One of the most iconic events in history is Apollo 11 landing on the lunar surface. During the descent, astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin are heard relaying commands and data back and forth to mission control across 385,000 kilometers (240,000 miles) of outer space as the lunar module “Eagle” slowly inched its way into the history books.
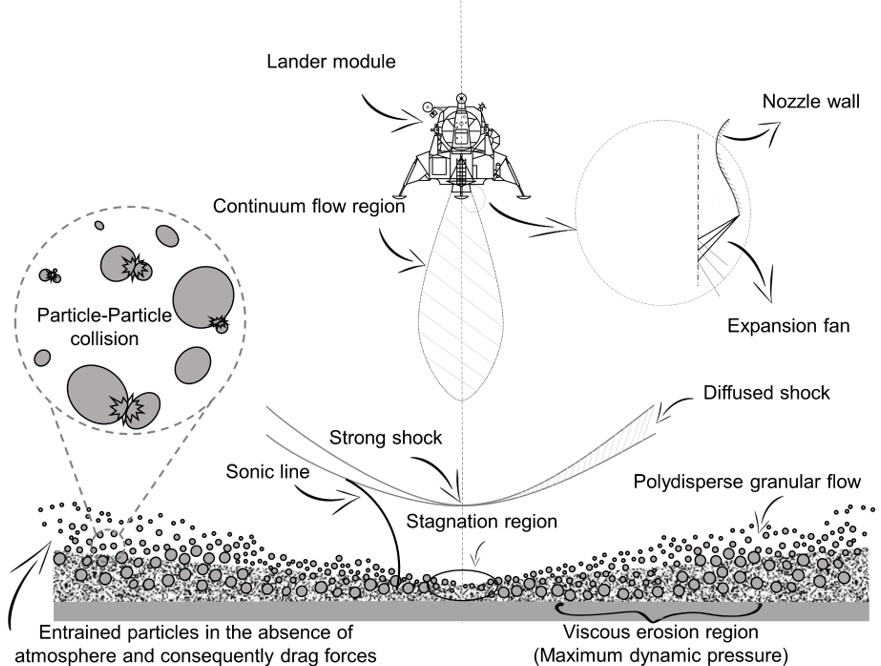
In the final moments before touchdown, Aldrin can be heard saying, “Picking up some dust”, followed by large dust clouds shooting outward from underneath from the spacecraft as the exhaust plumes interacted with the lunar surface, more commonly known as brownout or brownout effect. This significantly reduced the visibility for Armstrong and Aldrin as they landed, and while they successfully touched down on the Moon, future astronauts might not be so lucky.
Continue reading “It’s Time to Figure Out How to Land Large Spacecraft Safely on Other Worlds”