Kennedy Space Center – After overcoming a frightening thruster failure that could have spelled rapid doom on the heels of a breathtakingly beautiful launch, the privately developed Dragon spacecraft successfully berthed at the International Space Station (ISS) a short while ago, at 8:56 a.m. EST Sunday morning, March 3, 2013 – thereby establishing an indispensable American Lifeline to the massive orbiting lab complex.
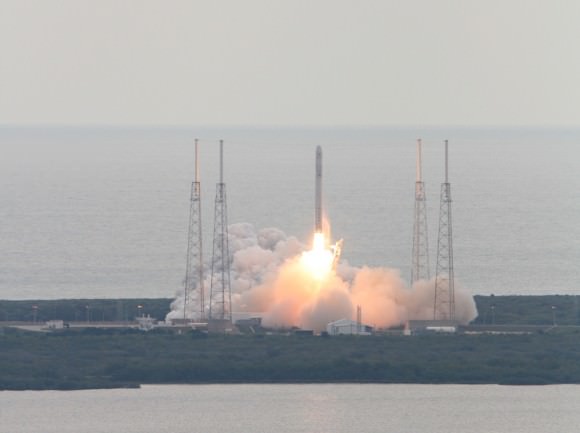
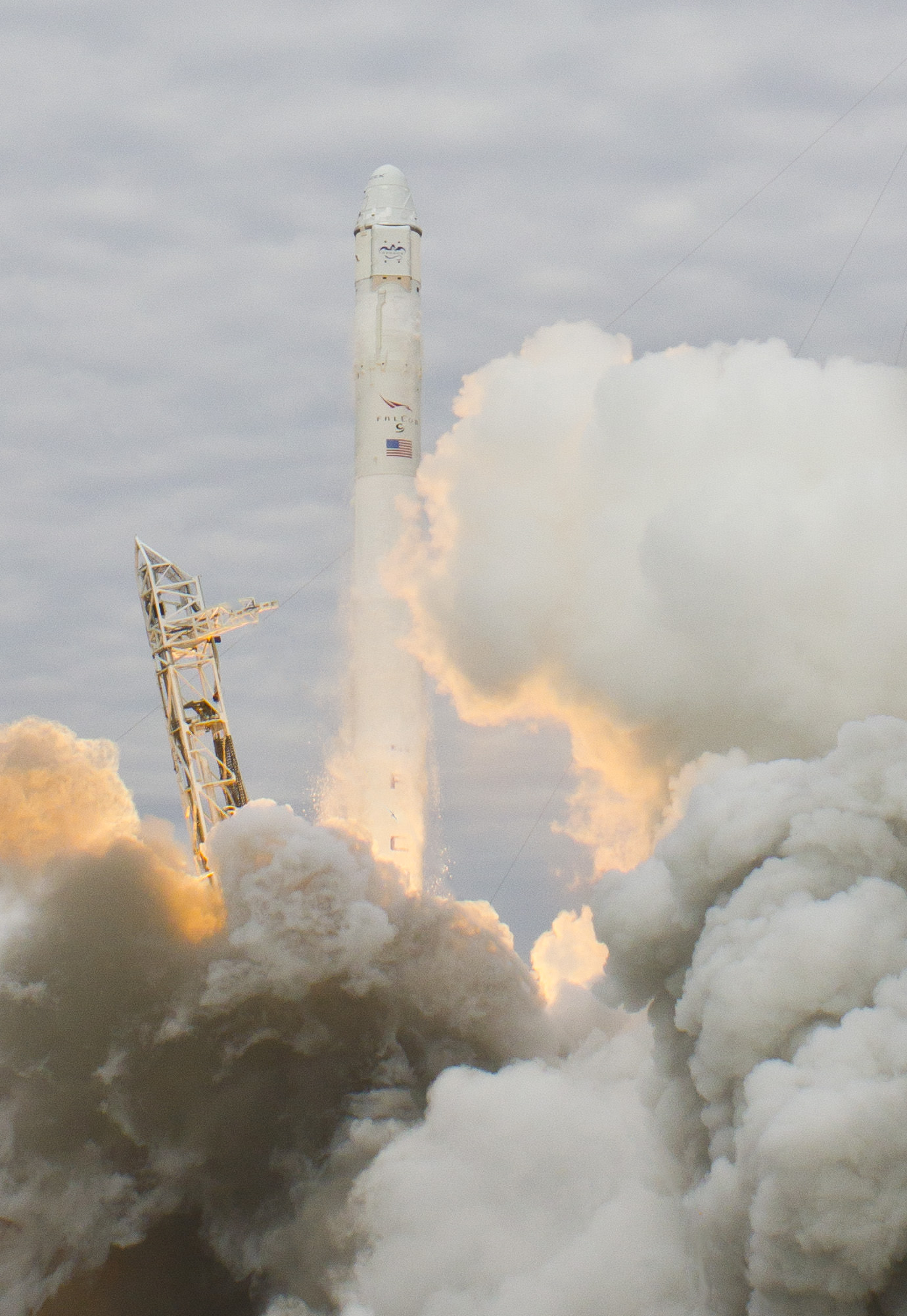
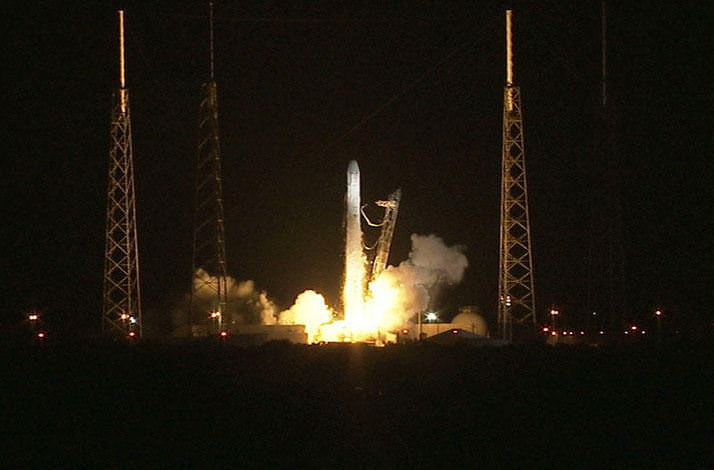
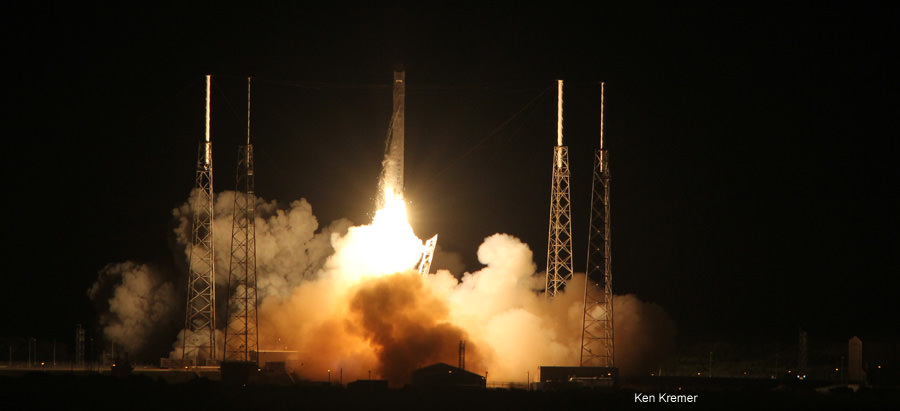
Hearts sank and hopes rose in the span of a few troubling hours following Friday’s (Mar. 1) flawless launch of the Dragon cargo resupply capsule atop the 15 story tall Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida and the initial failure of the life giving solar arrays to deploy and failure of the maneuvering thrusters to fire.
“Congrats to the @NASA/@SpaceX team. Great work getting #Dragon to the #ISS…our foothold for future exploration!” tweeted NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver.
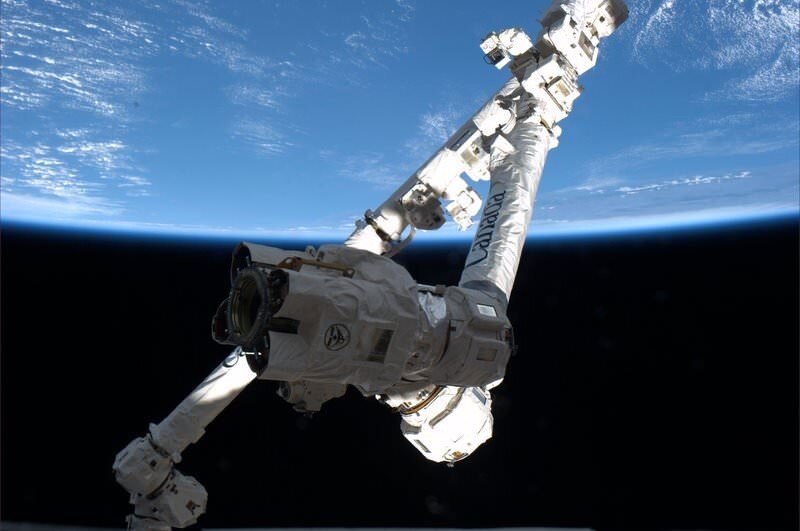
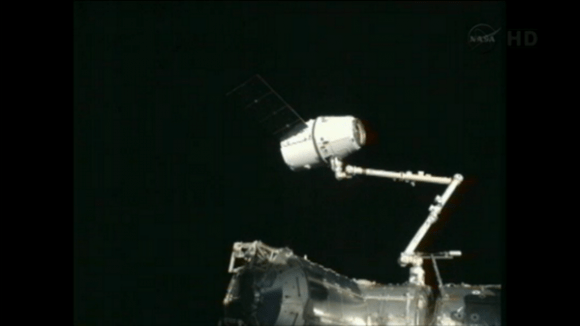
Space station Expedition 34 crew members Kevin Ford and Tom Marshburn of NASA used the station’s 58 foot long Canadian supplied robotic arm to successfully grapple and capture Dragon at 5:31 a.m. Sunday as the station was flying 253 miles above northern Ukraine. See the grappling video – here.

“The vehicle’s beautiful, space is beautiful, and the Canadarm2 is beautiful too”, said station commander Kevin Ford during the operation.
The capsule pluck from free space came one day, 19 hours and 22 minutes after the mission’s launch.
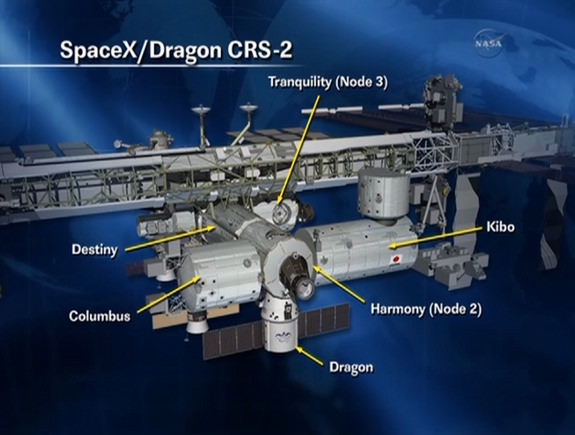
Ground controllers at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston then commanded the arm to install Dragon onto the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module – see schematic.
Originally, Dragon capture was slated only about 20 hours after launch. But that all went out the window following the serious post-launch anomalies that sent SpaceX engineers desperately scrambling to save the flight from a catastrophic finale.
The $133 million mission dubbed CRS-2 is only the 2nd contracted commercial resupply mission ever to berth at the ISS under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract. The contract is worth $1.6 Billion for at least a dozen resupply flights.
Following the forced retirement of NASA’s space shuttle orbiters in July 2011, American was left with zero capability to launch either cargo or astronauts to the primarily American ISS. NASA astronauts are 100% reliant on Russian Soyuz capsules for launch to the ISS.
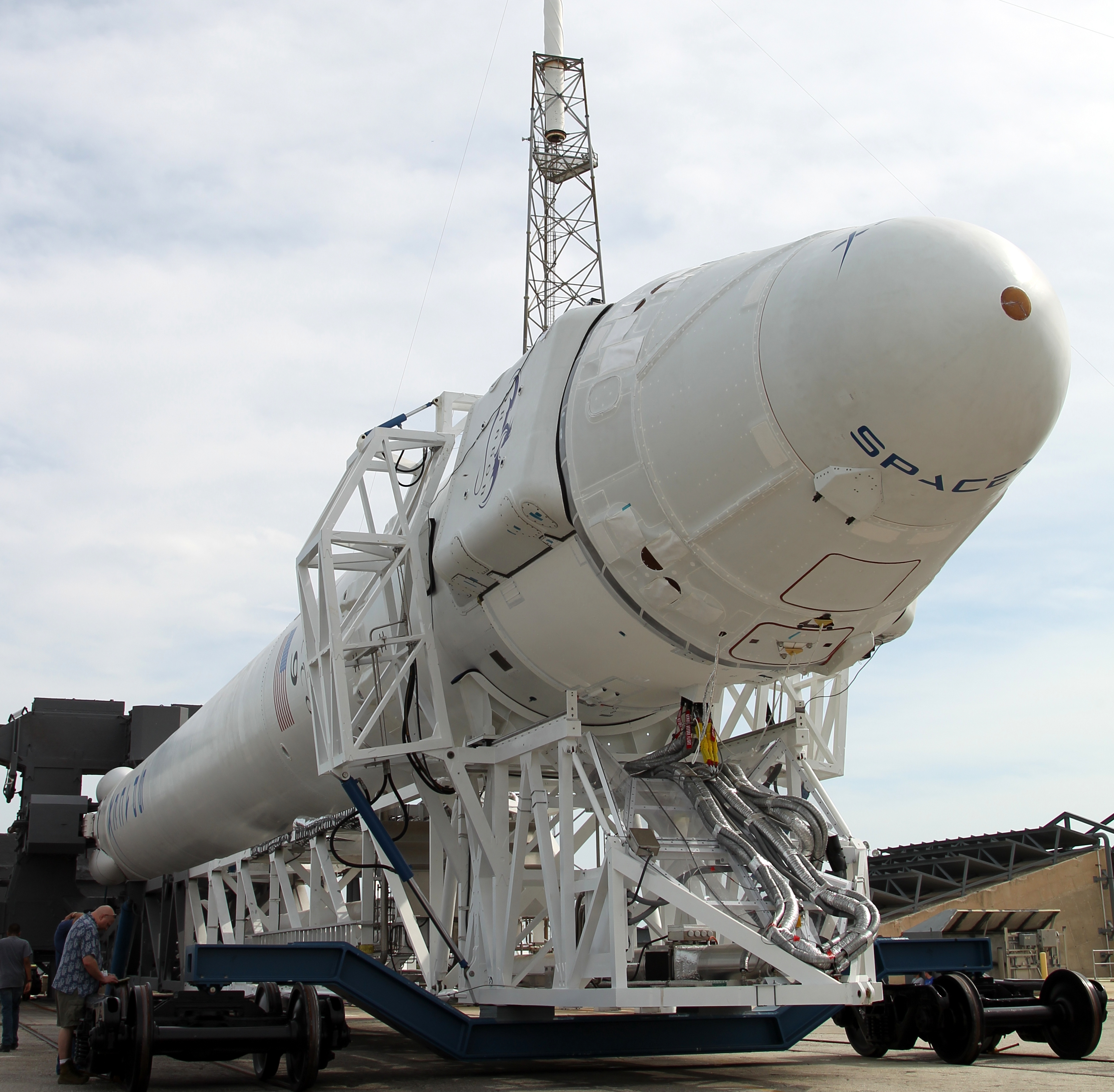
Both the Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft were designed and built by SpaceX Corporation based in Hawthorne, Calif., and are entirely American built.
The Falcon 9/Dragon commercial system restores America’s unmanned cargo resupply capability. But the time gap will be at least 3 to 5 years before American’s can again launch to the ISS aboard American rockets from American soil.
And continuing, relentless cuts to NASA’s budget are significantly increasing that human spaceflight gap and consequently forces more payments to Russia.
“Today we marked another milestone in our aggressive efforts to make sure American companies are launching resupply missions from U.S. shores,” said NASA Admisistrator Charles Bolden in a NASA statement.
“Our NASA-SpaceX team completed another successful berthing of the SpaceX Dragon cargo module to the International Space Station (ISS) following its near flawless launch on the Falcon-9 booster out of Cape Canaveral, Florida Friday morning. Launching rockets is difficult, and while the team faced some technical challenges after Dragon separation from the launch vehicle, they called upon their thorough knowledge of their systems to successfully troubleshoot and fully recover all vehicle capabilities. Dragon is now once again safely berthed to the station.”
“I was pleased to watch the launch from SpaceX’s facility in Hawthorne, CA, and I want to congratulate the SpaceX and NASA teams, who are working side by side to ensure America continues to lead the world in space.”
“Unfortunately, all of this progress could be jeopardized with the sequestration ordered by law to be signed by the President Friday evening. The sequester could further delay the restarting of human space launches from U.S. soil, push back our next generation space vehicles, hold up development of new space technologies, and jeopardize our space-based, Earth observing capabilities,” said Bolden.

Dragon is loaded with about 1,268 pounds (575 kilograms) of vital supplies and provisions to support the ongoing science research by the resident six man crew, including more than a ton of vital supplies, science gear, research experiments, spare parts, food, water and clothing.
NASA says that despite the one-day docking delay, the Dragon unberthing will still be the same day as originally planned on March 25 – followed by a parachute assisted splashdown in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of Baja California.
Dragon will spend 22 days docked to the ISS. The station crew will soon open the hatch and unload all the up mass cargo and research supplies. Then they will pack the Dragon with about 2,668 pounds (1,210 kilograms) of science samples from human research, biology and biotechnology studies, physical science investigations, and education activities for return to Earth.
Dragon is the only spacecraft in the world today capable of returning significant amounts of cargo to Earth.
Orbital Sciences Corp also won a $1.9 Billion cargo resupply contract from NASA to deliver cargo to the ISS using the firm’s new Antares rocket and Cygnus capsule.
NASA hopes the first Antares/Cygnus demonstration test flight from NASA’s Wallops Island Facility in Virginia will follow in April. Cygnus cargo transport is one way – to orbit only.
“SpaceX is proud to execute this important work for NASA, and we’re thrilled to bring this capability back to the United States,” said Gwynne Shotwell, President of SpaceX.
“Today’s launch continues SpaceX’s long-term partnership with NASA to provide reliable, safe transport of cargo to and from the station, enabling beneficial research and advancements in technology and research.”
The SpaceX CRS-3 flight is slated to blast off in September 2013.