The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is the most complex and sophisticated observatory ever deployed. Using its advanced suite of infrared instruments, coronographs, and spectrometers – contributed by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) – this observatory will spend the next ten to twenty years building on the achievements of its predecessor, the venerable Hubble. This includes exoplanet characterization, star and planet formation, and the formation and evolution of the earliest galaxies in the Universe.
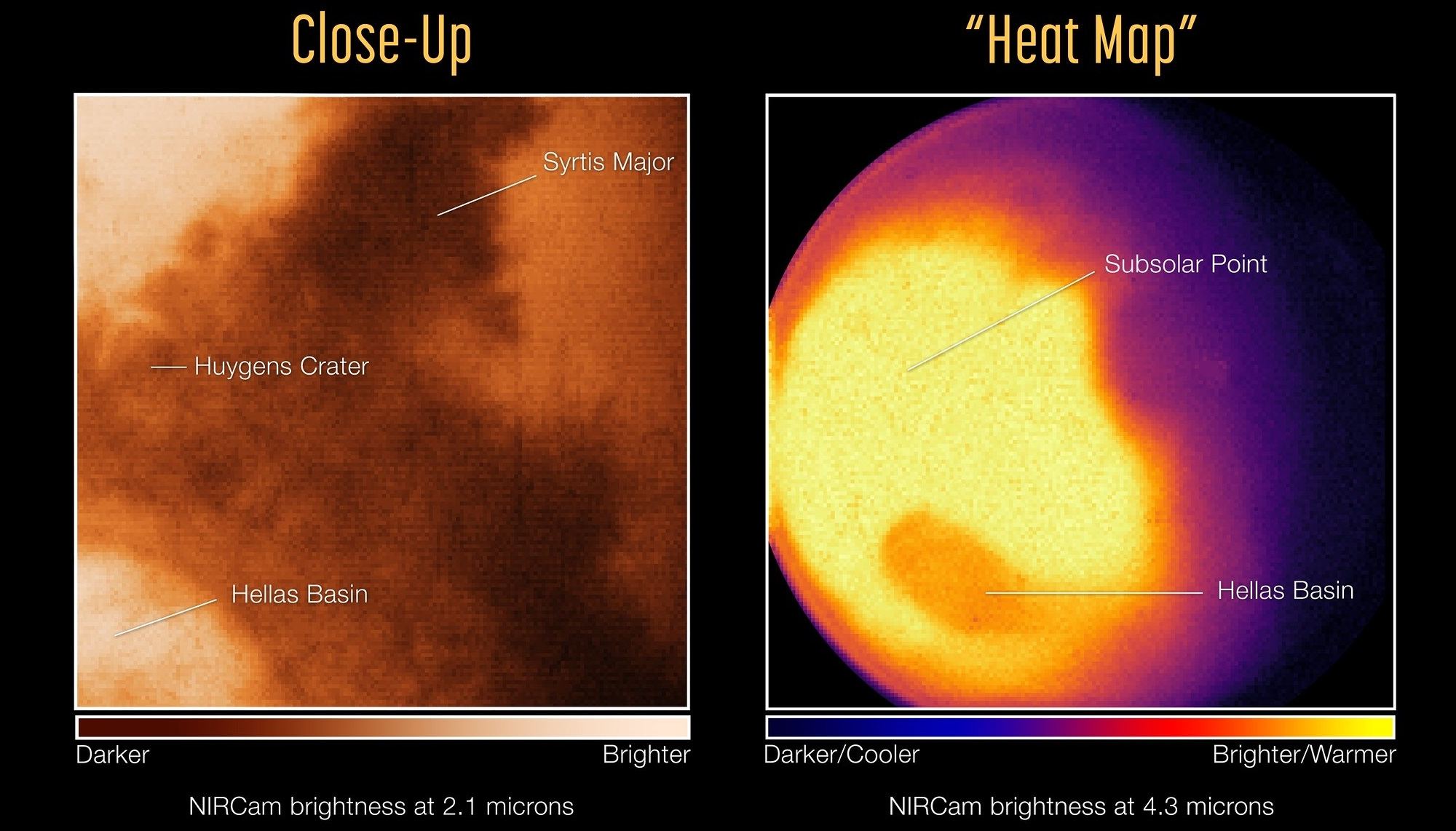
However, one of the main objectives of the JWST is to study the planets, moons, asteroids, comets, and other celestial bodies here in the Solar System. This includes Mars, the first Solar planet to get the James Webb treatment! The images Webb took (recently released by the ESA) provide a unique perspective on Mars, showing what the planet looks like in infrared wavelengths. The data yielded by these images could provide new insight into Mars’ atmosphere and environment, complimenting decades of observations by orbiters, landers, rovers, and other telescopes.
Continue reading “Webb Turns its Infrared Gaze on Mars”