Astronomers want to collect as much data as possible using as many systems as possible. Sometimes that requires coordination between instruments. The teams that run the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and the upcoming Atmospheric Remote-sensing Infrared Exoplanet Large-survey (Ariel) missions will have plenty of opportunity for that once both telescopes are online in the early 2030s. A new paper, available in pre-print on arXiv, from the Ariel-JWST Synergy Working Group details just how exactly the two systems can work together to better analyze exoplanets.
Continue reading

DOI: arXiv:2602.04840 | arXiv:2602.04840v1 Announce Type: new Abstract: The EXoplanet Climate Infrared TElescope (EXCITE) is a balloon-borne mission dedicated to measuring spectroscopic phase curves of hot Jupiter-type exoplanets. Phase curve measurements can be used to characterize an exoplanet's longitude-dependent atmospheric composition and energy circulation patterns. EXCITE carries a 0.5 m primary mirror and moderate resolution diffraction-limited spectrograph with spectral coverage from 0.8--3.5 um. EXCITE is...
Continue reading

NASA’s Magellan Mission to Venus is the gift the keeps on giving, providing Italian researchers with the first solid detection of a massive subsurface lava tube on Venus. They detail their findings in a new paper appearing in the journal Nature Communications.
Continue reading
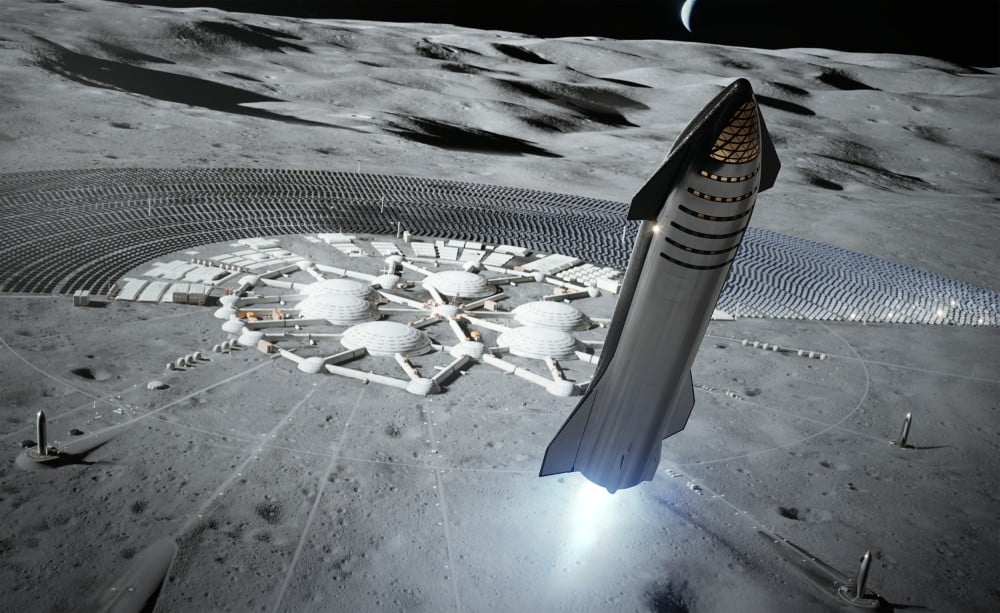
The commercial space giant SpaceX, which Elon Musk founded in 2002 to build a self-sustaining city on Mars, is no longer focusing on the Red Planet. According to a recent statement on X, SpaceX is now pivoting to the Moon as its intended destination for a human settlement.
Continue reading

In a clockwork predictable Universe, comets and how they will ultimately perform is always a big wild card. A new sungrazer comet discovered at the start of this year has given astronomers pause. C/2026 A1 MAPS could put on a memorable if brief show in early April, if it doesn’t join the long list of comets that failed to live up to expectations.
Continue reading

Sending a mission to the Solar Gravitational Lens (SGL) is the most effective way of actually directly imaging a potentially habitable planet, as well as its atmosphere, and even possibly some of its cities. But, the SGL is somewhere around 650-900 AU away, making it almost 4 times farther than even Voyager 1 has traveled - and that’s the farthest anything human has made it so far. It will take Voyager 1 another 130+ years to reach the SGL, so obviously traditional propulsion methods won’t work to get any reasonably sized craft there in any reasonable timeframe. A new paper by an SGL mission’s most vocal proponent, Dr. Slava Turyshev of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, walks through the different types of propulsion methods that might eventually get us there - and it looks like we would have a lot of work to do if we plan to do it anytime soon.
Continue reading

Free-Floating Planets, or as they are more commonly known, Rogue Planets, wander interstellar space completely alone. Saying there might be a lot of them is a bit of an understatement. Recent estimates put the number of Rogue Planets at something equivalent to the number of stars in our galaxy. Some of them, undoubtedly, are accompanied by moons - and some of those might even be the size of Earth. A new paper, accepted for publication into the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, and also available in pre-print on arXiv, by David Dahlbüdding of the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich and his co-authors, describes how some of those rogue exo-moons might even have liquid water on their surfaces.
Continue reading

Observations by NASA’s SPHEREx (Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer) show the infrared light emitted by the dust, water, organic molecules, and carbon dioxide contained within comet 3I/ATLAS’s coma.
Continue reading

So we did that. And we found nothing. So far, with all of our experiments around the world, we find no evidence of missing momentum, and no signs of towers of gravitons slipping away into hidden dimensions.
Continue reading
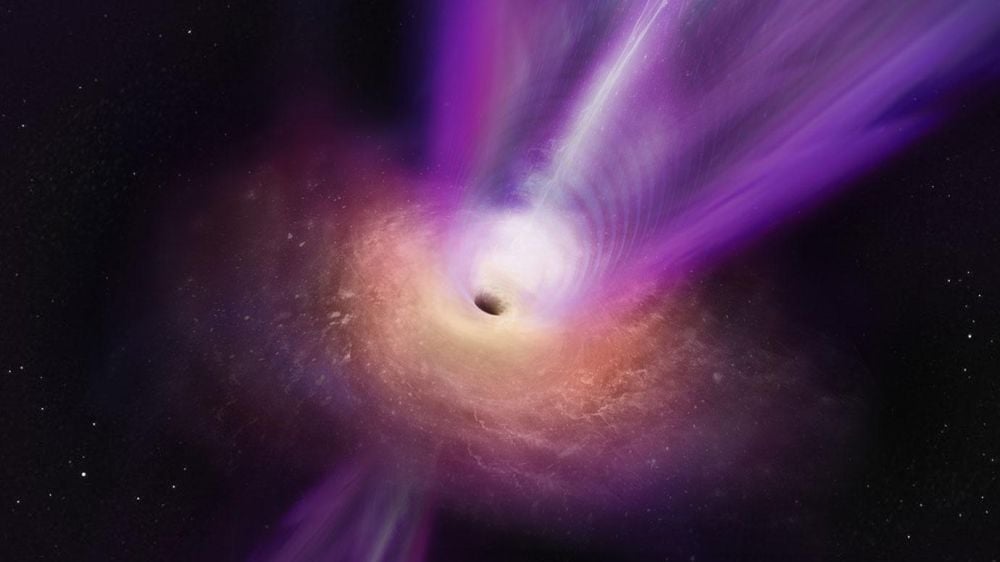

Astronomers used the XRISM x-ray satellite to observe two supermassive black holes in two separate galaxy clusters. Researchers know that SMBH have powerful effects on star formation and galaxy evolution. The observations reveal new details in how it all works.
Continue reading

The Moon has a long history of being smacked by large rocks. Its pock-marked, cratered surface is evidence of that. Scientists expect that, as part of those impacts, some debris would be scattered into space - and that we should be able to track it down. But so far, there have been startlingly few discoveries of these Lunar-origin Asteroids (LOAs) despite their theoretical abundance. A new paper from Yixuan Wu and their colleagues at Tsinghua University explains why - and how the Vera Rubin Observatory might help with finding them.
Continue reading

Mars’ water disappeared somewhere, but scientists have been disagreeing for years about where exactly it went. Data from rovers like Perseverance and Curiosity, along with orbiting satellites such as the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and ExoMars have shown that Mars used to be a wet world with an active hydrodynamic cycle. Obviously it isn’t anymore, but where did all the water go? A new paper that collects data from at least six different instruments on three different spacecraft provides some additional insight into that question - by showing that dust storms push water into the Red Planet’s atmosphere, where it is actively destroyed, all year round.
Continue reading
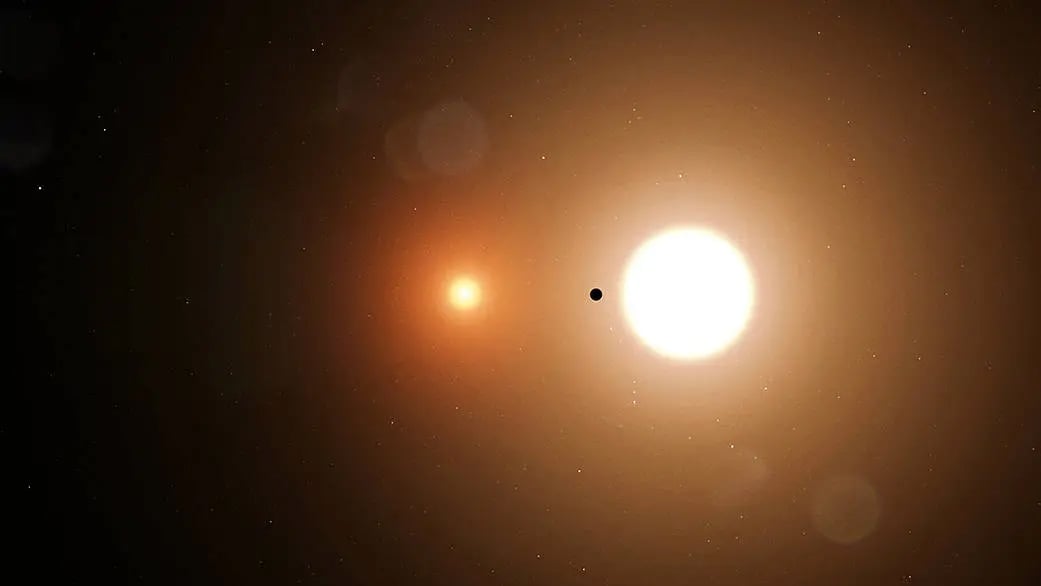

Why are planets rarely found orbiting a pair of stars? UC Berkeley and American University of Beirut physicists find that general relativity makes the orbit of a tight binary pair precess. As the orbit shrinks because of tidal effects, the precesion increases. Eventually the precession matches the orbital precession of any circumbinary planet, creating a resonance that makes the planet’s orbit wildly eccentric. The planet either gets expelled from the system or is engulfed by one of the stars.
Continue reading

To test it, I want you to imagine rolling up a piece of paper into a tight cylinder. Or, if you happen to be near a source of paper, doing it in real life. The analogy works either way.
Continue reading

There's been widespread agreement that a supermassive black hole resides in the Milky Way's Center. But that may not be true. Researchers say that a dense clump of fermionic dark matter can also explain the motions of stars and gas clouds in the region. Crucially, it can also explain the famous Event Horizon Telescope image of the SMBH.
Continue reading
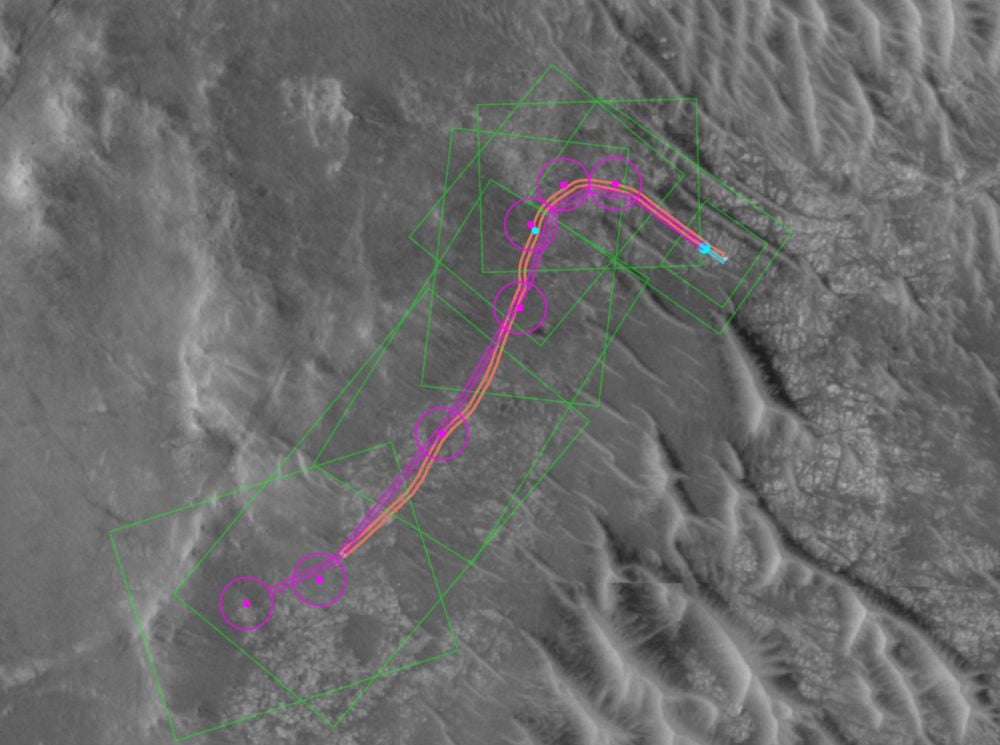
NASA has taken another step towards greater autonomy for planetary exploration rovers. In December, the space agency used AI to generate waypoints for Perseverance's route on two separate days. The rover drove more than 450 meters without human input.
Continue reading

Origami and space exploration might not seem like they have much in common, but the traditional paper-folding technique solves one massive problem for space exploration missions - volume. Satellites and probes that launch in rocket housings are constrained by very restrictive requirements about their physical size, and options for assembling larger structures in orbit are limited to say the least. Anything that can fold up like an origami structure and then expand out to reach a fully functional size is welcome in the space community, and a new paper published in Communications Engineering by Xin Ning of the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC) and his lab describes a novel use case for the idea - electromagnetic waveguides.
Continue reading

A major theme in communist governments is the idea of central planning. Every five years, the central authorities in communist countries lay out their goals for the country over the course of the next five years, which can range from limiting infant mortality to increasing agricultural yield. China, the largest current polity ruled by communists, recently released its fifteenth five-year plan, which lays out its priorities for 2026-2030. This one, accompanied by a press release of the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), the country’s state-owned giant aerospace corporation, has plenty of ambitious goals for its space sector.
Continue reading

The problem that large extra dimensions just might solve is called the hierarchy problem, and it’s one of the nastiest outstanding problems in modern physics.
Continue reading
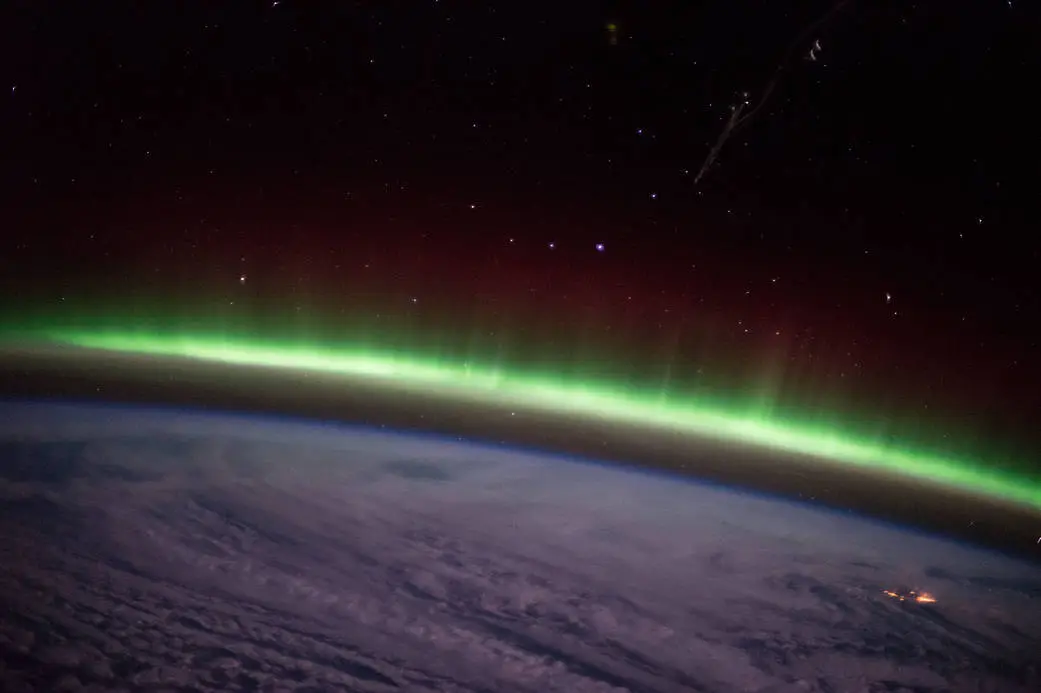

A new study co-led by the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences at The University of Hong Kong (HKU) and the Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) reveals that plasma waves traveling along Earth’s magnetic field lines act like an invisible power source, fueling the stunning auroral displays we see in the sky.
Continue reading

 Universe Today
Universe Today


















