Forty years ago, Canadian physicist Bill Unruh made a surprising prediction regarding quantum field theory. Known as the Unruh effect, his theory predicted that an accelerating observer would be bathed in blackbody radiation, whereas an inertial observer would be exposed to none. What better way to mark the 40th anniversary of this theory than to consider how it could affect human beings attempting relativistic space travel?
Such was the intent behind a new study by a team of researchers from Sao Paulo, Brazil. In essence, they consider how the Unruh effect could be confirmed using a simple experiment that relies on existing technology. Not only would this experiment prove once and for all if the Unruh effect is real, it could also help us plan for the day when interstellar travel becomes a reality.
To put it in layman’s terms, Einstein’s Theory of Relativity states that time and space are dependent upon the inertial reference frame of the observer. Consistent with this is the theory that if an observer is traveling at a constant speed through empty vacuum, they will find that the temperature of said vacuum is absolute zero. But if they were to begin to accelerate, the temperature of the empty space would become hotter.

This is what William Unruh – a theorist from the University of British Columbia (UBC), Vancouver – asserted in 1976. According to his theory, an observer accelerating through space would be subject to a “thermal bath” – i.e. photons and other particles – which would intensify the more they accelerated. Unfortunately, no one has ever been able to measure this effect, since no spacecraft exists that can achieve the kind of speeds necessary.
For the sake of their study – which was recently published in the journal Physical Review Letters under the title “Virtual observation of the Unruh effect” – the research team proposed a simple experiment to test for the Unruh effect. Led by Gabriel Cozzella of the Institute of Theoretical Physics (IFT) at Sao Paulo State University, they claim that this experiment would settle the issue by measuring an already-understood electromagnetic phenomenon.
Essentially, they argue that it would be possible to detect the Unruh effect by measuring what is known as Larmor radiation. This refers to the electromagnetic energy that is radiated away from charged particles (such as electrons, protons or ions) when they accelerate. As they state in their study:
“A more promising strategy consists of seeking for fingerprints of the Unruh effect in the radiation emitted by accelerated charges. Accelerated charges should back react due to radiation emission, quivering accordingly. Such a quivering would be naturally interpreted by Rindler observers as a consequence of the charge interaction with the photons of the Unruh thermal bath.”
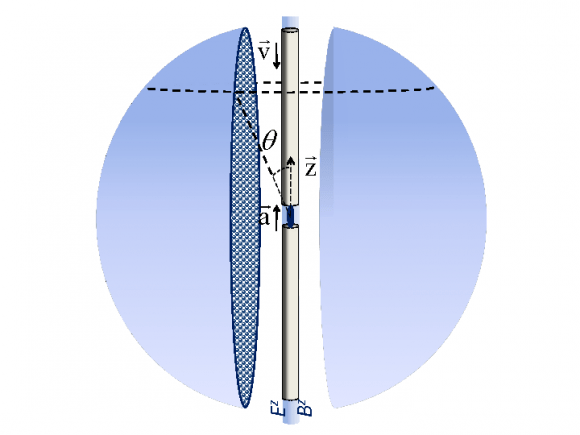
As they describe in their paper, this would consist of monitoring the light emitted by electrons within two separate reference frames. In the first, known as the “accelerating frame”, electrons are fired laterally across a magnetic field, which would cause the electrons to move in a circular pattern. In the second, the “laboratory frame”, a vertical field is applied to accelerate the electrons upwards, causing them to follow a corkscrew-like path.
In the accelerating frame, Cozzella and his colleagues assume that the electrons would encounter the “fog of photons”, where they both radiate and emit them. In the laboratory frame, the electrons would heat up once vertical acceleration was applied, causing them to show an excess of long-wavelength photons. However, this would be dependent on the “fog” existing in the accelerated frame to begin with.
In short, this experiment offers a simple test which could determine whether or not the Unruh effect exists, which is something that has been in dispute ever since it was proposed. One of the beauties of the proposed experiment is that it could be conducted using particle accelerators and electromagnets that are currently available.
On the other side of the debate are those who claim that the Unruh effect is due to a mathematical error made by Unruh and his colleagues. For those individuals, this experiment is useful because it would effectively debunk this theory. Regardless, Cozzella and his team are confident their proposed experiment will yield positive results.

“We have proposed a simple experiment where the presence of the Unruh thermal bath is codified in the Larmor radiation emitted from an accelerated charge,” they state. “Then, we carried out a straightforward classical-electrodynamics calculation (checked by a quantum-field-theory one) to confirm it by ourselves. Unless one challenges classical electrodynamics, our results must be virtually considered as an observation of the Unruh effect.”
If the experiments should prove successful, and the Unruh effect is proven to exist, it would certainly have consequences for any future deep-space missions that rely on advanced propulsion systems. Between Project Starshot, and any proposed mission that would involve sending a crew to another star system, the added effects of a “fog of photons” and a “thermal bath” will need to be factored in.
Further Reading: arXiv, ScienceMag