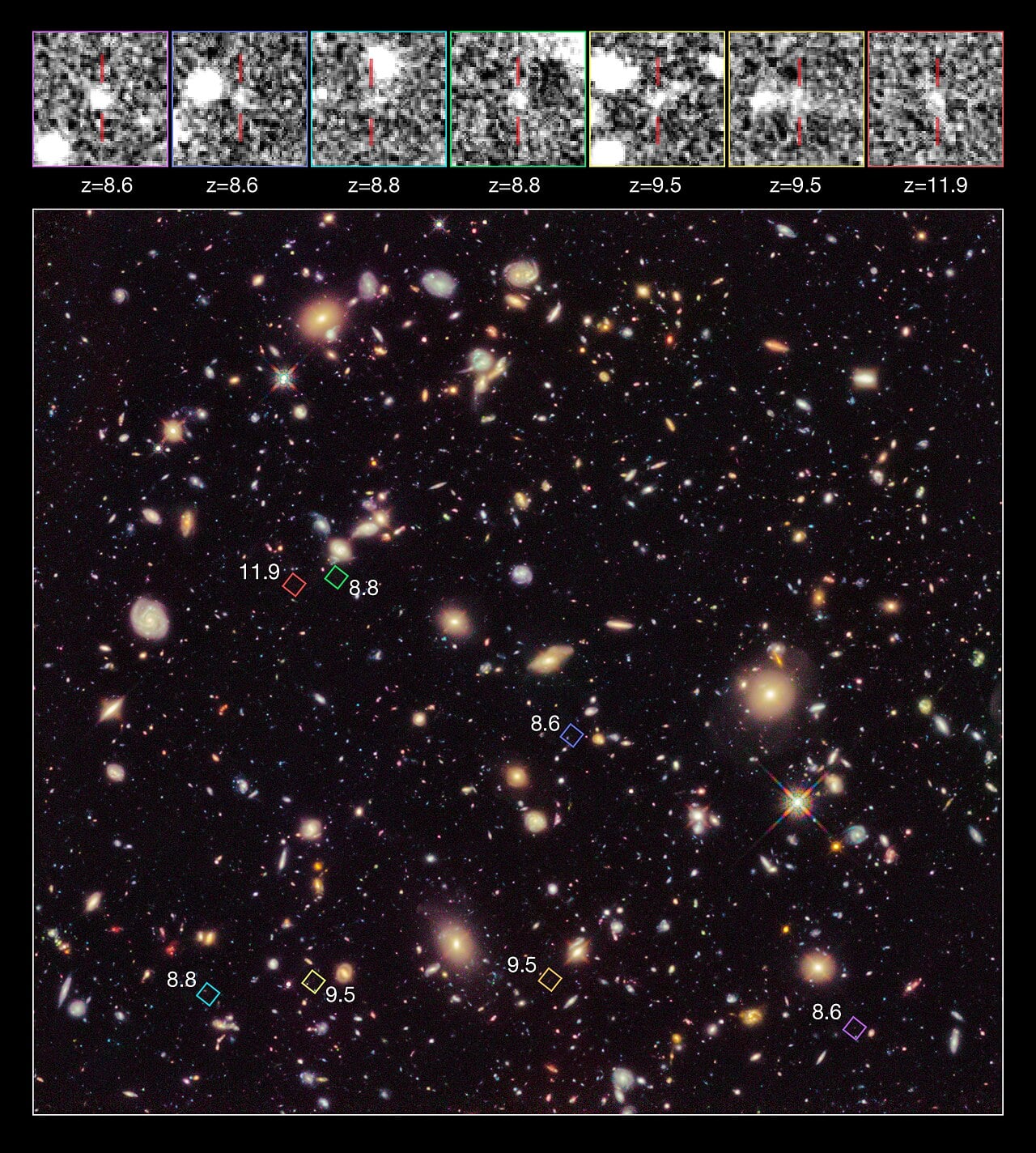

Solving the Century Old Puzzle of Our Galaxy's Neighborhood
January 28, 2026Nearly a century after Edwin Hubble discovered the universe's expansion, astronomers have finally explained the nagging mystery of why most nearby galaxies rush away from us as if the Milky Way's gravity doesn't exist? The answer lies in a vast, flat sheet of dark matter stretching tens of millions of light years around us, with empty voids above and below that make the expansion appear smoother than it should.
-
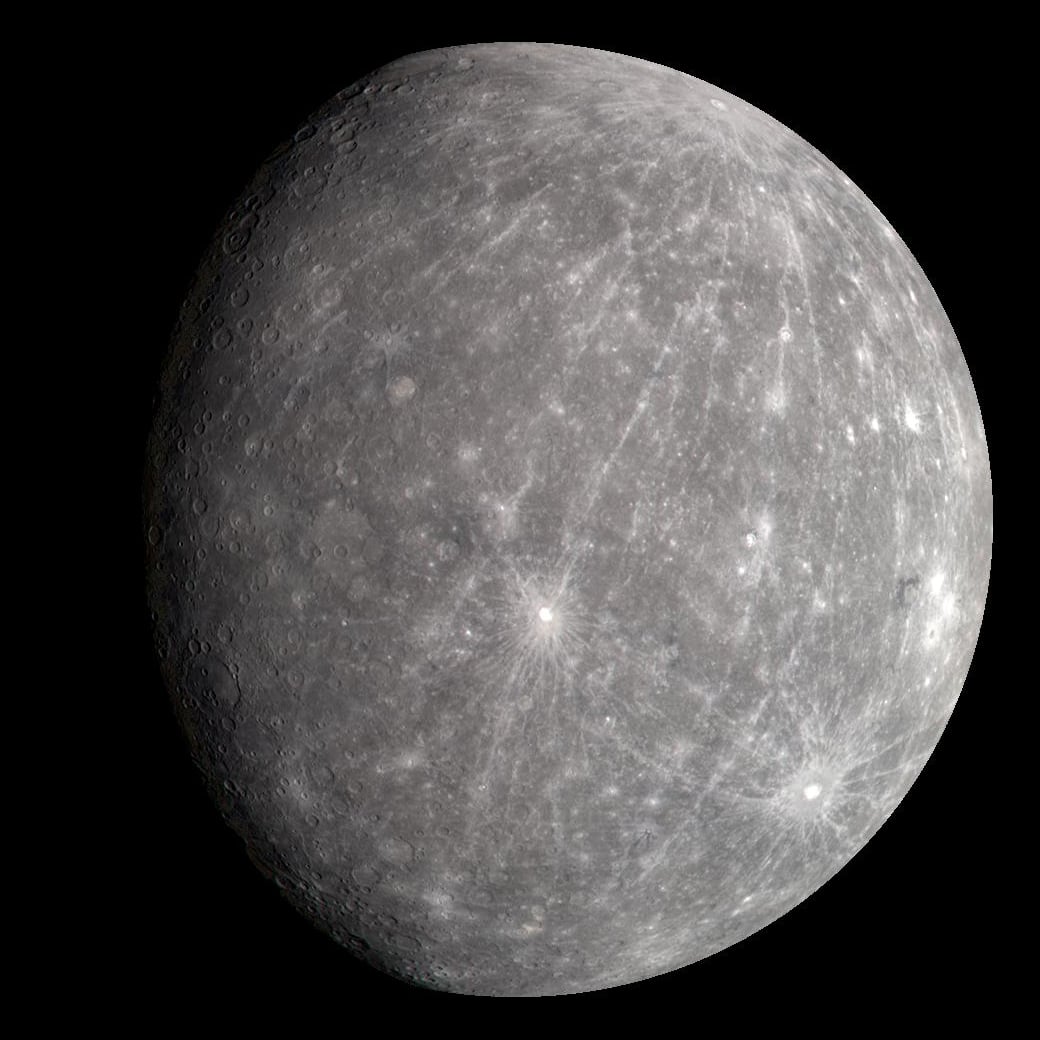

Mercury May Not Be "Dead" After All
January 28, 2026Researchers using machine learning have discovered hundreds of mysterious bright streaks on Mercury's surface that appear to be caused by gases escaping from the planet's interior. The finding suggests the Solar System's smallest planet isn't the static, geologically dead world we thought it was, Mercury might still be active today, continuously releasing material into space even billions of years after its formation.
-
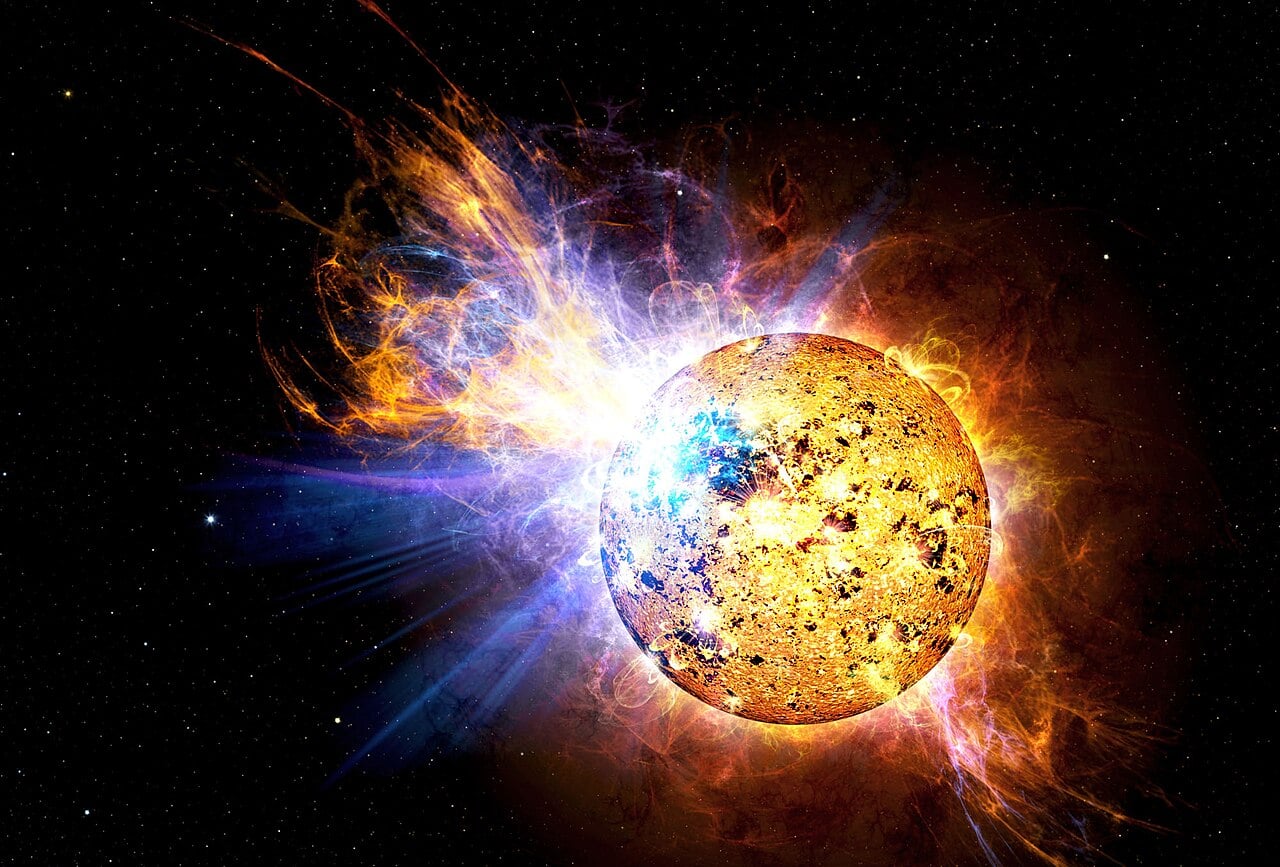

Stellar Fireworks at the Heart of the Milky Way
January 27, 2026Using the South Pole Telescope, astronomers have detected powerful stellar flares erupting from stars near the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way. Operating at millimetre wavelengths that can penetrate the dust obscuring our view of the core of the Galaxy, the telescope caught these dramatic magnetic energy releases in one of the most extreme environments in our Galaxy. The discovery opens a new observational window for studying stellar behaviour in regions previously hidden from view and provides insights into how stars survive and behave in the intense gravitational and radiation environment surrounding the Milky Way's central black hole.
-
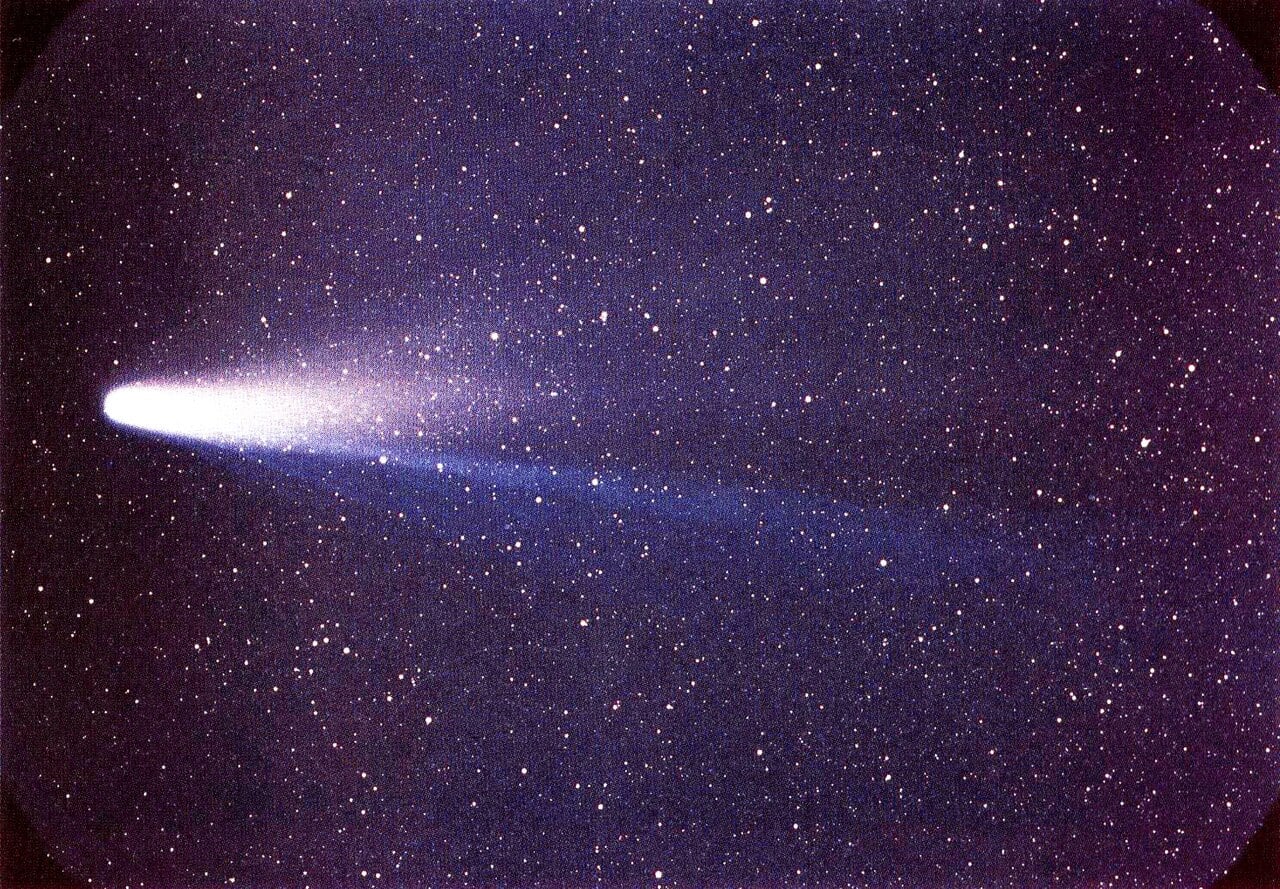

The Monk Who Recognised Halley's Comet First
January 27, 2026The comet bearing Edmond Halley's name may have been misnamed! New research from Leiden University reveals that an 11th Century English monk recognised the famous comet's periodicity centuries before the British astronomer. Eilmer of Malmesbury witnessed the comet's appearances in both 989 and 1066, linking the two observations and understanding they represented the same celestial visitor returning after decades, a realisation documented by the medieval chronicler William of Malmesbury but overlooked by scholars until now. The discovery challenges whether history's most famous comet should continue bearing Halley's name when a Benedictine monk beat him to the discovery by more than 600 years.
-
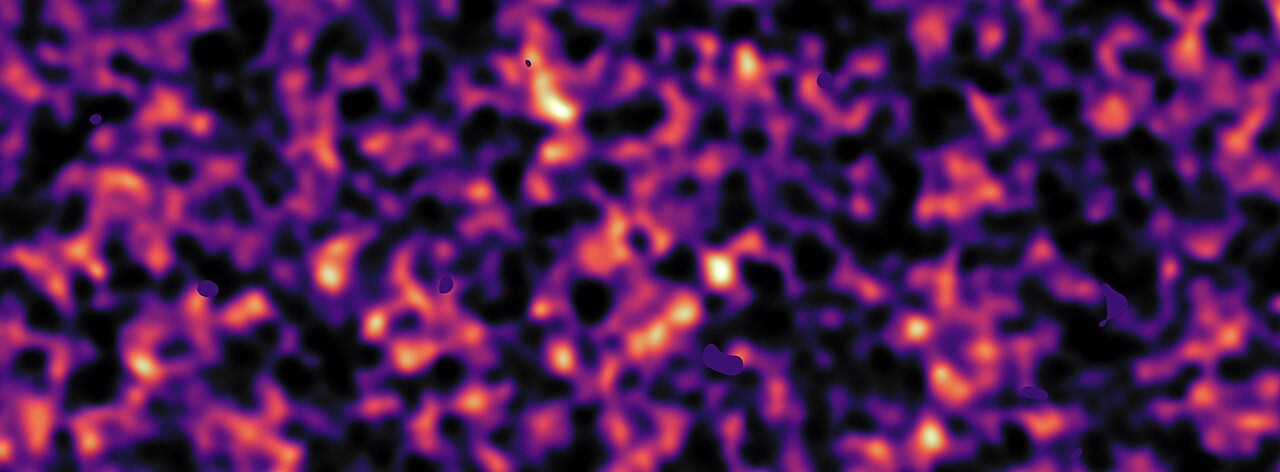
Mapping the Invisible
January 27, 2026Dark matter remains invisible to our telescopes, yet its gravitational fingerprints pervade the universe. Using NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, scientists have produced one of the most detailed dark maps ever created, revealing with unprecedented clarity how dark matter and ordinary matter have grown up together. The map shows that wherever galaxies cluster in their thousands, equally massive concentrations of dark matter occupy the same space, a close alignment that confirms dark matter's gravity has been shepherding regular matter into stars, galaxies, and ultimately the complex planets capable of supporting life.
-
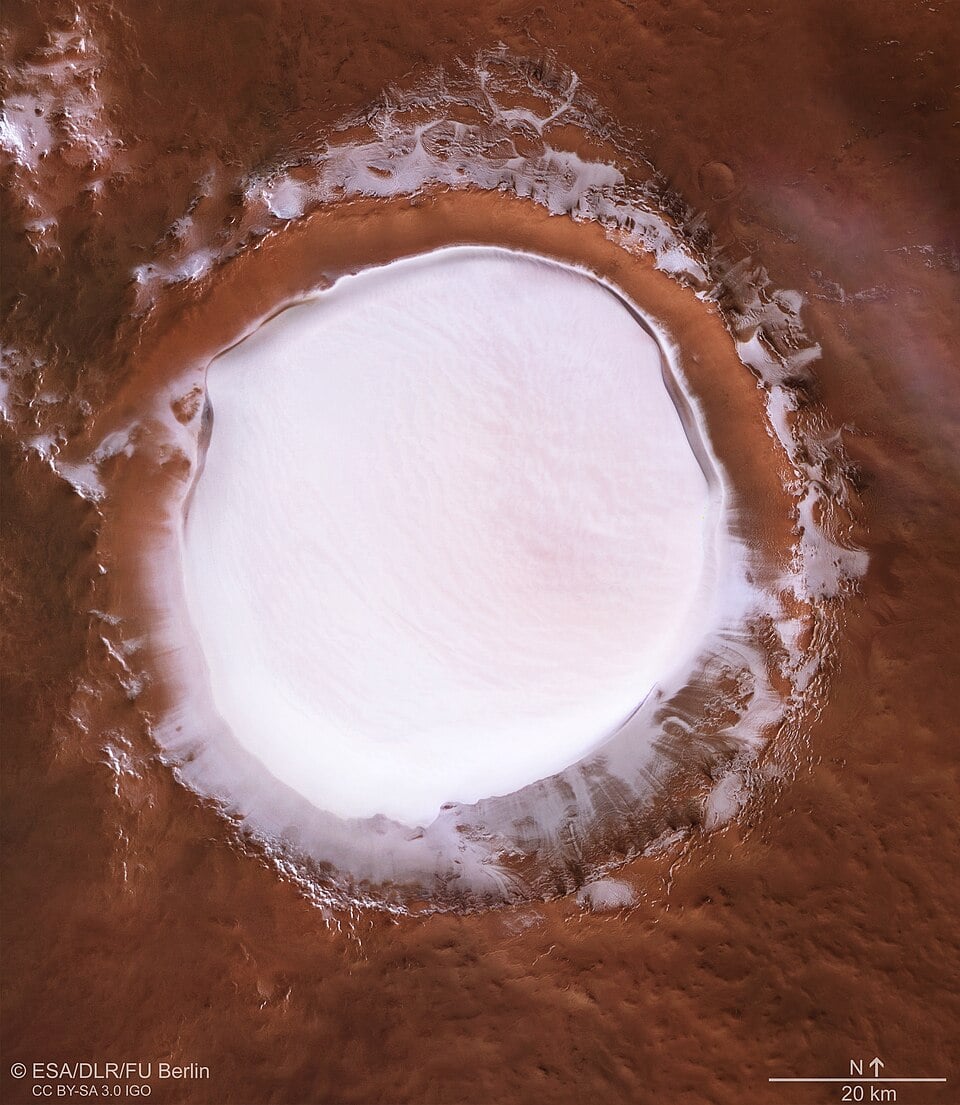

Finding Water on Mars
January 26, 2026Water exists across Mars in underground ice, soil moisture, and atmospheric vapour, yet most of it remains frustratingly beyond practical reach for future explorers. A new comparative study from the University of Strathclyde evaluates the technologies that could extract this vital resource from various Martian sources, assessing each method's energy demands, scalability, and suitability for the Red Planet's harsh conditions.
-
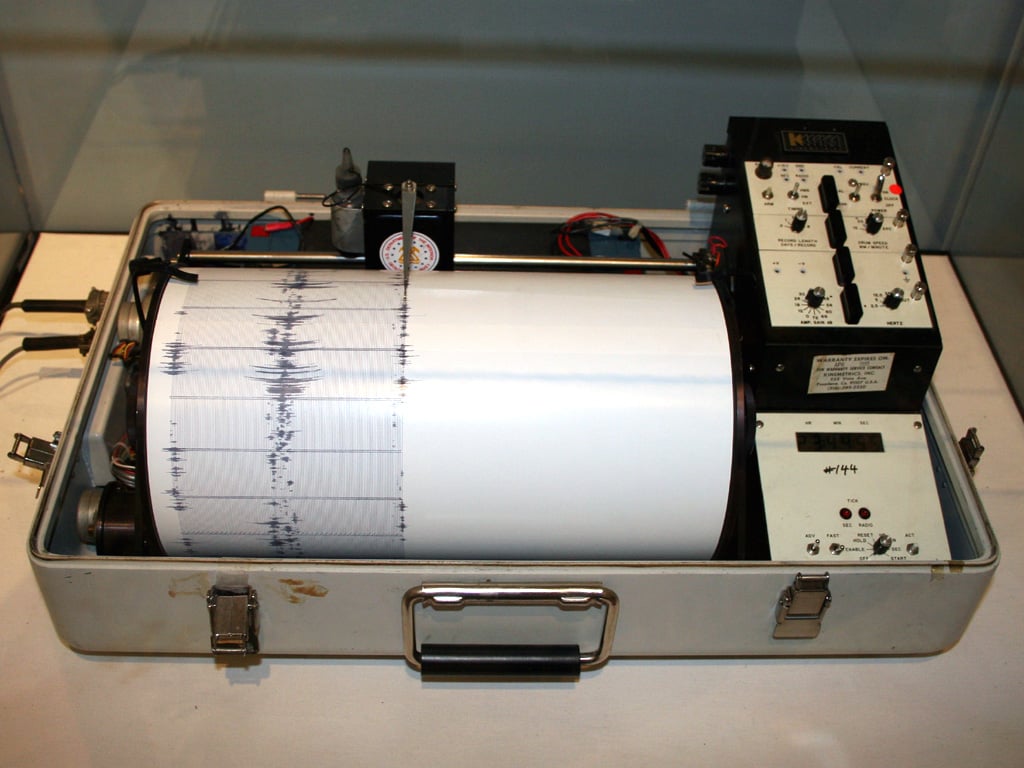

How Earthquake Detectors Track Space Junk
January 26, 2026Thousands of pieces of abandoned spacecraft orbit Earth, and when gravity finally pulls them down, authorities rarely know exactly where they'll land. Now researchers at Johns Hopkins University have demonstrated a clever solution. Surprisingly they have found using earthquake detecting seismometers they can track falling space debris in real time by listening for the sonic booms it produces. The technique successfully traced a Chinese spacecraft module as it streaked across California at Mach 25-30, revealing its actual trajectory lay 25 miles north of predictions, a significant improvement that could help authorities quickly locate potentially toxic debris and protect people from contamination.
-
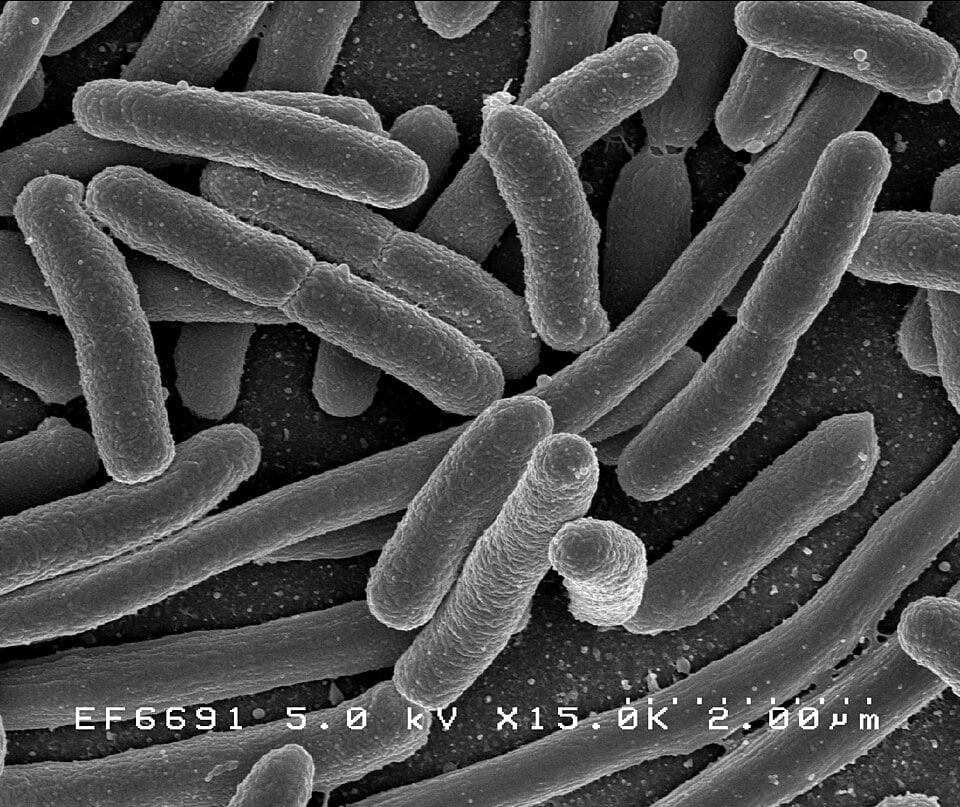
The Unexpected Evolution Aboard the ISS
January 26, 2026New research from the International Space Station reveals that in near weightless conditions, both bacteriophages and their *E. coli* hosts mutate in ways not seen on Earth. This unexpected finding not only deepens our understanding of how microbial life adapts to extreme environments but has already yielded practical benefits. Some of the mutations discovered in space dwelling viruses led researchers to create superior viruses that specifically infect and kill bacteria, capable of fighting drug resistant bacterial infections back on Earth.
-
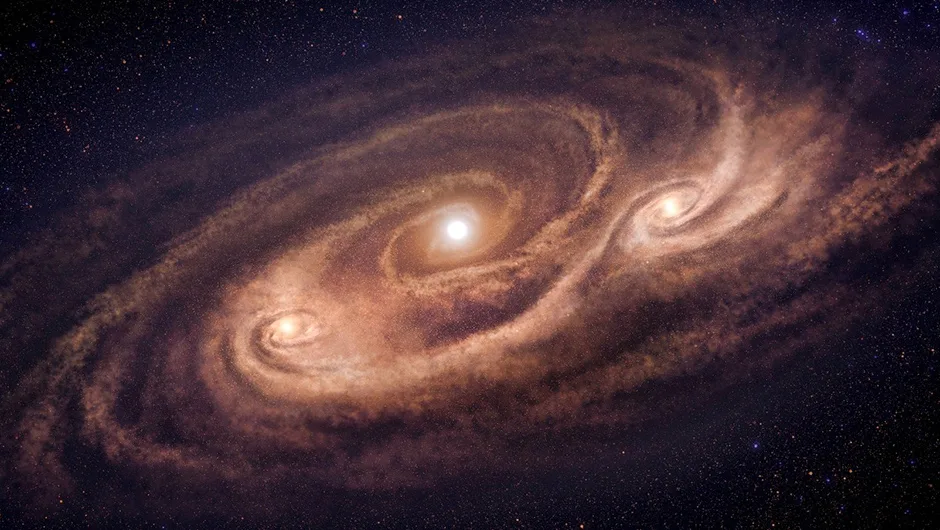

The Many Faces of Monster Galaxies
January 23, 2026The earliest galaxies in the universe earned the nickname "monster galaxies" for good reason, they formed stars at rates hundreds of times faster than the Milky Way, growing rapidly after the dawn of time. Astronomers using ALMA and the James Webb Space Telescope have now revealed that three such monsters each achieved their extraordinary growth through completely different mechanisms. By comparing where stars are forming today with where they formed in the past, researchers discovered that galaxy collisions, internal instability, and minor mergers can all trigger these growth spurts, fundamentally changing our understanding of how the universe's most massive galaxies came to be.
-
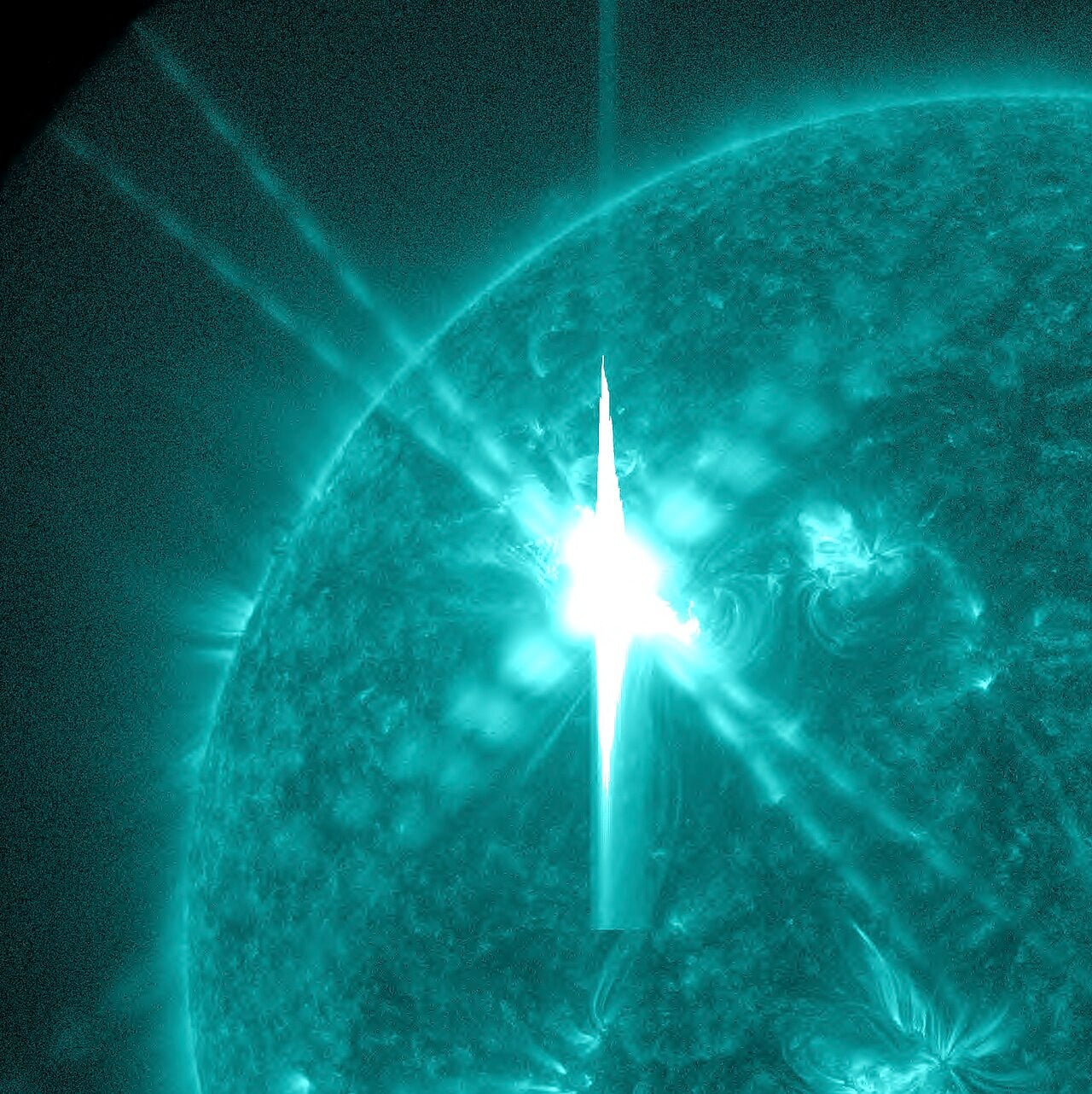
Unmasking the Sun’s Hidden Gamma Ray Factory
January 15, 2026Scientists have finally identified where some of the most powerful radiation bursts from solar flares originate, solving a mystery that has puzzled solar physicists for decades. Researchers at the New Jersey Institute of Technology traced intense gamma rays back to a previously unknown population of particles supercharged to millions of electron volts in the Sun’s atmosphere, revealing the mechanism behind these strange signals.
-
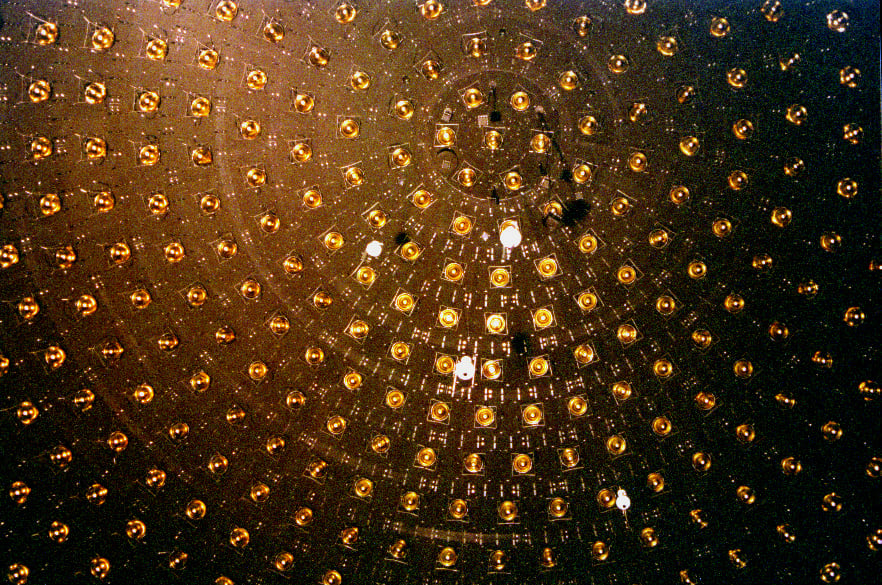
A New Atlas of the Milky Way’s Ghost Particles
January 15, 2026Every second, a trillion ghost particles stream through your body unnoticed, invisible messengers carrying secrets from the hearts of distant stars. Astrophysicists at the University of Copenhagen have now mapped exactly where these neutrinos originate across our Milky Way Galaxy and how many reach Earth, creating the most comprehensive picture yet of these elusive particles.
-
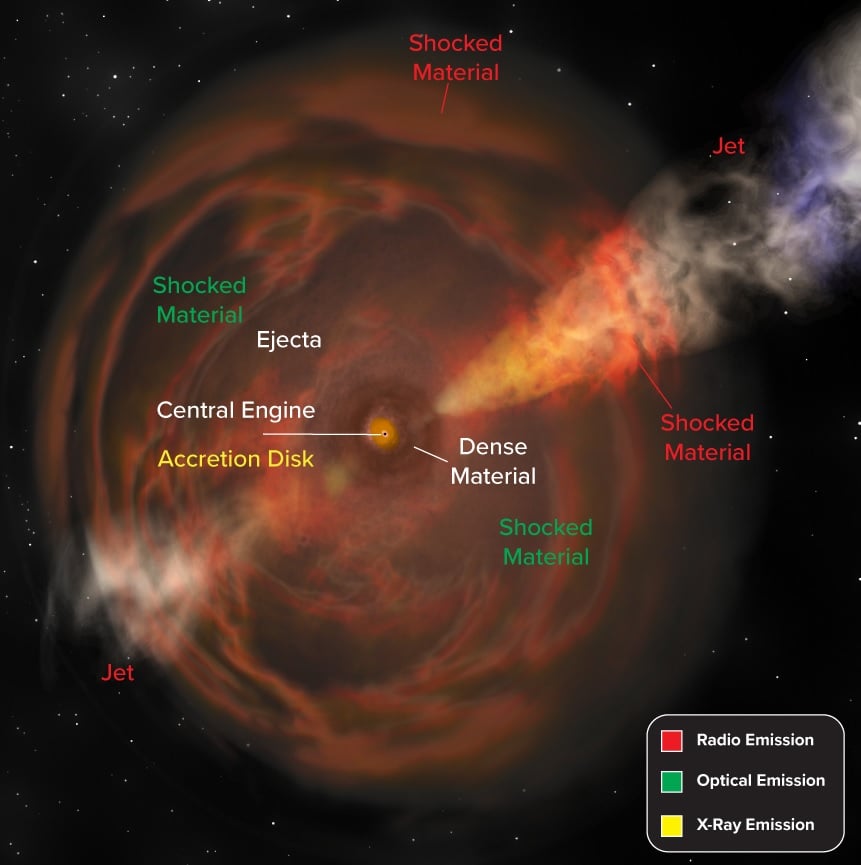
Solving the Mystery of Blue Flashes
January 14, 2026Brief, brilliant flashes of blue light occasionally appear across the universe, burning hundreds of times brighter than ordinary supernovae before fading within days. Astronomers have puzzled over these luminous fast blue optical transients for years, unable to determine whether they were unusual stellar explosions or something else entirely. Observations of AT 2024wpp, the brightest example ever detected, have finally solved the mystery.
-
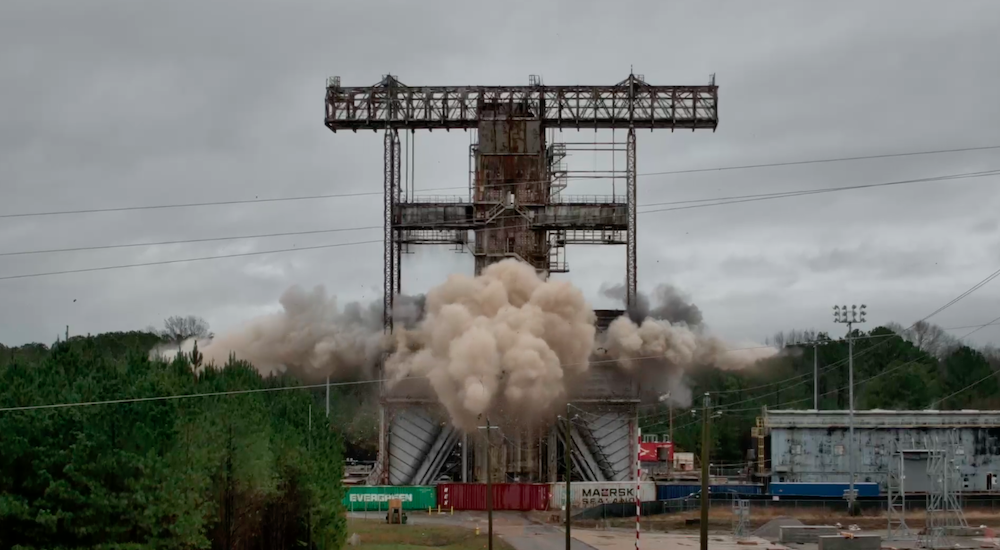

NASA Bids Farewell to Historic Test Stands That Built the Space Age
January 14, 2026Two towering buildings that helped launch humanity's greatest space achievements came down on January 10 at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Centre in Alabama. The Dynamic Test Stand and the T-tower, both designated National Historic Landmarks, played crucial roles in developing the Saturn V rockets that carried Apollo astronauts to the Moon and the Space Shuttle that defined an era of spaceflight. Their carefully orchestrated demolition marks a transformation, as NASA clears the way for a modernised infrastructure ready to support the next generation of space exploration.
-
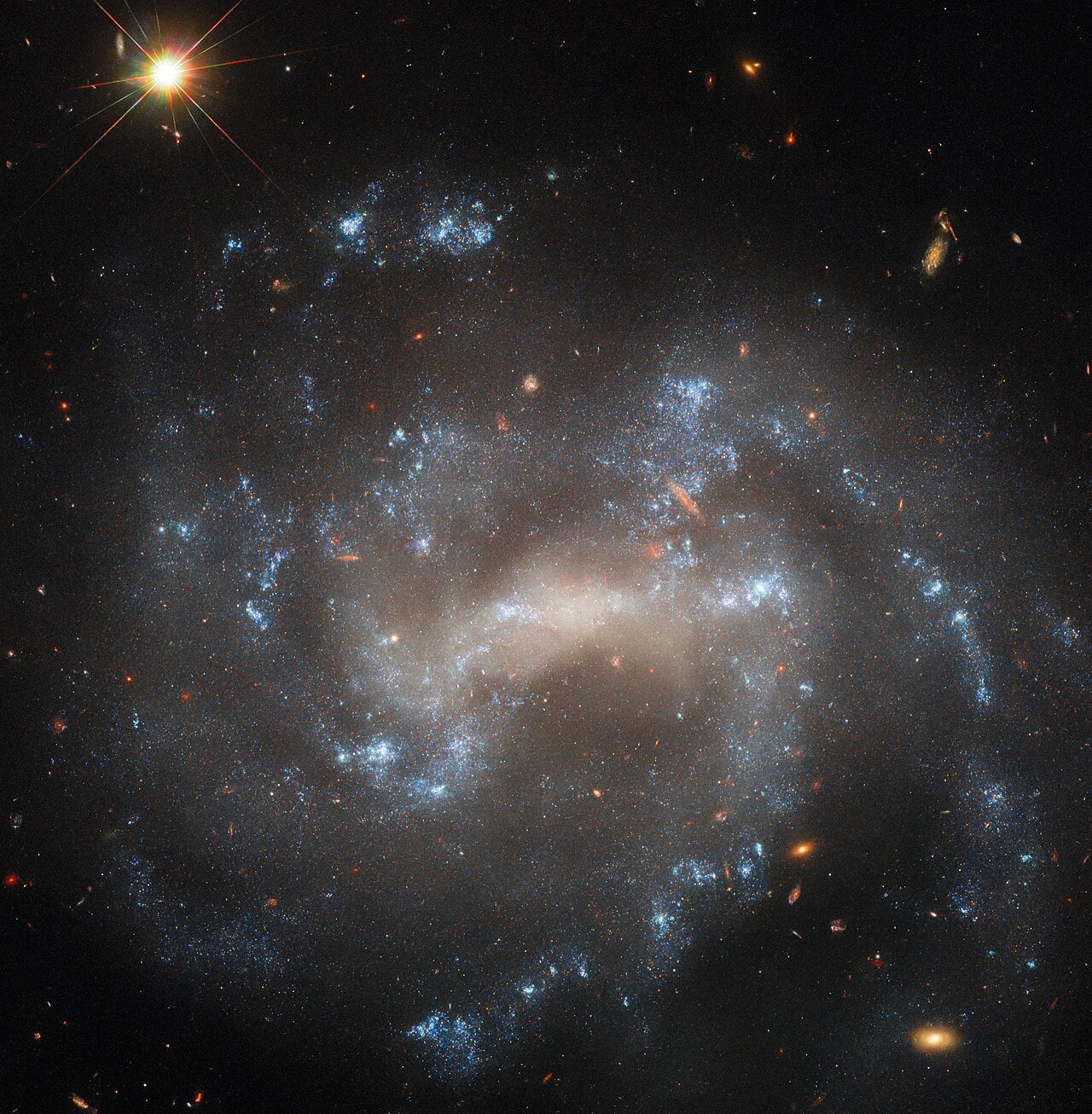

A Supernova That Shouldn't Exist
January 14, 2026For decades, astronomers believed that the most massive stars in the universe lived fast and died quietly, collapsing directly into black holes without the spectacular fireworks of a supernova explosion. That understanding has been dramatically overturned by observations of SN 2022esa, a peculiar supernova that erupted from an incomprehensibly massive star and is now destined to become a black hole binary system.
-
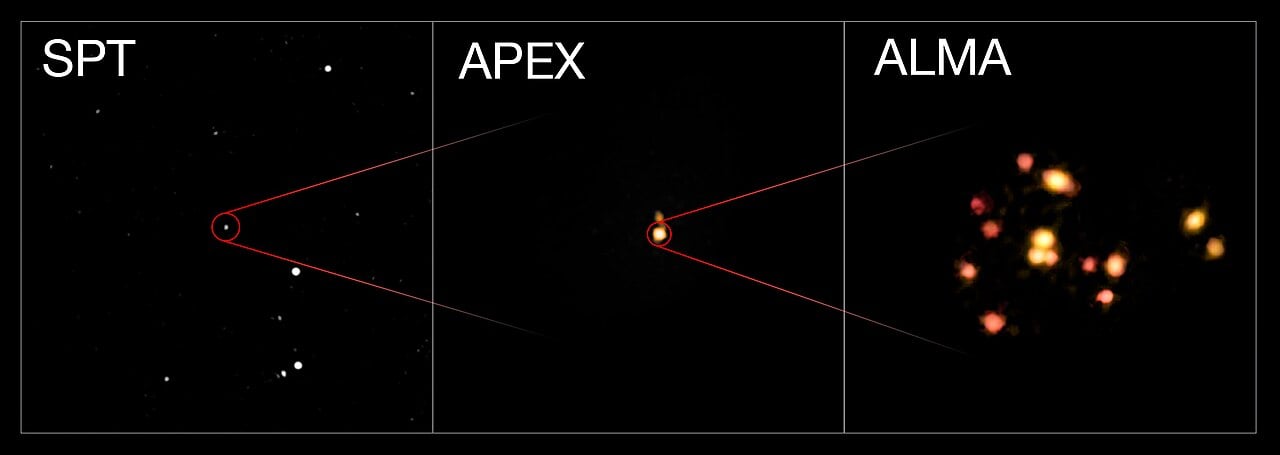

The Surprising Heat of Early Clusters
January 14, 2026Astronomers using ALMA have detected the earliest hot galaxy cluster atmosphere ever observed, revealing a massive reservoir of superheated gas in the infant cluster SPT2349-56 just 1.4 billion years after the Big Bang. The gas is far hotter and more pressurised than current theories predicted for such a young system, forcing scientists to completely rethink how galaxy clusters evolved in the early universe. This discovery suggests that violent processes like supermassive black hole outbursts and intense starbursts heated these cluster atmospheres much earlier and more efficiently than anyone expected, fundamentally challenging our understanding of how the universe’s largest structures formed.
 Universe Today
Universe Today