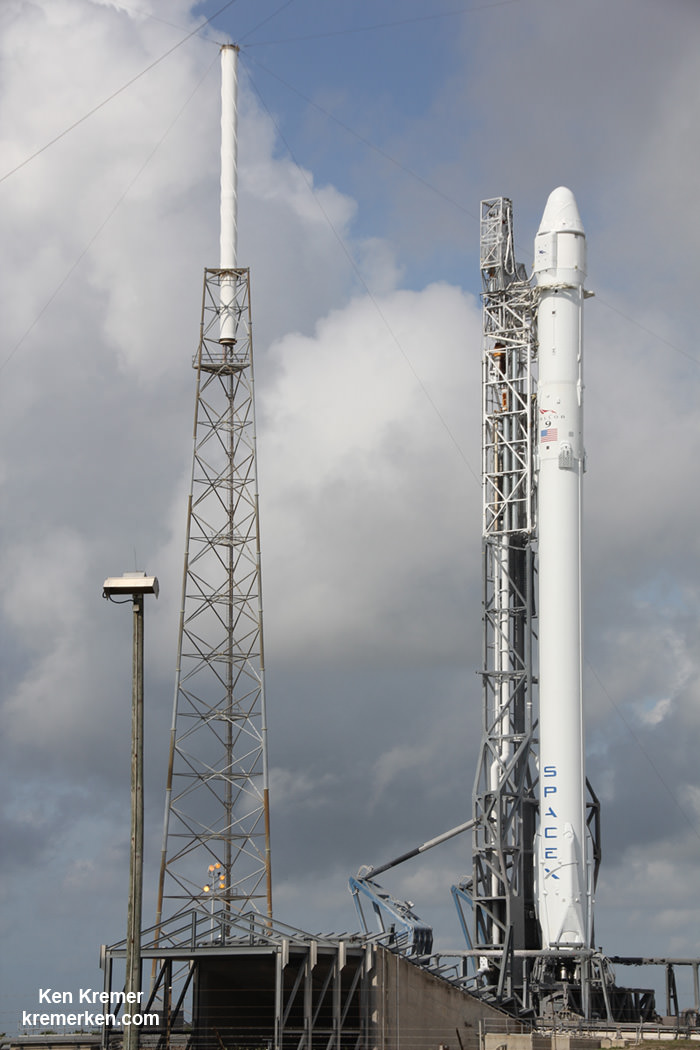
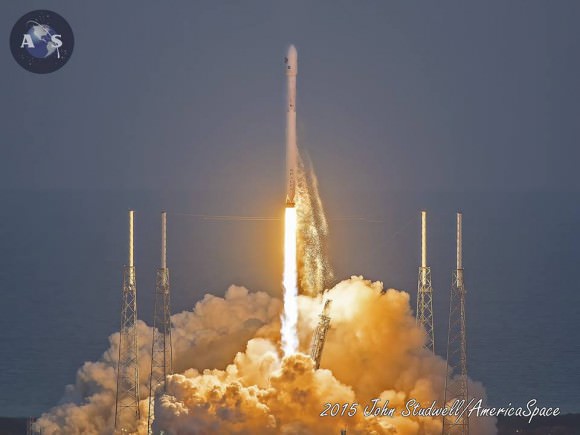
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – The skies are clear at the moment for today’s, April 14, second attempt to launch the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon resupply capsule on a critical mission for science bound for the International Space Station (ISS) and a bold effort to land the boosters first stage on a tiny barge in the vast expanse of the Atlantic Ocean.
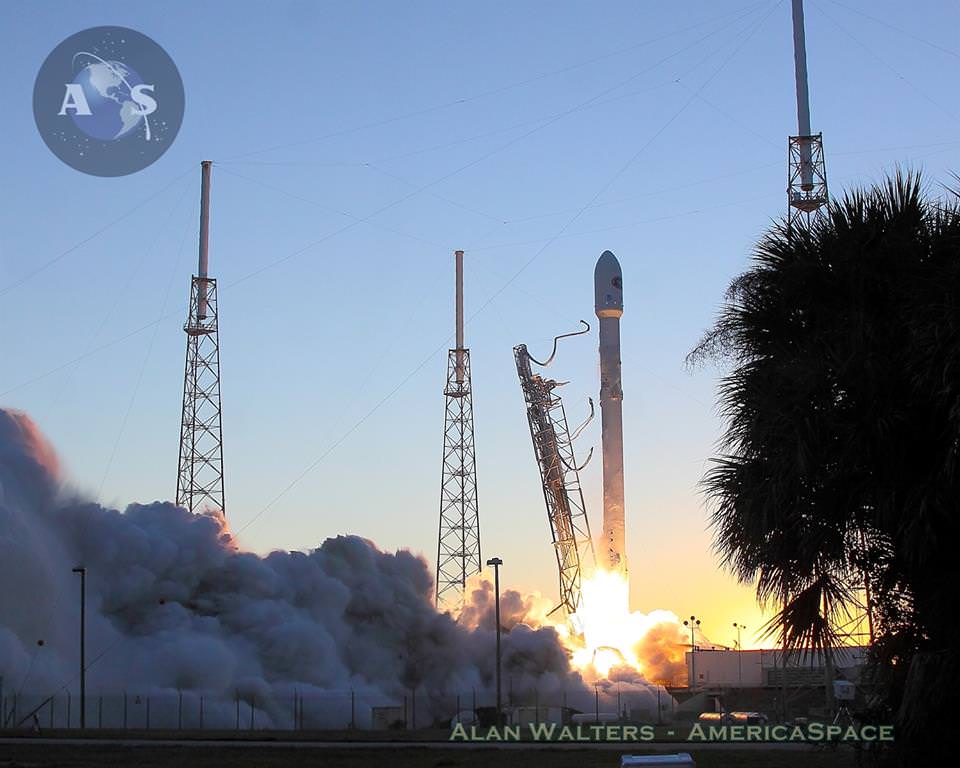
The first attempt to launch the rocket and CRS-6 Dragon cargo capsule on Monday, April 13, was scrubbed just about three minutes before the scheduled blastoff at approximately 4:33 p.m. EDT from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, due to a violation of the launch weather constraints.
Today’s second liftoff attempt 24 hours later, is slated for approximately 4:10 p.m. from SLC-41.
NASA Television plans live launch coverage starting at 3:00 p.m EDT:
You can watch the launch live on NASA TV here: http://www.nasa.gov/nasatv
SpaceX also plans live launch coverage beginning at 4:15 p.m. EDT: www.spacex.com/webcast
The launch window is instantaneous, meaning that the rocket must liftoff at the precisely appointed time. Any delays like on Monday due to weather or technical factors will force a scrub.
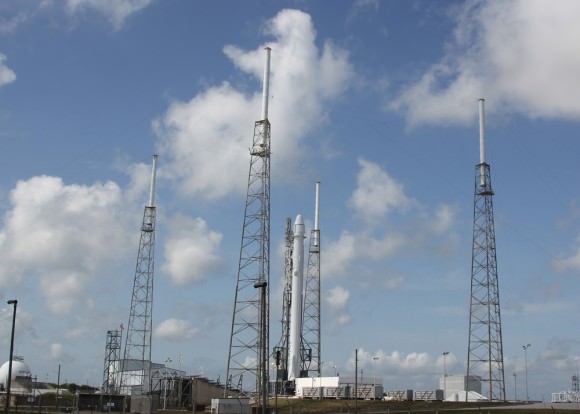

Another delay would likely result in at least a 48 hour scrub.
U.S. Air Force weather forecasters from the 45th Weather Squadron currently rate the chances of favorable conditions at launch time as 60 percent GO for liftoff of the sixth SpaceX commercial resupply services mission (CRS-6) to the ISS. That’s the same as Monday’s launch attempt.
Air Force meteorologists will be watching for storms or thick clouds moving close to the launch site, as happened in the final hour prior to Monday’s try.
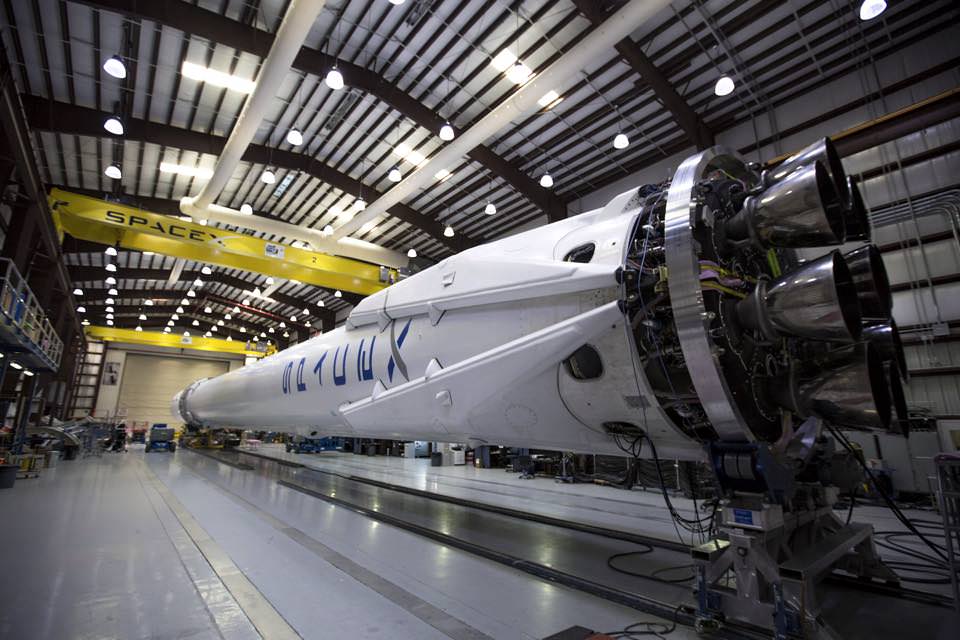
The Falcon 9 first stage is outfitted with four landing legs and grid fins to enable the landing attempt, which is a secondary objective of SpaceX. Cargo delivery to the station is the overriding primary objective and the entire reason for the CRS-6 mission.
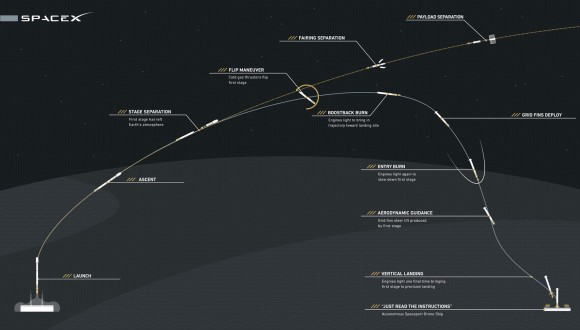
Overall CRS-6 is the sixth SpaceX commercial resupply services mission and the seventh trip by a Dragon spacecraft to the station since 2012.
CRS-6 marks the company’s sixth operational resupply mission to the ISS under a $1.6 Billion contract with NASA to deliver 20,000 kg (44,000 pounds) of cargo to the station during a dozen Dragon cargo spacecraft flights through 2016 under NASA’s original Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract.
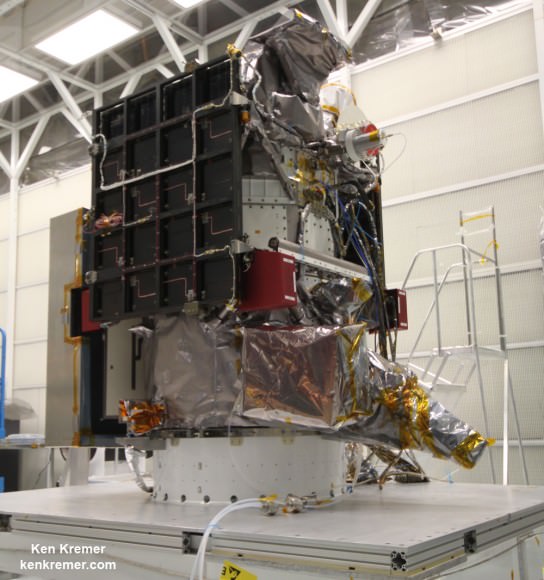
Dragon is packed with more than 4,300 pounds (1915 kilograms) of scientific experiments, technology demonstrations, crew supplies, spare parts, food, water, clothing and assorted research gear for the six person Expedition 43 and 44 crews serving aboard the ISS.
The ship will remain berthed at the ISS for about five weeks.
Watch for Ken’s continuing onsite coverage of the CRS-6 launch from the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
Ken Kremer
………….
Learn more about SpaceX, Mars rovers, Orion, Antares, MMS, NASA missions and more at Ken’s upcoming outreach events:
Apr 11-14: “SpaceX, Orion, Commercial crew, Curiosity explores Mars, MMS, Antares and more,” Kennedy Space Center Quality Inn, Titusville, FL, evenings
Apr 18/19: “Curiosity explores Mars” and “NASA Human Spaceflight programs” – NEAF (NorthEast Astronomy Forum), 9 AM to 5 PM, Suffern, NY, Rockland Community College and Rockland Astronomy Club