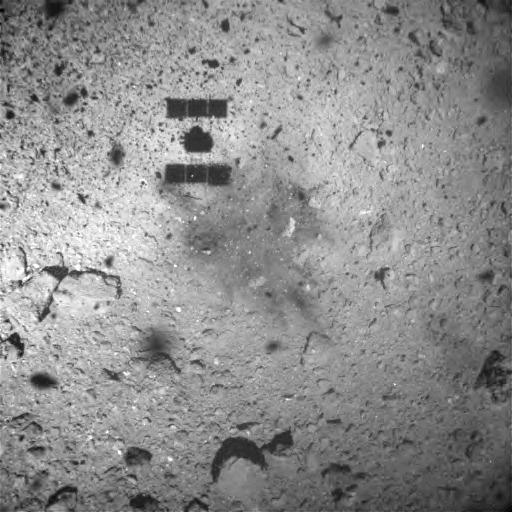
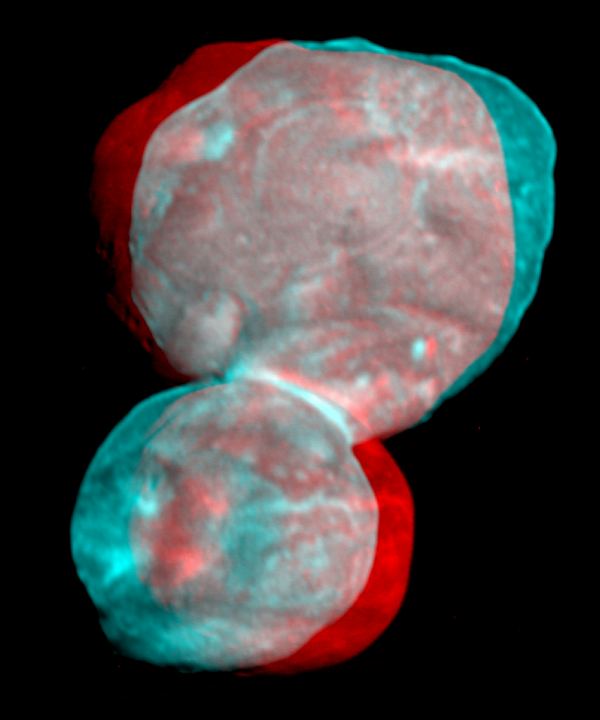
Got your 3D glasses handy? Then prepare for the most realistic views of Ultima Thule yet! Yes, it seems that every few weeks, there’s a new image of the Kuiper Belt Object (KBO) that promises the same thing. But whereas all the previous contenders were higher-resolution images that allowed for a more discernible level of detail, these images are the closest we will get to seeing the real thing up close!
Continue reading “Now You Can See MU69 in Thrilling 3D”Now You Can See MU69 in Thrilling 3D