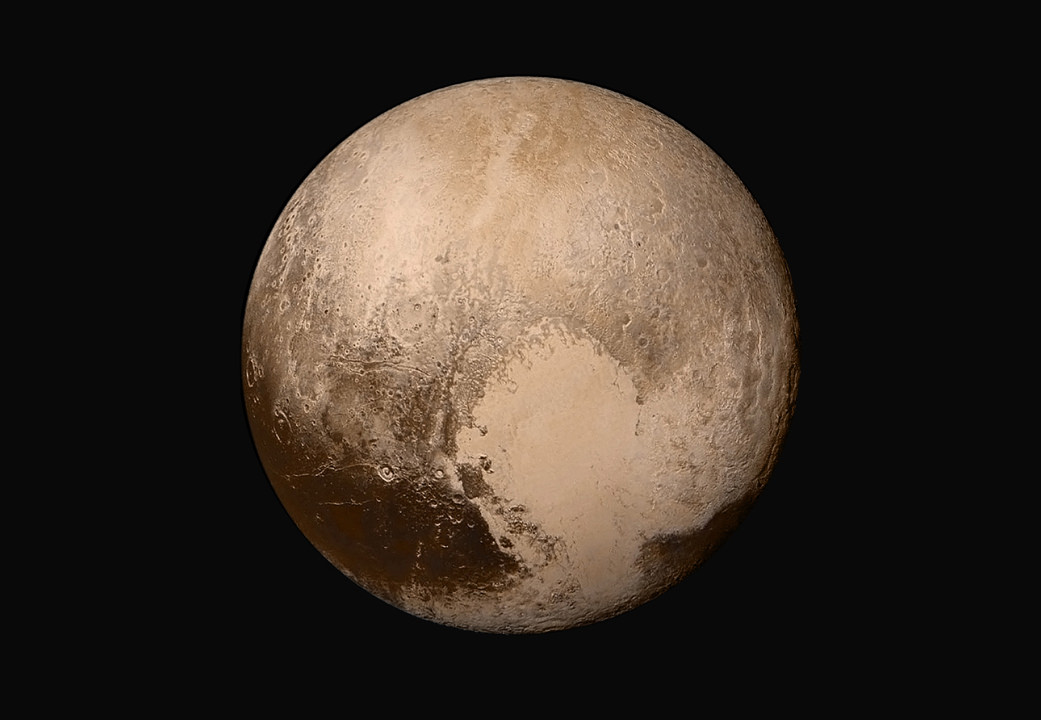
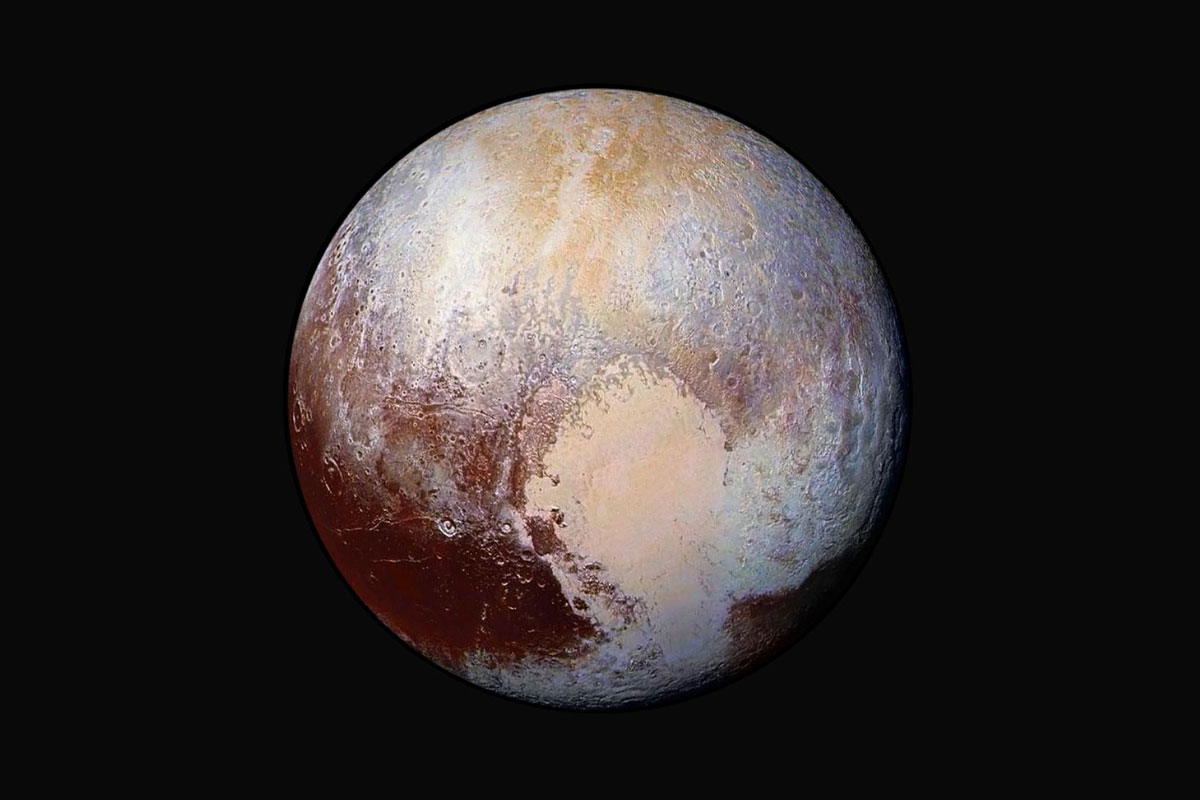
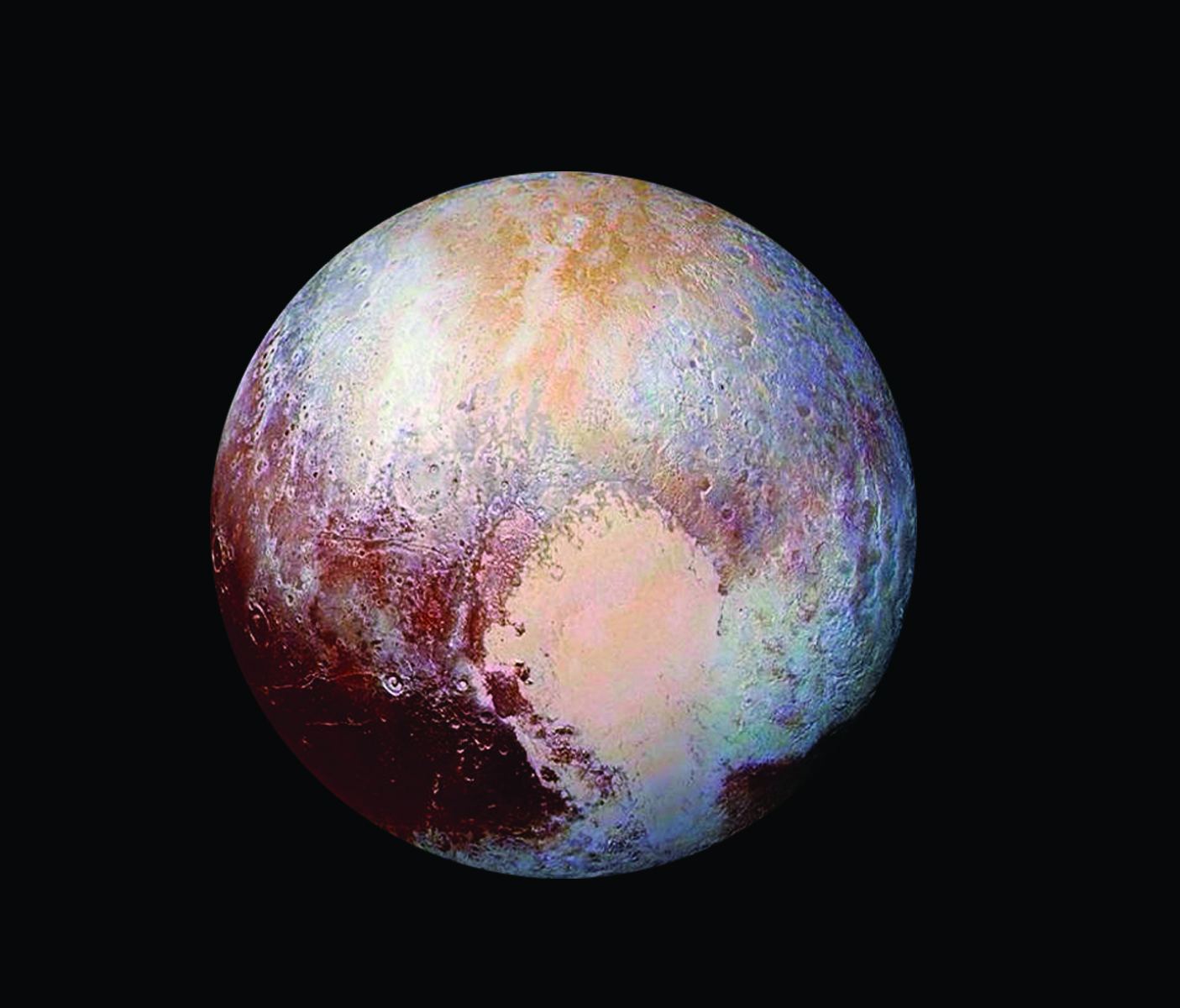
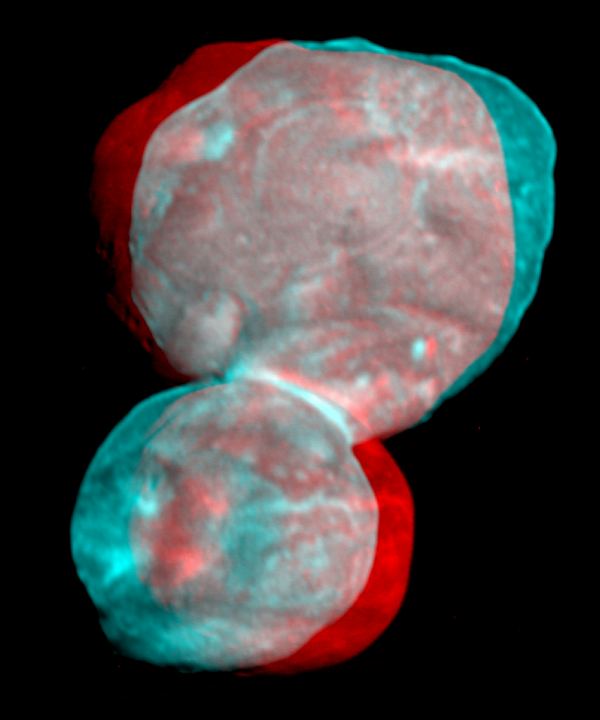
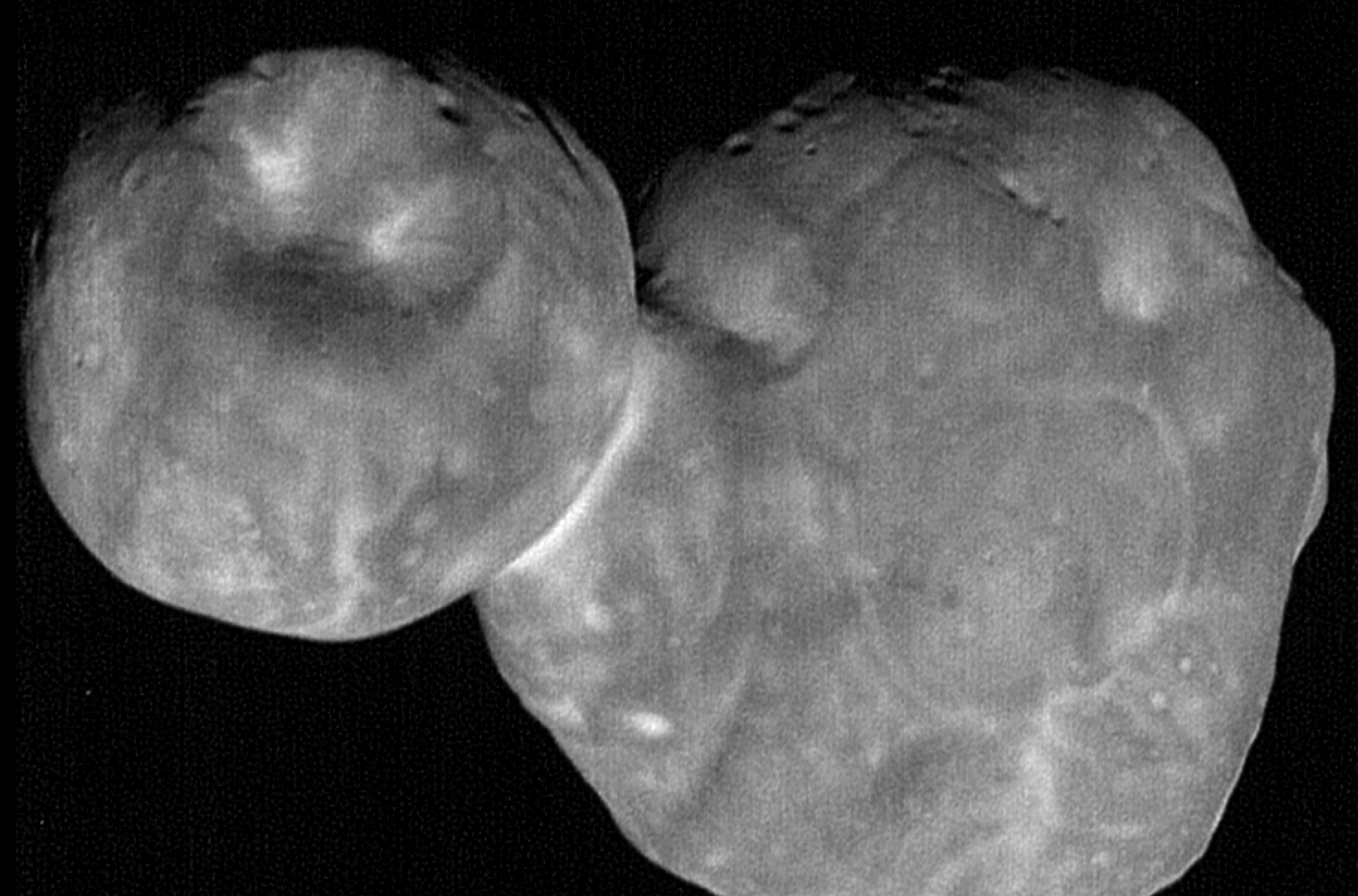
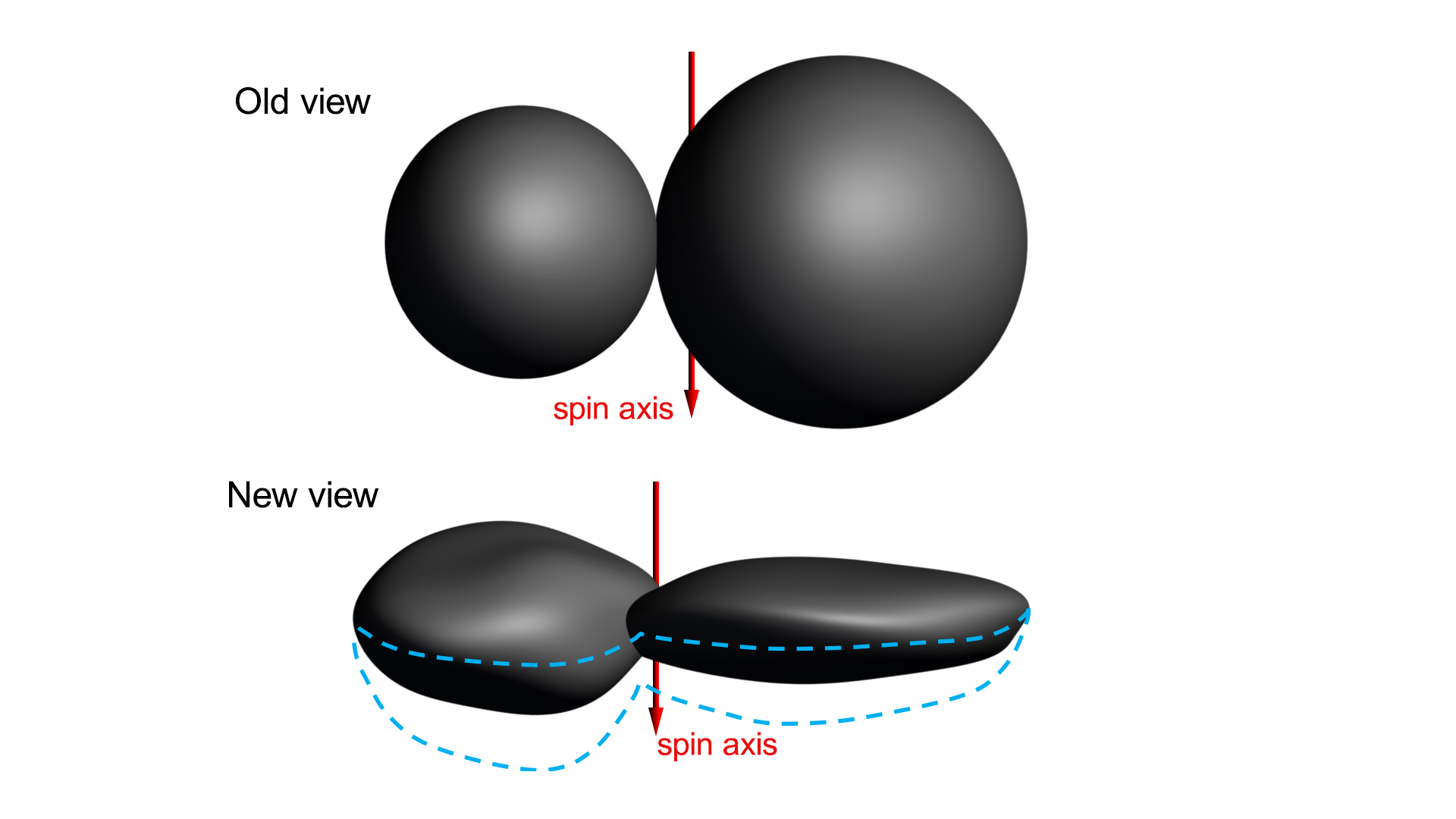
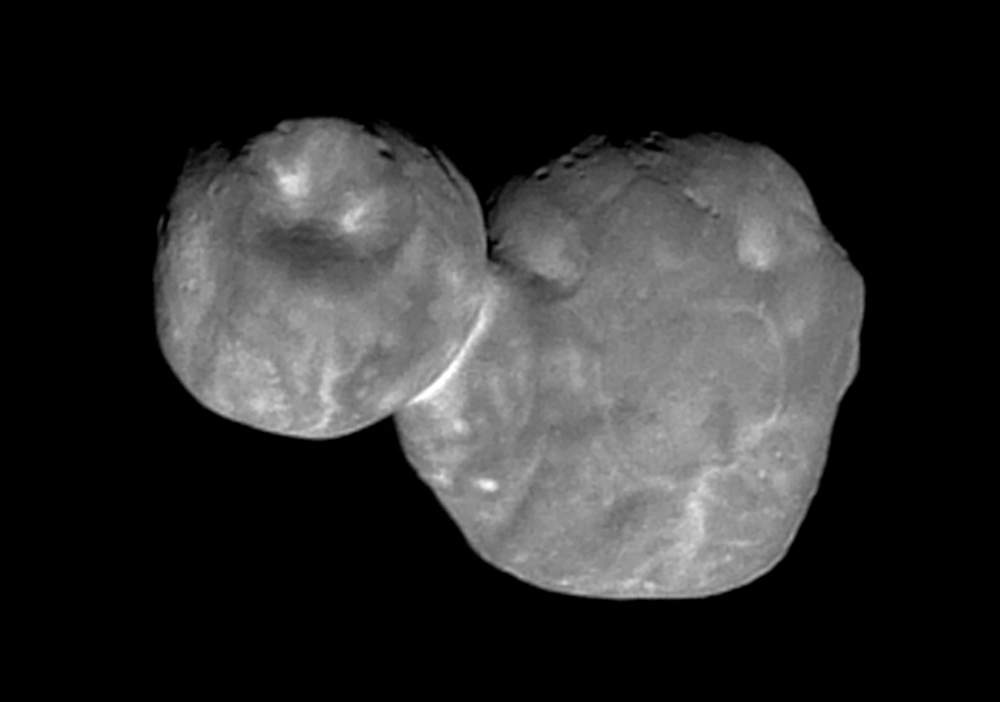
On July 14th, 2015, the New Horizons made the first-ever flyby of Pluto. As if that wasn’t enough, the mission made history again with the flyby of the Kuiper Belt Object (KBO) 2014 MU69 on December 31st, 2018. This constituted the farthest encounter from Earth with a celestial object, which the team had nicknamed Ultima Thule – a mythical northern island beyond the borders of the known world in Medieval literature.
Unfortunately, this name has generated some controversy due to the fact that it is also the name white supremacists use to refer to a mythical homeland. So with the consent of the tribal elders and representatives of the Powhatan nations, the New Horizons’ team recommended a new name for the KBO. Henceforth, it will be known as “Arrokoth“, the word for “sky” in the Powhatan/Algonquian language.
Continue reading “New Horizon’s Flyby Target 2014 MU69 Gets its Official Name: Arrokoth”