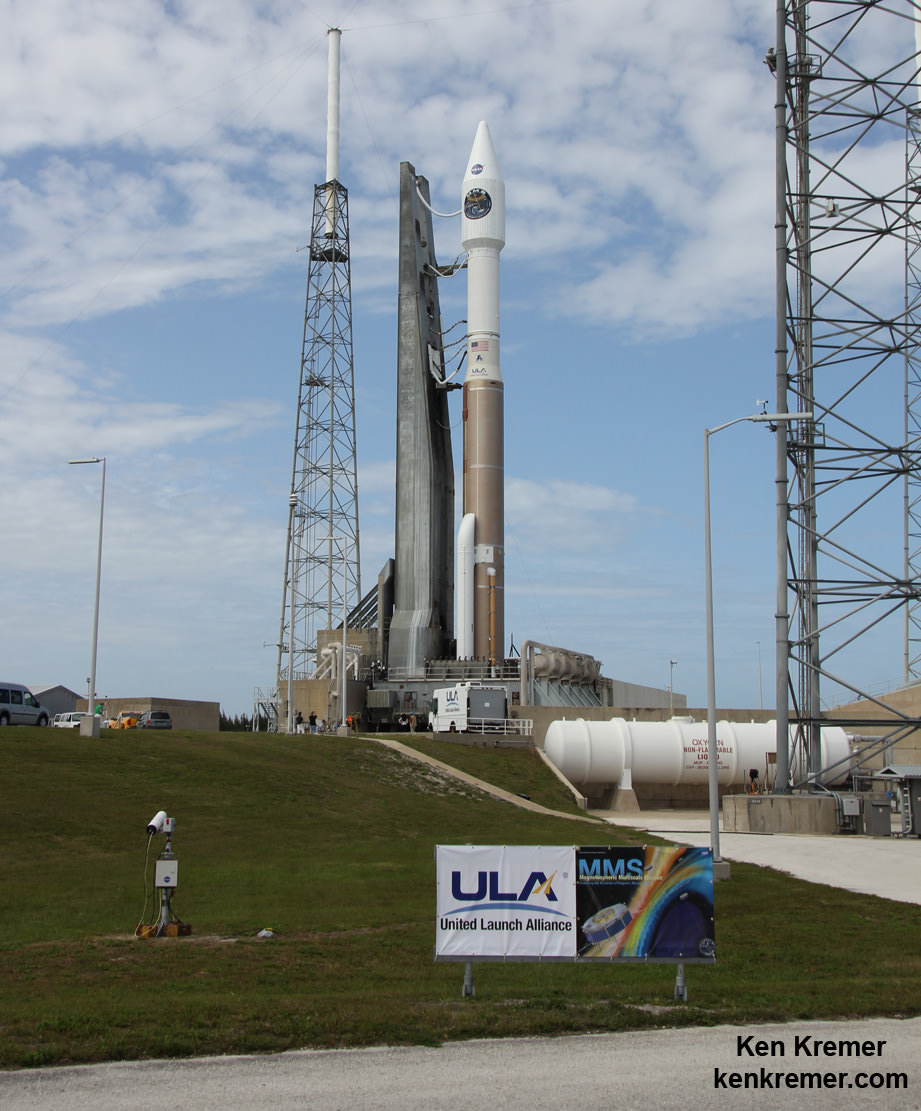
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – A state of the art quartet of identical science satellites aimed at unraveling the mysteries of the process known as magnetic reconnection is slated for a spectacular nighttime blastoff tonight, March 12, atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Cape Canaveral, Florida.
The $1.1 Billion Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission is comprised of four formation flying and identically instrumented observatories whose objective is providing the first three-dimensional views of a fundamental process in nature known as magnetic reconnection.
Magnetic reconnection is a little understood natural process whereby magnetic fields around Earth connect and disconnect while explosively releasing vast amounts of energy. It occurs throughout the universe.
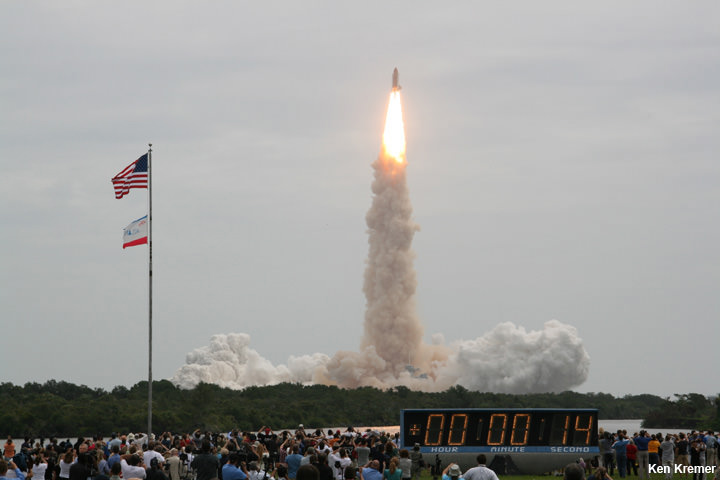
Liftoff is slated for 10:44 p.m. EDT Thursday March 12 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
The launch window extends for 30 minutes. You can watch the MMS launch live on NASA TV, below, starting at 8 p.m.
Broadcast live streaming video on Ustream
Spectators ringing the Florida space coast region and ranging well beyond should be treated to a magnificent fireworks display and skyward streak of perhaps several minutes – weather and clouds permitting.
Currently the weather forecast is 70 percent “GO” for favorable conditions at launch time. The primary concerns for a safe and successful launch are for cumulus clouds and thick clouds.
In the event of a 24 hour delay for any reason the weather forecast is 60 percent “GO.”

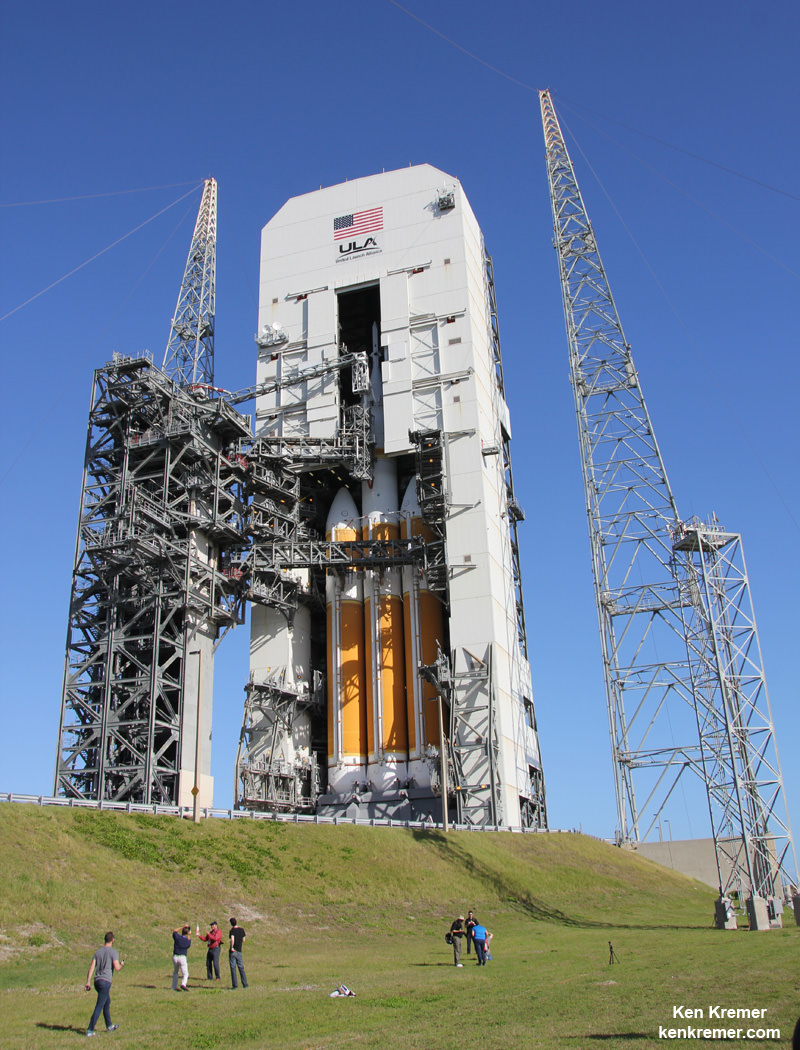
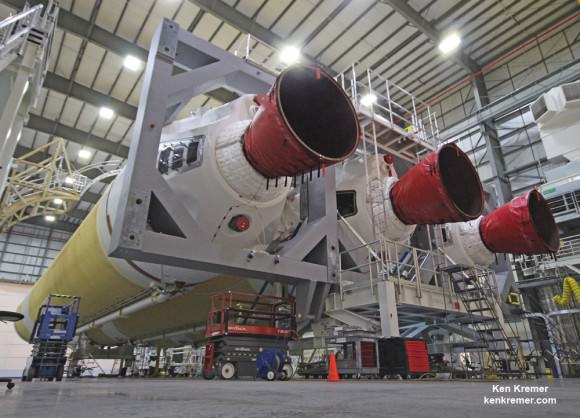
The 195 foot tall rocket and encapsulated MMS satellite payload were rolled out to Space Launch Complex-41 on Wednesday March 10 at 10 a.m. on the Mobile Launch Platform (MLP) about 1800 feet from the Vertical Integration Facility or VIF to the Cape Canaveral pad.
The two stage Atlas V rocket will deliver the MMS constellation to a highly elliptical orbit.
The venerable rocket with a 100% success rate will launch in the Atlas V 421 configuration with a 4-meter diameter Extra Extended Payload Fairing along with two Aerojet Rocketdyne solid rocket motors attached to the Atlas booster first stage.

The Atlas first stage is powered by the RD AMROSS RD-180 engine and the Centaur upper stage is powered by the Aerojet Rocketdyne RL10A engine producing 22,300 lb of thrust.
The first stage is 12.5 ft in diameter and fueled with liquid propellants. The RD-180 burns RP-1 highly purified kerosene and liquid oxygen and delivers 860,200 lb of sea level thrust.
This is ULA’s 4th launch in 2015, the 53nd Atlas V mission and the fourth Atlas V 421 launch.
“This is the perfect time for this mission,” said Jim Burch, principal investigator of the MMS instrument suite science team at Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) in San Antonio, Texas.
“MMS is a crucial next step in advancing the science of magnetic reconnection. Studying magnetic reconnection near Earth will unlock the ability to understand how this process works throughout the entire universe.”
After a six month check out phase the probes will start science operation in September.
Unlike previous missions to observe the evidence of magnetic reconnection events, MMS will have sufficient resolution to measure the characteristics of ongoing reconnection events as they occur.
The four probes were built in-house by NASA at the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland where I visited them during an inspection tour by NASA Administrator Charles Bolden.
I asked Bolden to explain the goals of MMS during a one-on-one interview.
“MMS will help us study the phenomena known as magnetic reconnection and help us understand how energy from the sun – magnetic and otherwise – affects our own life here on Earth,” Bolden told Universe Today.
“MMS will study what effects that process … and how the magnetosphere protects Earth.”
MMS measurements should lead to significant improvements in models for yielding better predictions of space weather and thereby the resulting impacts for life here on Earth as well as for humans aboard the ISS and robotic satellite explorers in orbit and the heavens beyond.
The best place to study magnetic reconnection is ‘in situ’ in Earth’s magnetosphere. This will lead to better predictions of space weather phenomena.
Magnetic reconnection is also believed to help trigger the spectacular aurora known as the Northern or Southern lights.
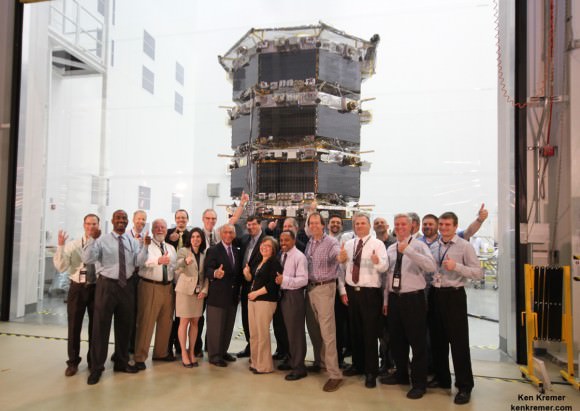

MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes Program, or STP, mission within NASA’s Heliophysics Division
Watch for Ken’s ongoing MMS coverage and he’ll be onsite at the Kennedy Space Center in the days leading up to the launch on March 12.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing MMS, Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.