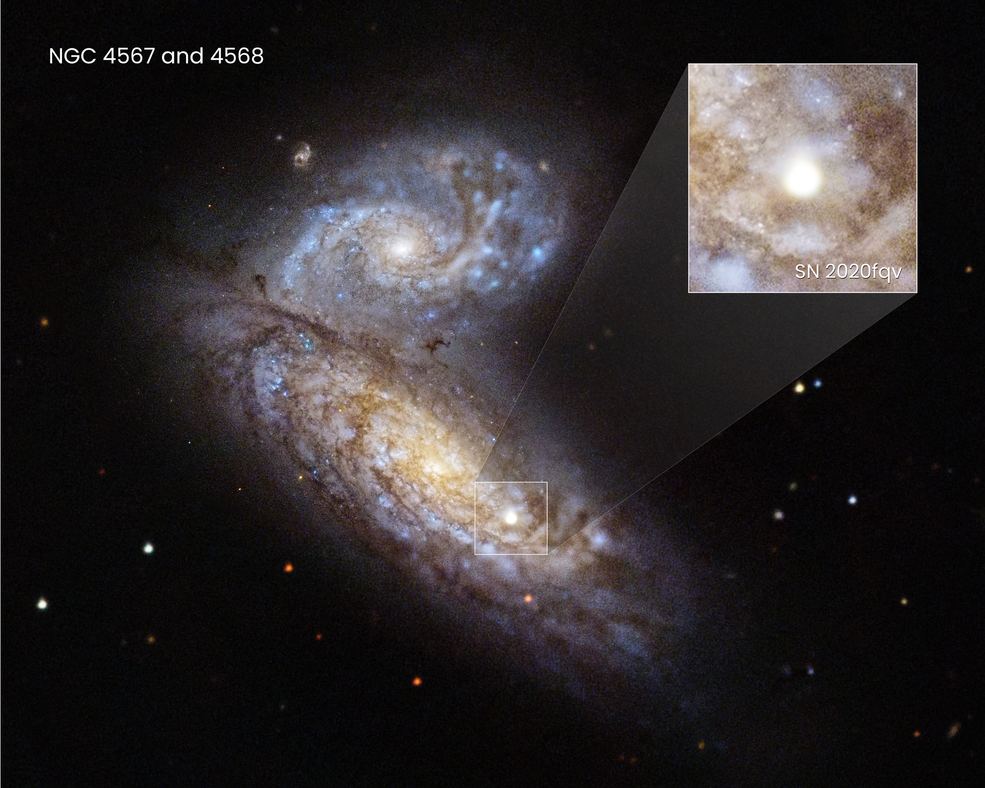
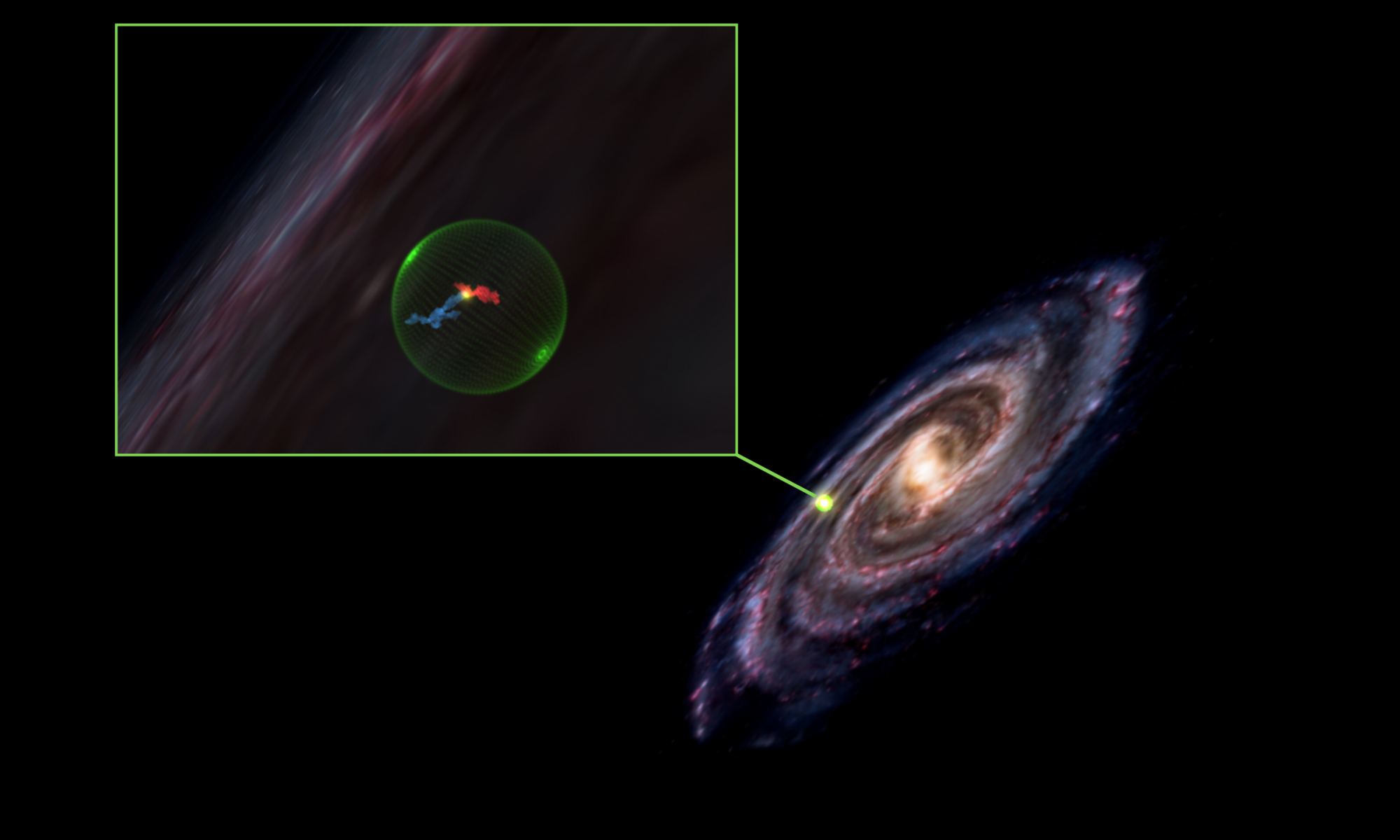
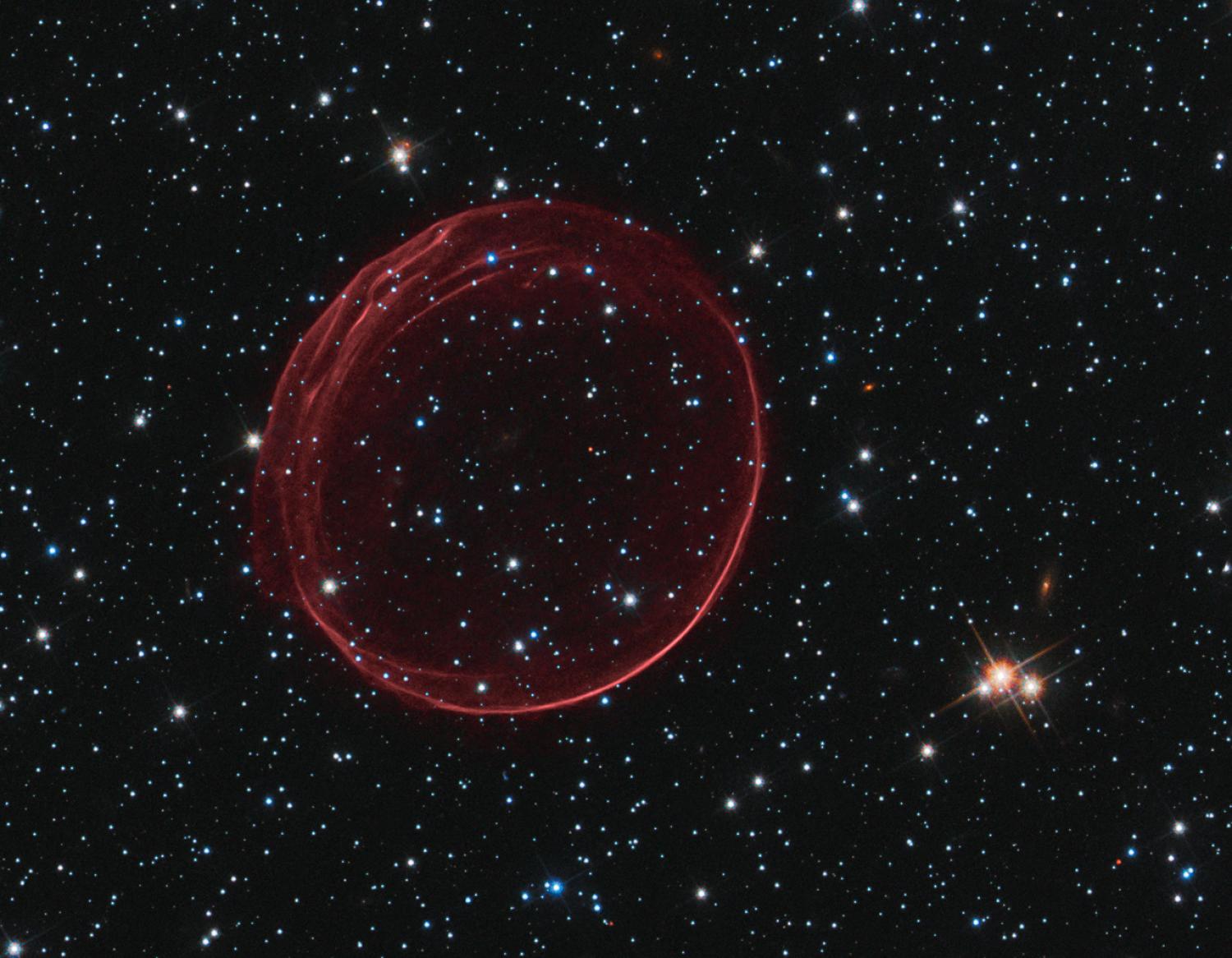
If it weren’t for supernova remnants we wouldn’t have much knowledge of supernovae themselves. If a supernova explosion is the end of a star’s life, then we can also thank forensic astrophysics for much of our knowledge. The massive exploding stars leave behind brilliant and mesmerizing evidence of their catastrophic ends, and much of what we know about supernovae comes from studying the remnants rather than the explosions themselves. Supernova remnants like the Crab Nebula and SN 1604 (Kepler’s Supernova) are some of our most-studied objects.
Observing an active supernova in the grip of its own destruction can be difficult. But it looks like the Hubble Space Telescope is up to the task.
Continue reading “Quick Action Let Hubble Watch the Earliest Stages of an Unfolding Supernova Detonation”