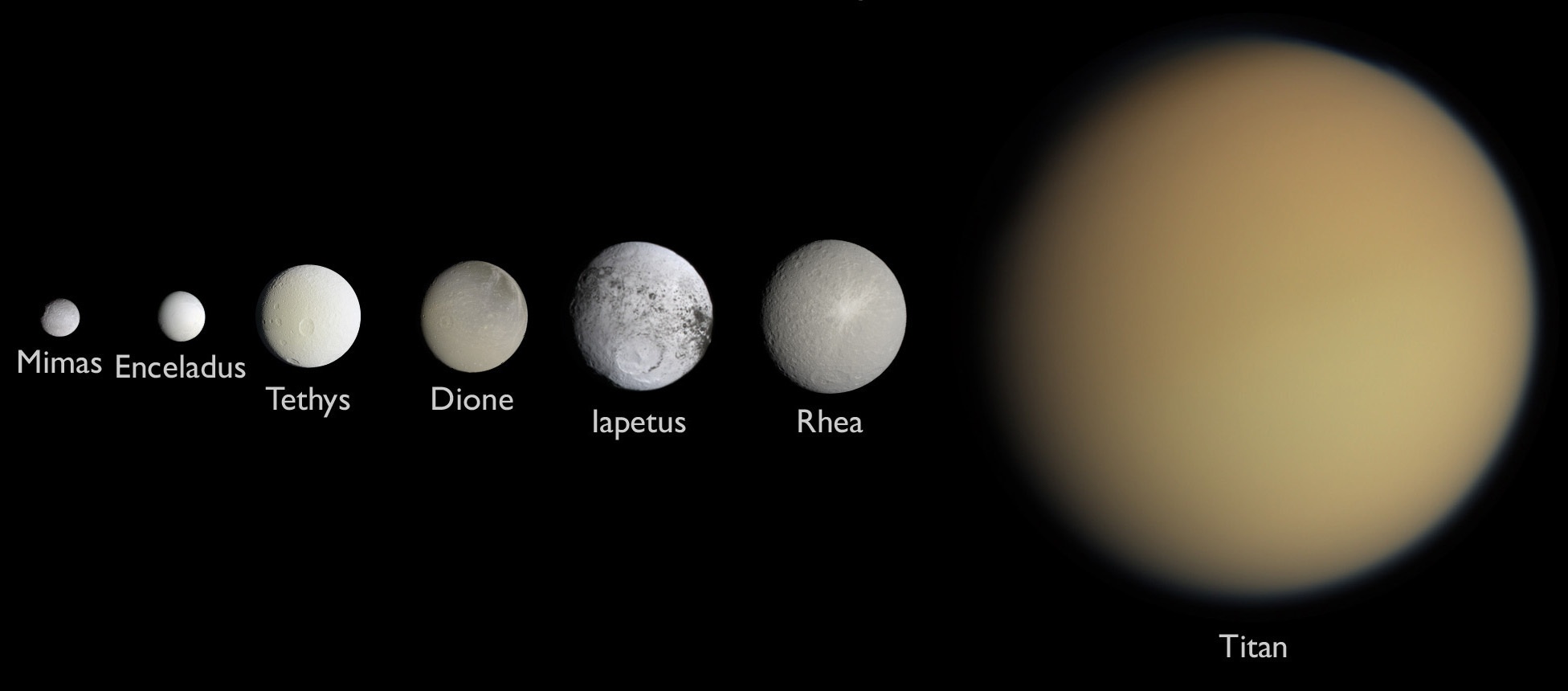
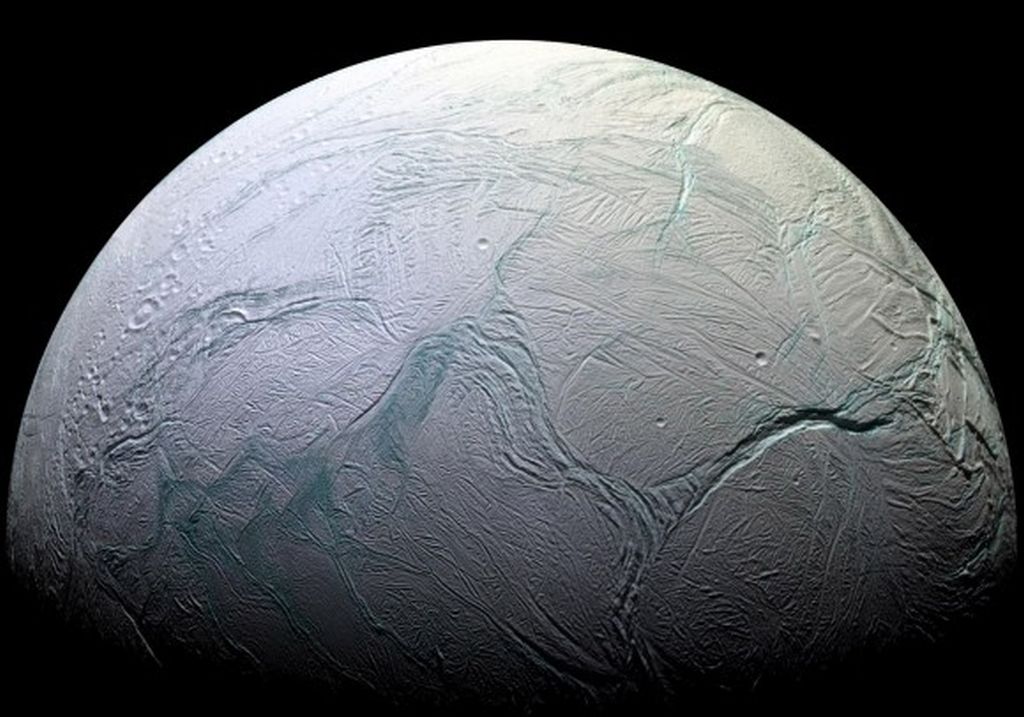
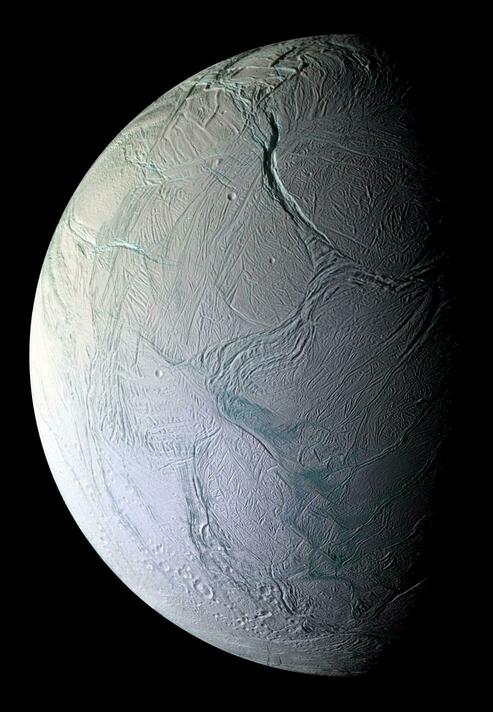
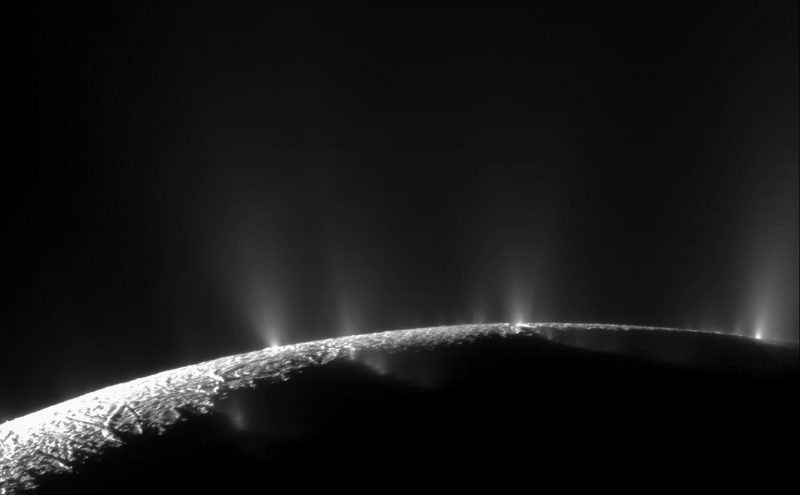
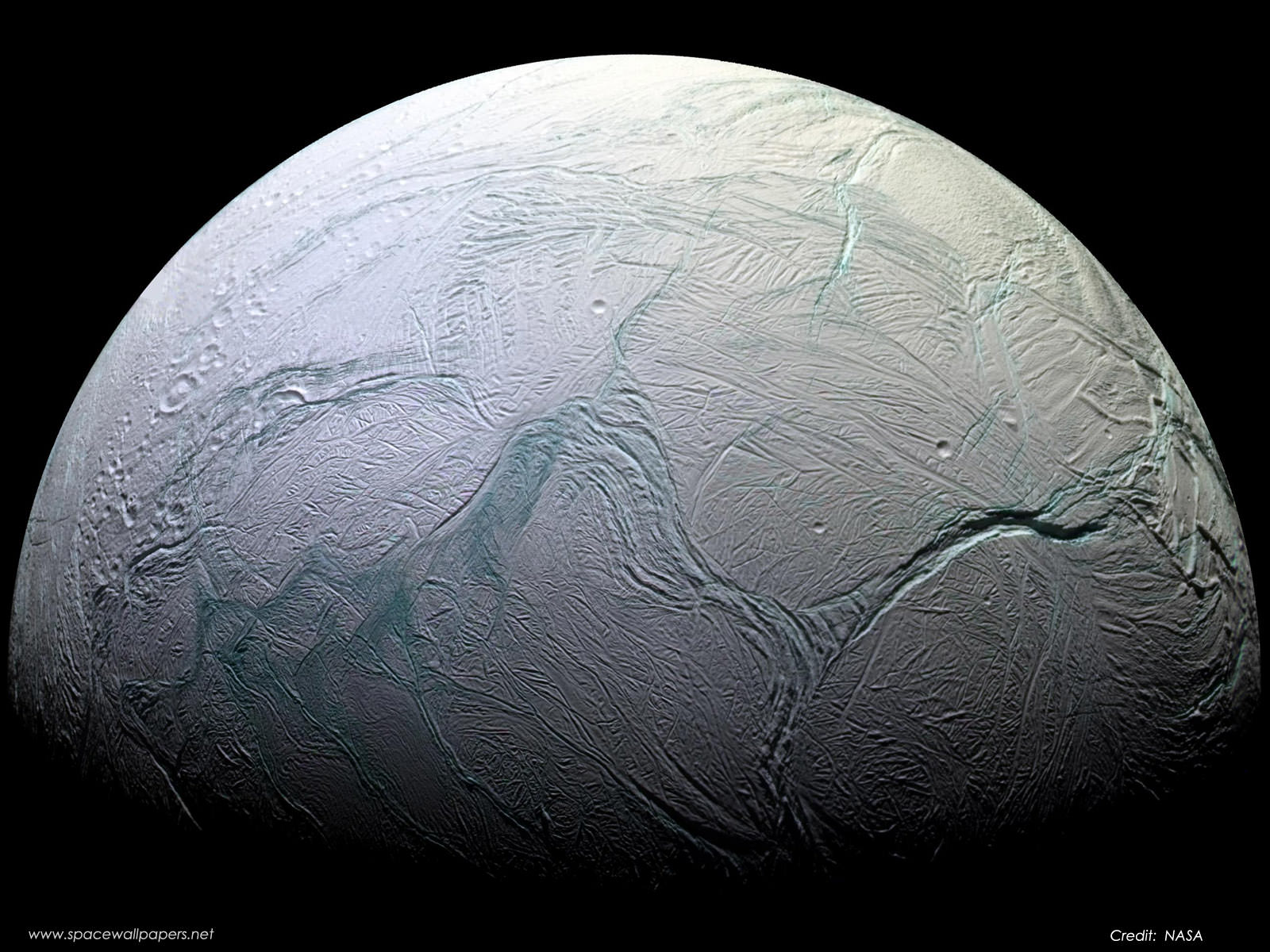
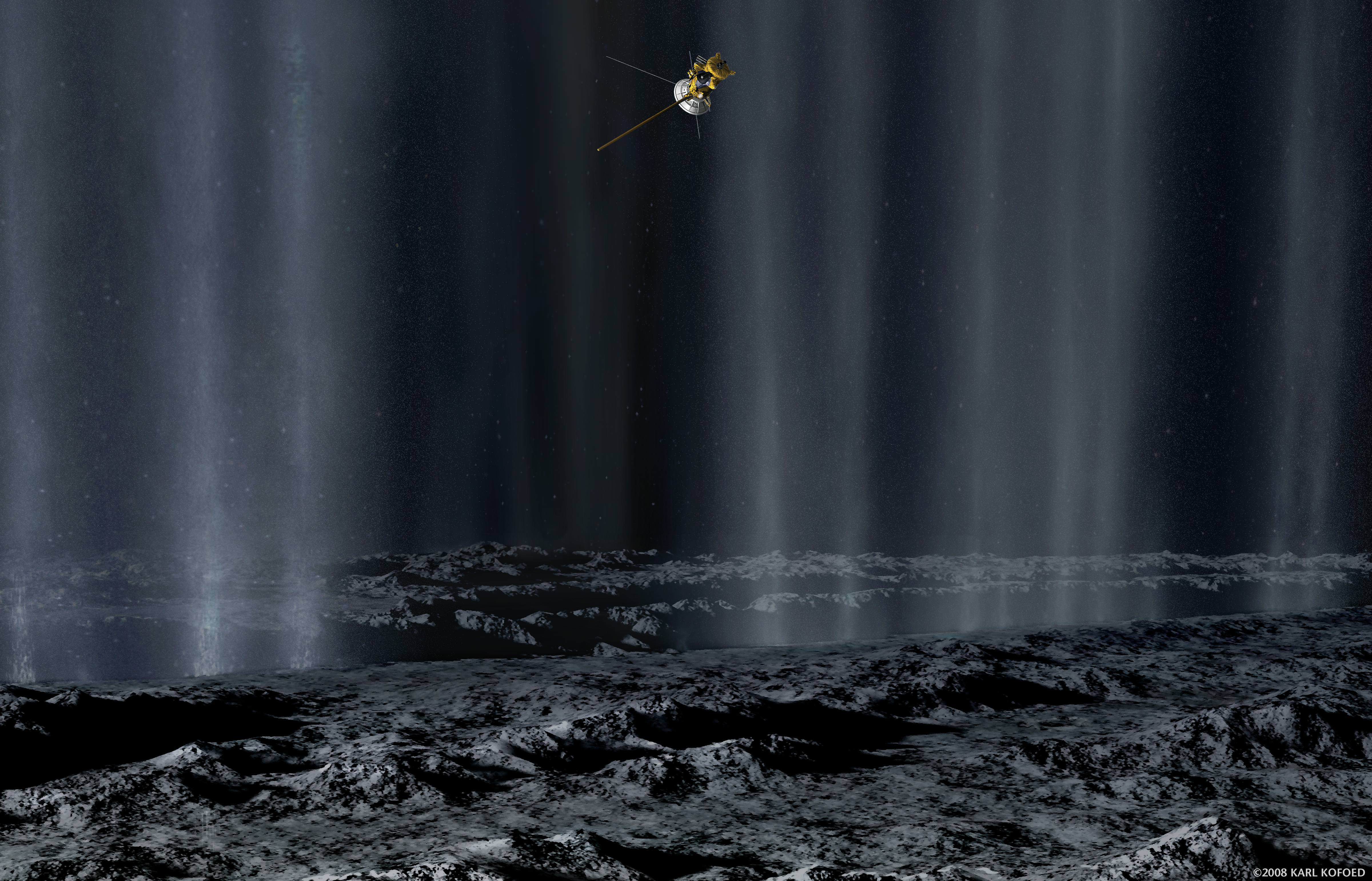
For astrobiologists, the scientists dedicated to the search for life beyond Earth, the moons of Saturn are a virtual treasure trove of possibilities. Enceladus is especially compelling because of the active plumes of water emanating from its southern polar region. Not only are these vents thought to be connected directly to an ocean beneath the moon’s icy surface, but the Cassini mission detected traces of organic molecules and other chemicals associated with biological processes. Like Europa, Ganymede, and other “Ocean Worlds,” astrobiologists think this could indicate hydrothermal activity at the core-mantle boundary.
Both NASA and the ESA are hoping to send missions to Enceladus that could study its plumes in more detail. These include the Enceladus Orbitlander recommended in the Planetary Science and Astrobiology Decadal Survey 2023-2032 and the ESA’s Enceladus Moonraker, which could depart Earth in the next decade, taking advantage of a favorable alignment between the planets. In anticipation of what these missions could find, an international team of researchers used data from the Cassini mission to establish how samples of plume material could constrain how much biomass Enceladus has within it.
Continue reading “How Could We Detect Life Inside Enceladus?”