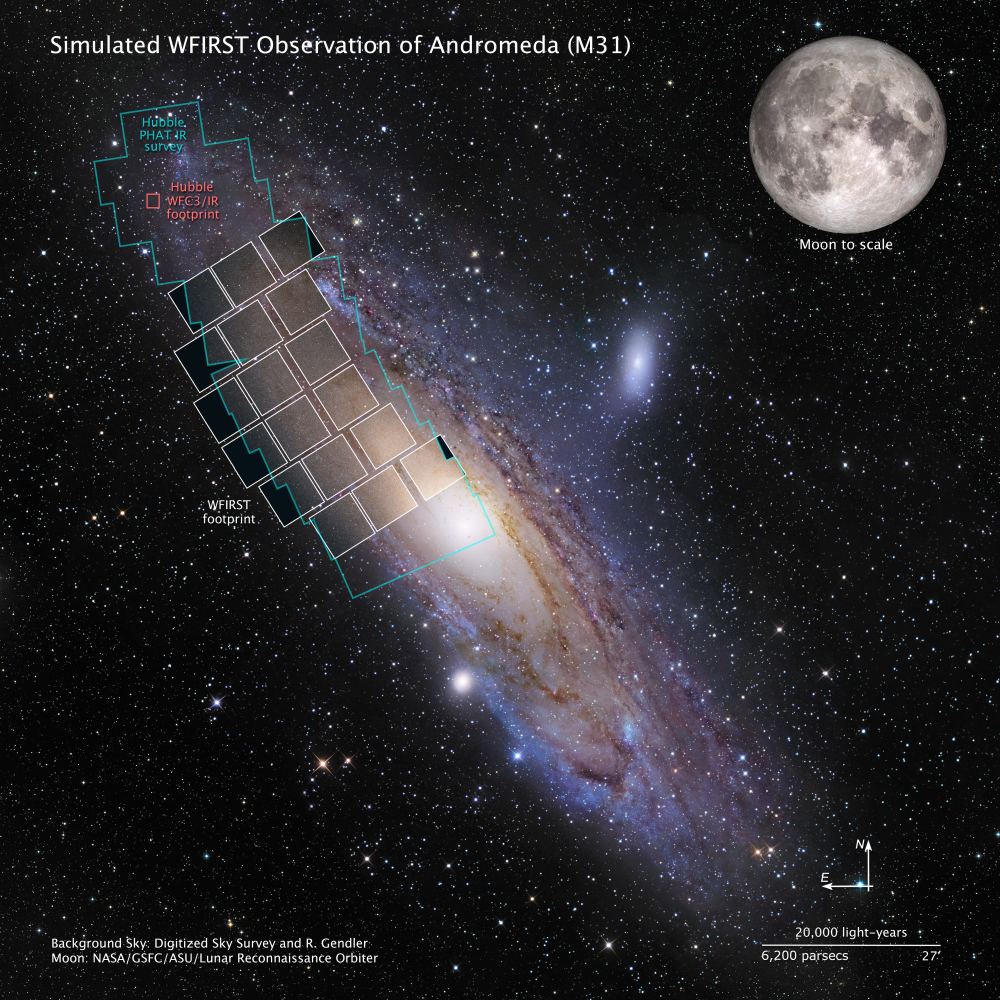
In 2025, NASA’s next-generation telescope, the Wide-Field Infrared Survey Telescope (WFIRST), will take to space and join in the search for extrasolar planets. Between its 2.4-meter (8 ft) telescope, 18 detectors, 300-megapixel camera, and the extraordinary survey speed it will offer, the WFIRST will be able to scan areas of the sky a hundred times greater than the Hubble Space Telescope.
Beyond its high-sensitivity and advanced suite of instruments, WFIRST will also rely on a technique known as Gravitational Microlensing to search for and characterize exoplanets. This is essentially a small-scale version of the gravitational lensing technique, where the gravitational force of a massive object between the observer and the target is used to focus and magnify the light coming from a distant source.
Continue reading “WFIRST Will Use Relativity to Find More Exoplanets!”