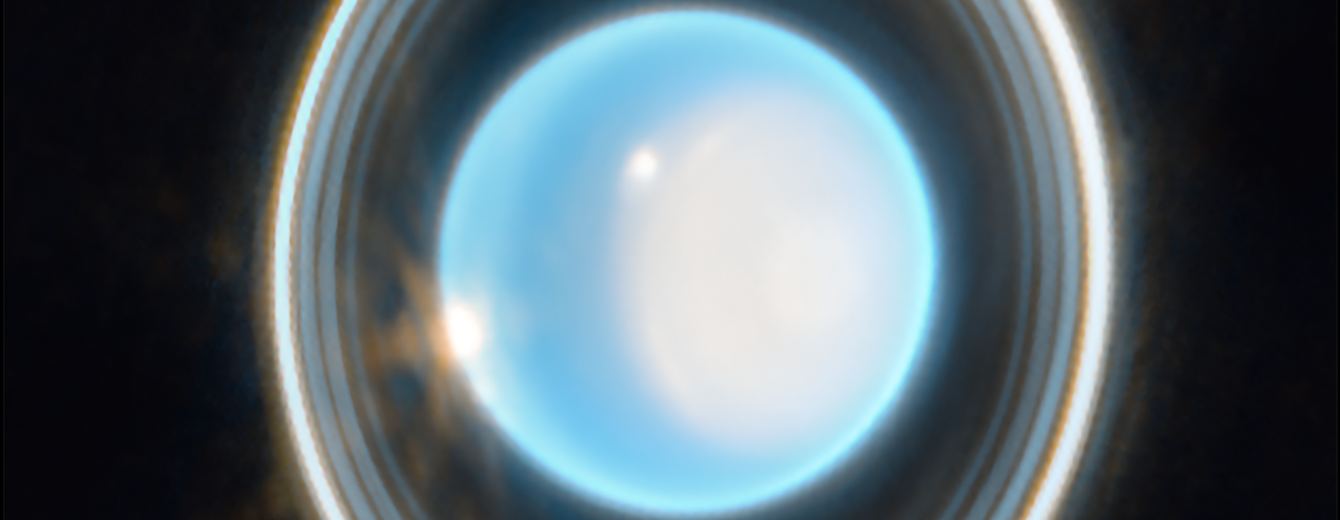
The James Webb Space Telescope has taken a stunning new image of the ice giant world Uranus. But what stands out most is the dramatic new view of the planet’s rings, which show up as never before with JWST’s infrared eyes.
Instead of being faint and wispy, the rings show up brilliantly. Additionally, bright, luminous features in the planet’s atmosphere show how an extensive storm system at the north pole of this planet getting larger and brighter.
But you’ll also want to see the full-frame image view, which also shows the six largest of Uranus’ 27 known moons. And, as we’ve become accustomed to seeing in JWST images, several distant background galaxies. Yes, every JWST image is a Deep Field!
Continue reading “The Rings of Uranus Shine Bright in Stunning New JWST Image”