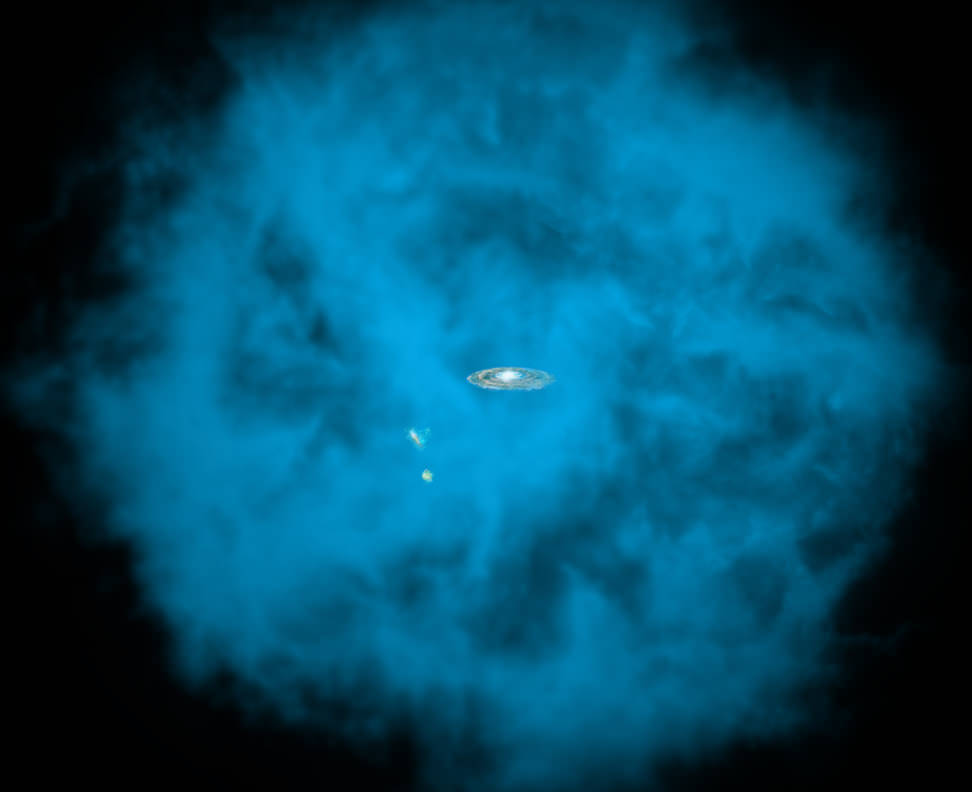
Artist’s illustration of a hot gas halo enveloping the Milky Way and Magellanic Clouds (NASA/CXC/M.Weiss; NASA/CXC/Ohio State/A.Gupta et al.)
Our galaxy — and the nearby Large and Small Magellanic Clouds as well — appears to be surrounded by an enormous halo of hot gas, several hundred times hotter than the surface of the Sun and with an equivalent mass of up to 60 billion Suns, suggesting that other galaxies may be similarly encompassed and providing a clue to the mystery of the galaxy’s missing baryons.
The findings were reported today by a research team using data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory.
In the artist’s rendering above our Milky Way galaxy is seen at the center of a cloud of hot gas. This cloud has been detected in measurements made with Chandra as well as with the European Space Agency’s XMM-Newton space observatory and Japan’s Suzaku satellite. The illustration shows it to extend outward over 300,000 light-years — and it may actually be even bigger than that.
 While observing bright x-ray sources hundreds of millions of light-years distant, the researchers found that oxygen ions in the immediate vicinity of our galaxy were “selectively absorbing” some of the x-rays. They were then able to measure the temperature of the halo of gas responsible for the absorption.
While observing bright x-ray sources hundreds of millions of light-years distant, the researchers found that oxygen ions in the immediate vicinity of our galaxy were “selectively absorbing” some of the x-rays. They were then able to measure the temperature of the halo of gas responsible for the absorption.
The scientists determined the temperature of the halo is between 1 million and 2.5 million kelvins — a few hundred times hotter than the surface of the Sun.
But even with an estimated mass anywhere between 10 billion and 60 billion Suns, the density of the halo at that scale is still so low that any similar structure around other galaxies would escape detection. Still, the presence of such a large halo of hot gas, if confirmed, could reveal where the missing baryonic matter in our galaxy has been hiding — a mystery that’s been plaguing astronomers for over a decade.
Unrelated to dark matter or dark energy, the missing baryons issue was discovered when astronomers estimated the number of atoms and ions that would have been present in the Universe 10 billion years ago. But current measurements yield only about half as many as were present 10 billion years ago, meaning somehow nearly half the baryonic matter in the Universe has since disappeared.
Recent studies have proposed that the missing matter is tied up in the comic web — vast clouds and strands of gas and dust that surround and connect galaxies and galactic clusters. The findings announced today from Chandra support this, and suggest that the missing ions could be gathered around other galaxies in similarly hot halos.
Even though previous studies have indicated halos of warm gas existing around our galaxy as well as others, this new research shows a much hotter, much more massive halo than ever detected.
“Our work shows that, for reasonable values of parameters and with reasonable assumptions, the Chandra observations imply a huge reservoir of hot gas around the Milky Way,” said study co-author Smita Mathur of Ohio State University in Columbus. “It may extend for a few hundred thousand light-years around the Milky Way or it may extend farther into the surrounding local group of galaxies. Either way, its mass appears to be very large.”
Read the full news release from NASA here, and learn more about the Chandra mission here. (The team’s paper can be found on arXiv.org.)
Inset image: NASA’s Chandra spacecraft (NASA/CXC/NGST)
NOTE: the initial posting of this story mentioned that this halo could be dark matter. That was incorrect and not implied by the actual research, as dark matter is non-baryonic matter while the hot gas in the halo is baryonic — i.e., “normal” — matter. Edited. – JM