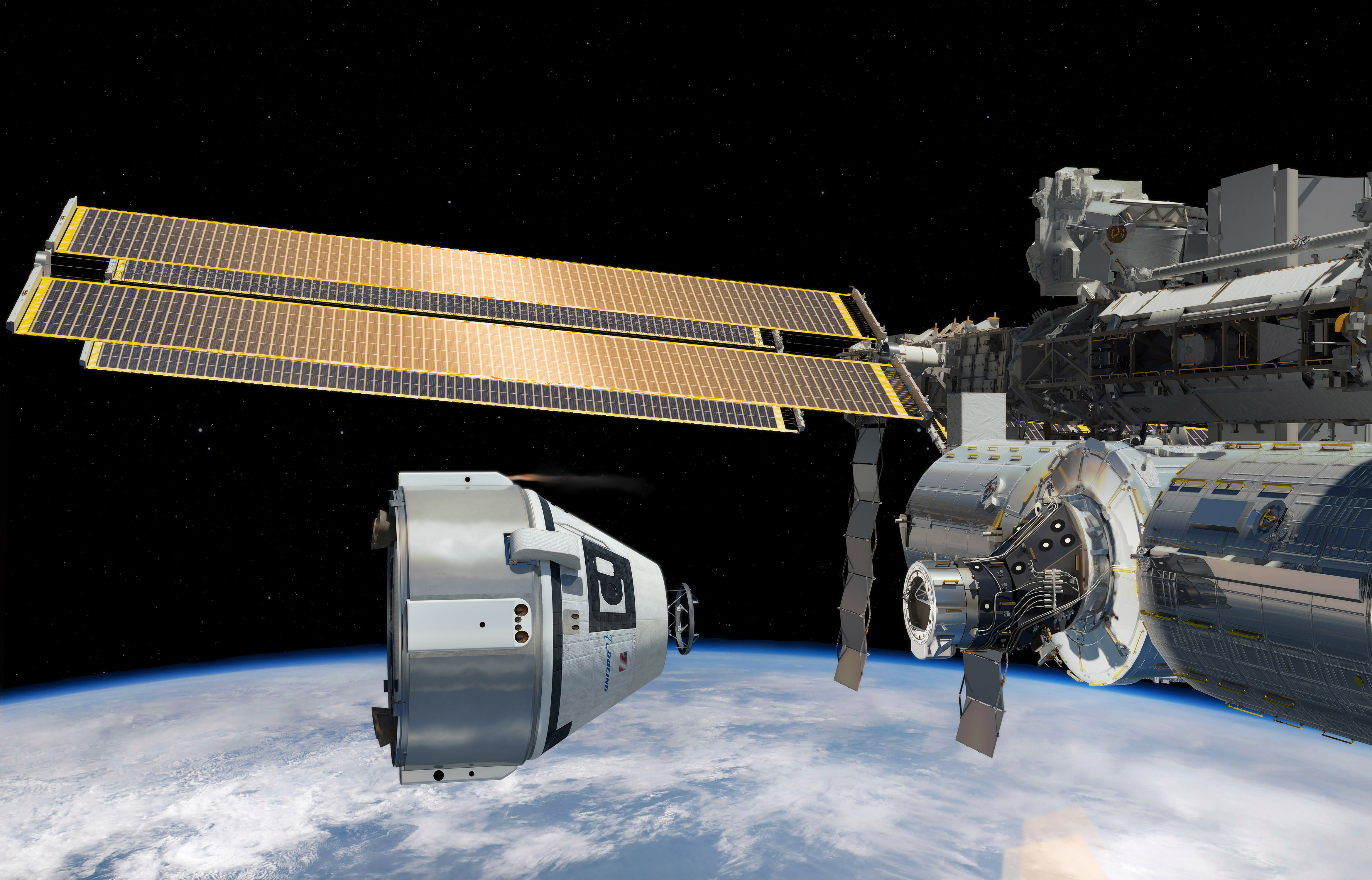
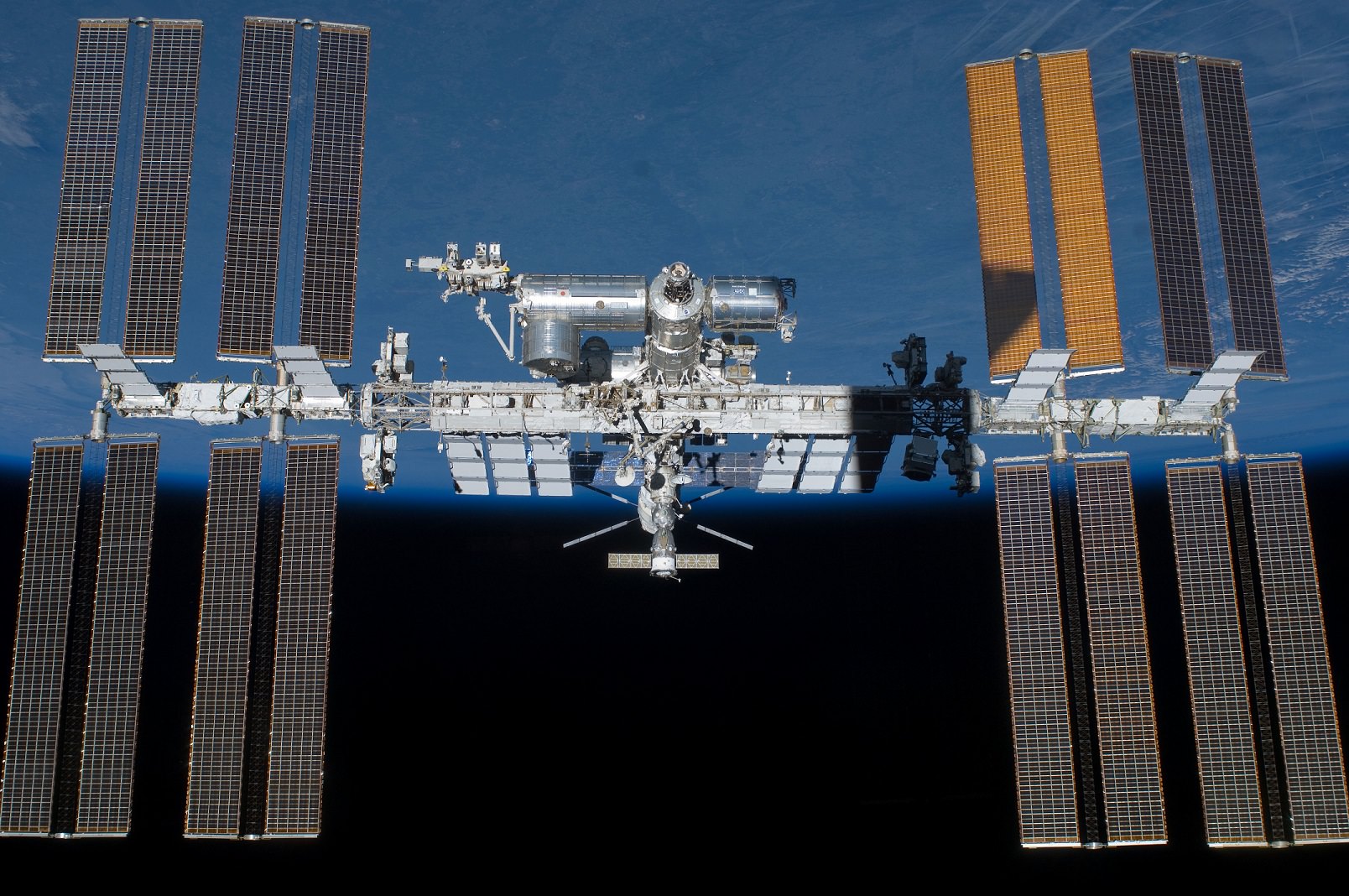
The restoration of America’s ability to launch American astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS) from American soil in 2017 took a major step forward when NASA ordered the first ever commercial human spaceflight mission from Boeing.
NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) office gave the first commercial crew rotation mission award to the Boeing Company to launch its CST-100 astronaut crew capsule to the ISS by late 2017, so long as the company satisfactorily meets all of NASA’s human spaceflight certification milestones.
Thus begins the history making new era of commercial human spaceflight.
“This occasion will go in the books of Boeing’s nearly 100 years of aerospace and more than 50 years of space flight history,” said John Elbon, vice president and general manager of Boeing’s Space Exploration division, in a statement.
“We look forward to ushering in a new era in human space exploration.”
Boeing was awarded a $4.2 Billion contract in September 2014 by NASA Administrator Charles Bolden to complete development and manufacture of the CST-100 ‘space taxi’ under the agency’s Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap) program and NASA’s Launch America initiative.
“Final development and certification are top priority for NASA and our commercial providers, but having an eye on the future is equally important to the commercial crew and station programs,” said Kathy Lueders, manager of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
“Our strategy will result in safe, reliable and cost-effective crew missions.”

The CST-100 will be carried to low Earth orbit atop a manrated United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket launching from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Boeing will first conduct a pair of unmanned and manned orbital CST-100 test flights earlier in 2017 in April and July, prior to the operational commercial crew rotation mission to confirm that their capsule is ready and able and met all certification milestone requirements set by NASA.
“Orders under the CCtCap contracts are made two to three years prior to the missions to provide time for each company to manufacture and assemble the launch vehicle and spacecraft. In addition, each company must successfully complete the certification process before NASA will give the final approval for flight,” says NASA.
Boeing got the mission order from NASA because they have “successfully demonstrated to NASA that the Commercial Crew Transportation System has reached design maturity appropriate to proceed to assembly, integration and test activities.”
Boeing recently completed the fourth milestone in the CCtCap phase dubbed the delta integrated critical design review.
Read my earlier exclusive, in depth one-on-one interviews with Chris Ferguson – America’s last shuttle commander and who now leads Boeings CST-100 program; here and here.
The commercial crew program is designed to return human spaceflight launches to the United States and end our sole source reliance on Russia and the Soyuz capsule.
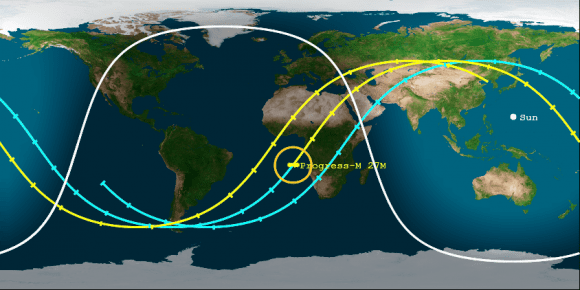
ISS Soyuz crew rotation missions are currently on hold due to the recent launch failure of the Russian Soyuz booster and Progress resupply vessel earlier this month.
Since the forced retirement of NASA’s shuttle orbiters in 2011, US astronauts have been totally dependent on the Russians for trips to space and back.

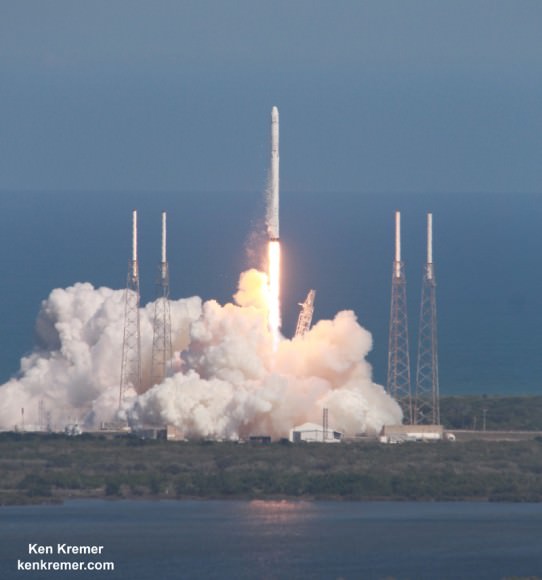
SpaceX also received a NASA award worth $2.6 Billion to build the Crew Dragon spacecraft for launch atop the firms man-rated Falcon 9 rocket.
SpaceX conducted a successful Pad Abort Test of the Crew Dragon on May 6, fulfilling a key NASA milestone, as I reported here.
NASA will order a commercial mission from SpaceX sometime later this year. At a later date NASA will decide which company will fly the first commercial crew rotation mission to the ISS.
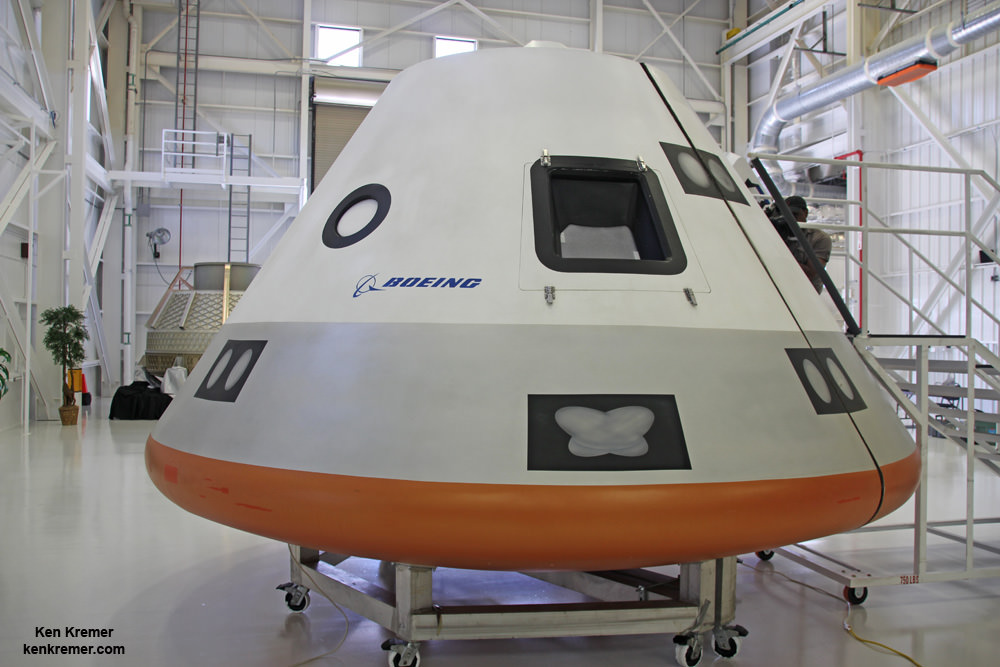
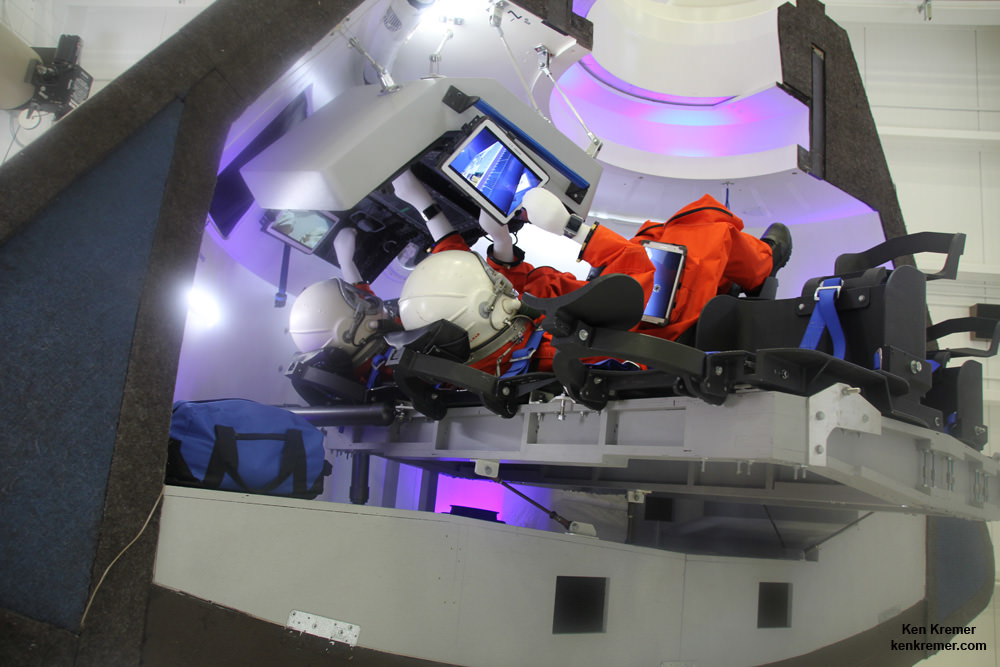
Both the CST-100 and Crew Dragon will typically carry a crew of four or five NASA or NASA-sponsored crew members, along with some 220 pounds of pressurized cargo. Each will also be capable of carrying up to seven crew members depending on how the capsule is configured.
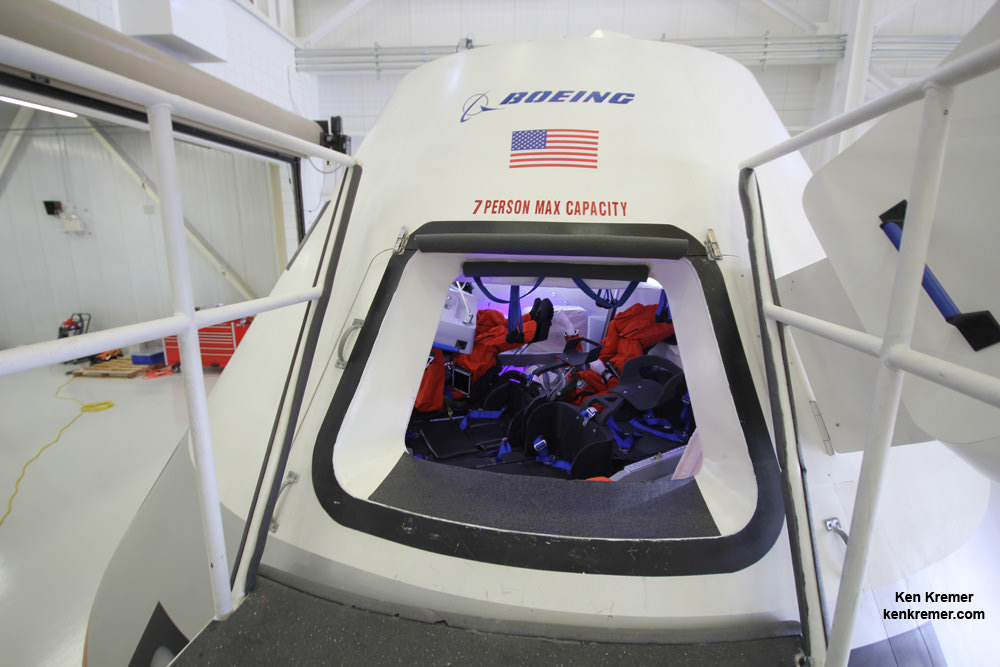

The spacecraft will be capable to remaining docked at the station for up to 210 days and serve as an emergency lifeboat during that time.
The NASA CCtCAP contracts call for a minimum of two and a maximum potential of six missions from each provider.
The station crew will also be enlarged to seven people that will enable a doubling of research time.
“Commercial Crew launches are critical to the International Space Station Program because it ensures multiple ways of getting crews to orbit,” said Julie Robinson, International Space Station chief scientist.
“It also will give us crew return capability so we can increase the crew to seven, letting us complete a backlog of hands-on critical research that has been building up due to heavy demand for the National Laboratory.”

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.