[/caption]
Scientists leading NASA’s Dawn mission have discovered a 2nd giant impact basin at the south pole of the giant asteroid Vesta, which has been unveiled as a surprisingly “dichotomous” and alien world. Furthermore, the cosmic collisions that produced these two basins shuddered through the interior and created vast Vestan troughs, a Dawn scientist told Universe Today.
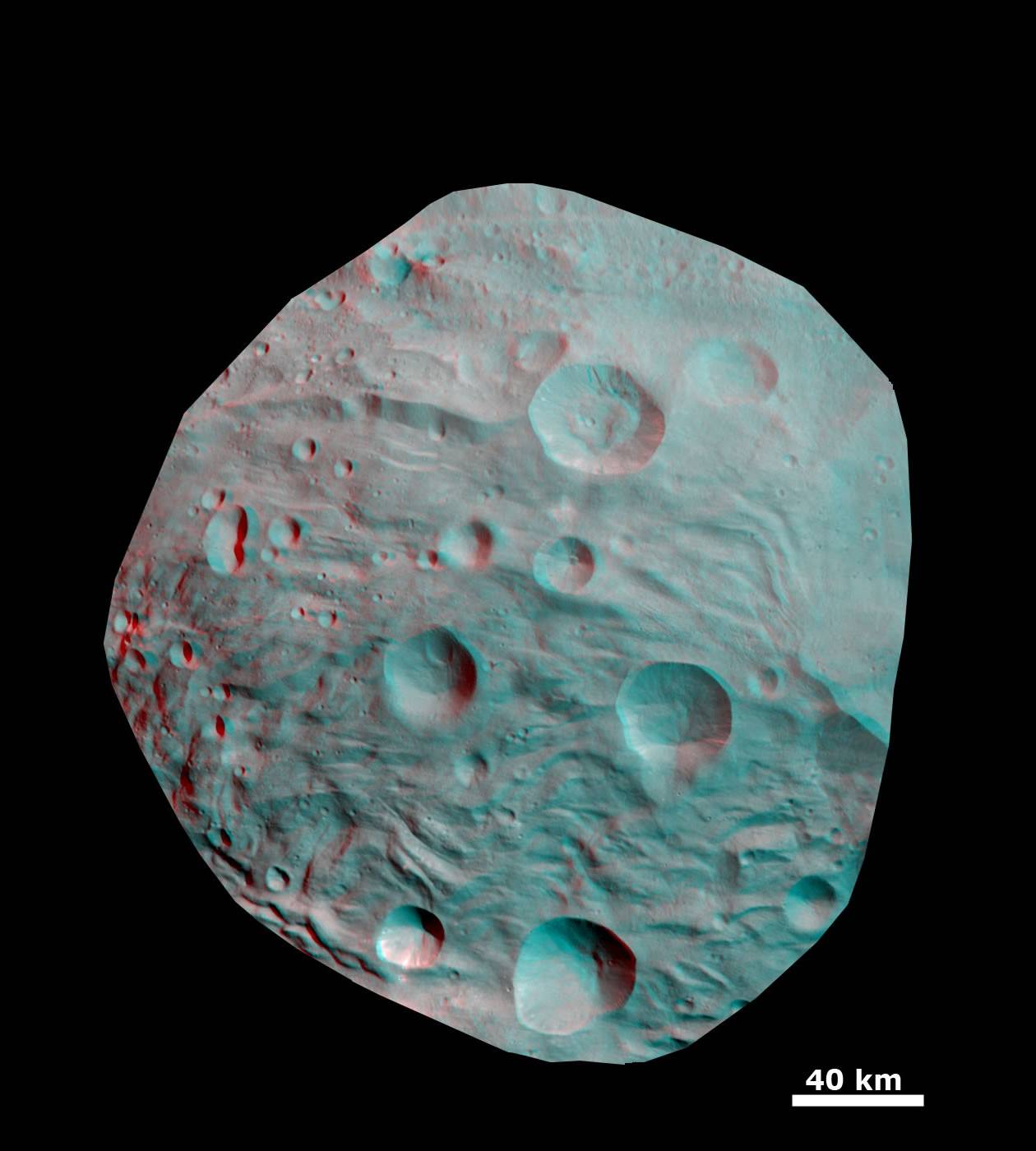
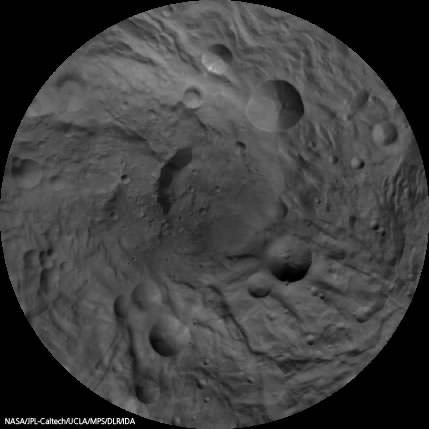
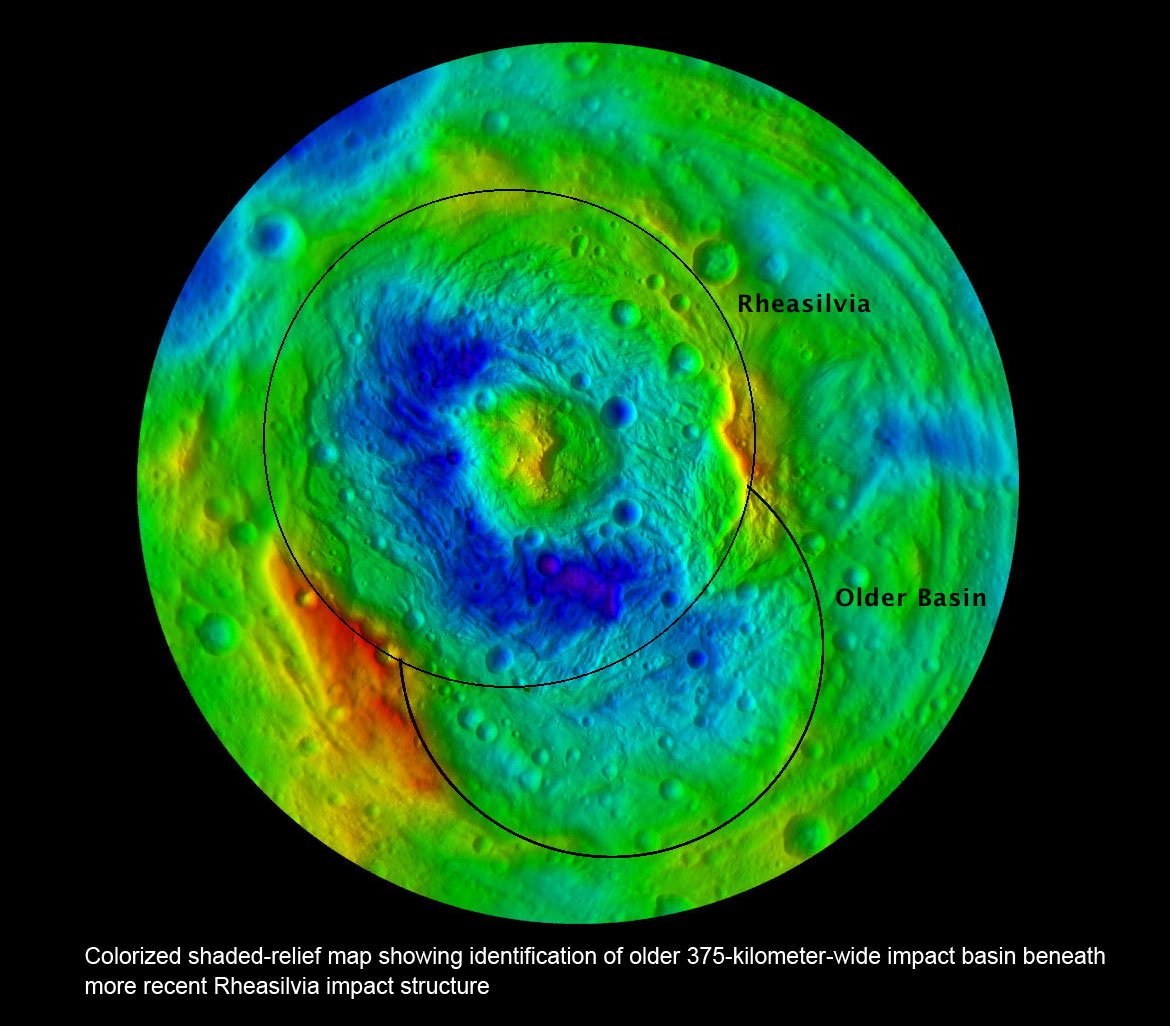
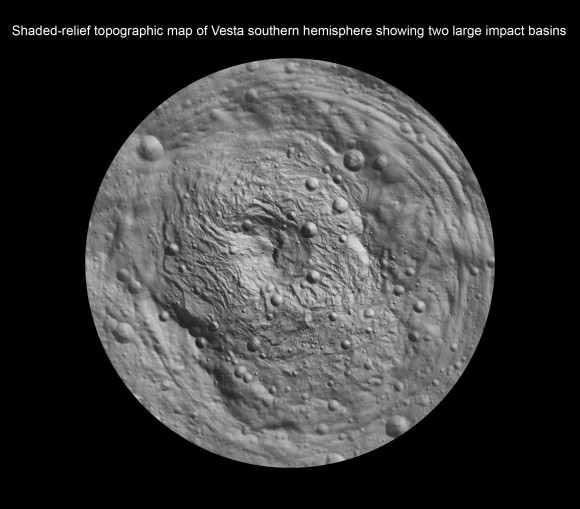
The newly discovered impact basin, nicknamed ‘Older Basin’, is actually significantly older in age compared to the initially discovered South Pole basin feature named ‘Rheasilvia’ – perhaps by more than a billion years. And that is just one of the many unexplained mysteries yet to be reconciled by the team as they begin to sift through the millions of bits of new data streaming back daily to Earth.
Scientists speculate that ‘Older Basin’ is on the order of 3.8 Billion years old, whereas ‘Rheasilvia’ might be as young as about 2.5 Billion years, but those are just tentative estimates at this time and subject to change. Measurements so far indicate Rheasilvia is composed of basaltic material.
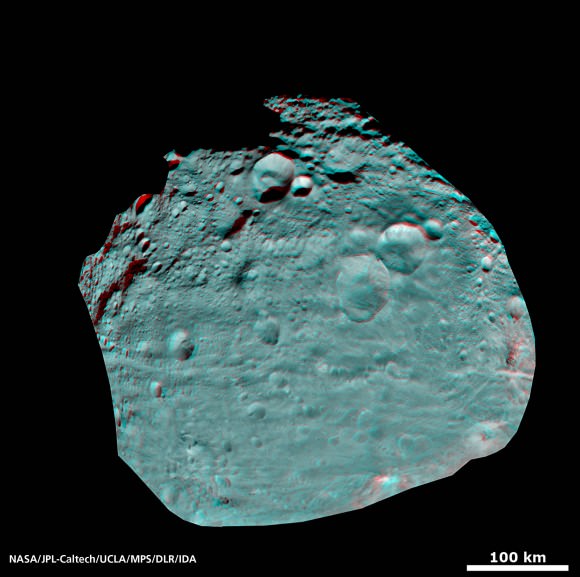
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA
“We found many surprising things at Vesta, which is quite unique and the results have exceeded our expectations”, said Dr. Carol Raymond, Dawn deputy principal investigator, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
Researchers presented the latest findings from Dawn’s initial science mapping orbit at a news briefing at the annual meeting of the Geological Society of America in Minneapolis, Minn., on Oct. 13.
The team considers Vesta to be the smallest terrestrial planet.
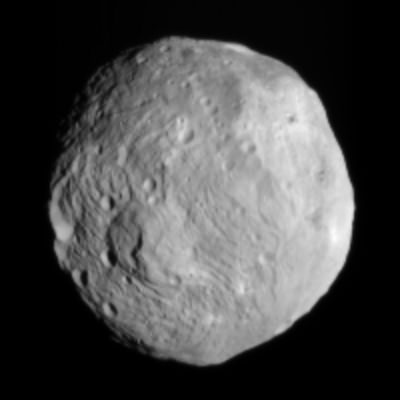
Since achieving orbit in July, Dawn’s Framing Cameras (FC) have imaged most of Vesta at about 250 meter resolution and the Visible and Infrared mapping spectrometer(VIR) at about 700 meter resolution. The measurements were collected at the survey orbit altitude of 2700 km. Before Dawn, Vesta was just a fuzzy blob in humankind’s most powerful telescopes.

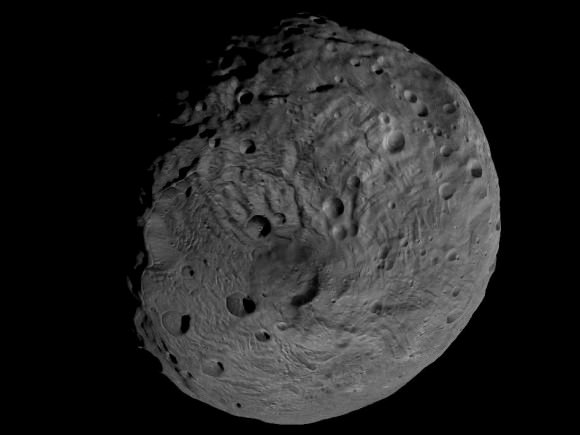
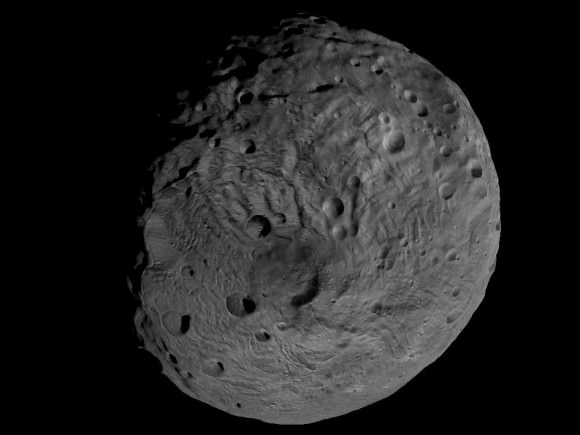
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA
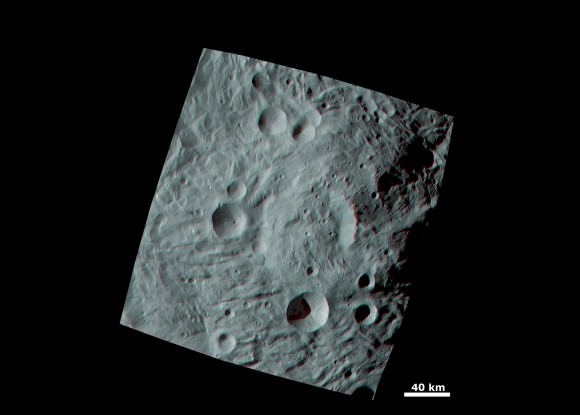
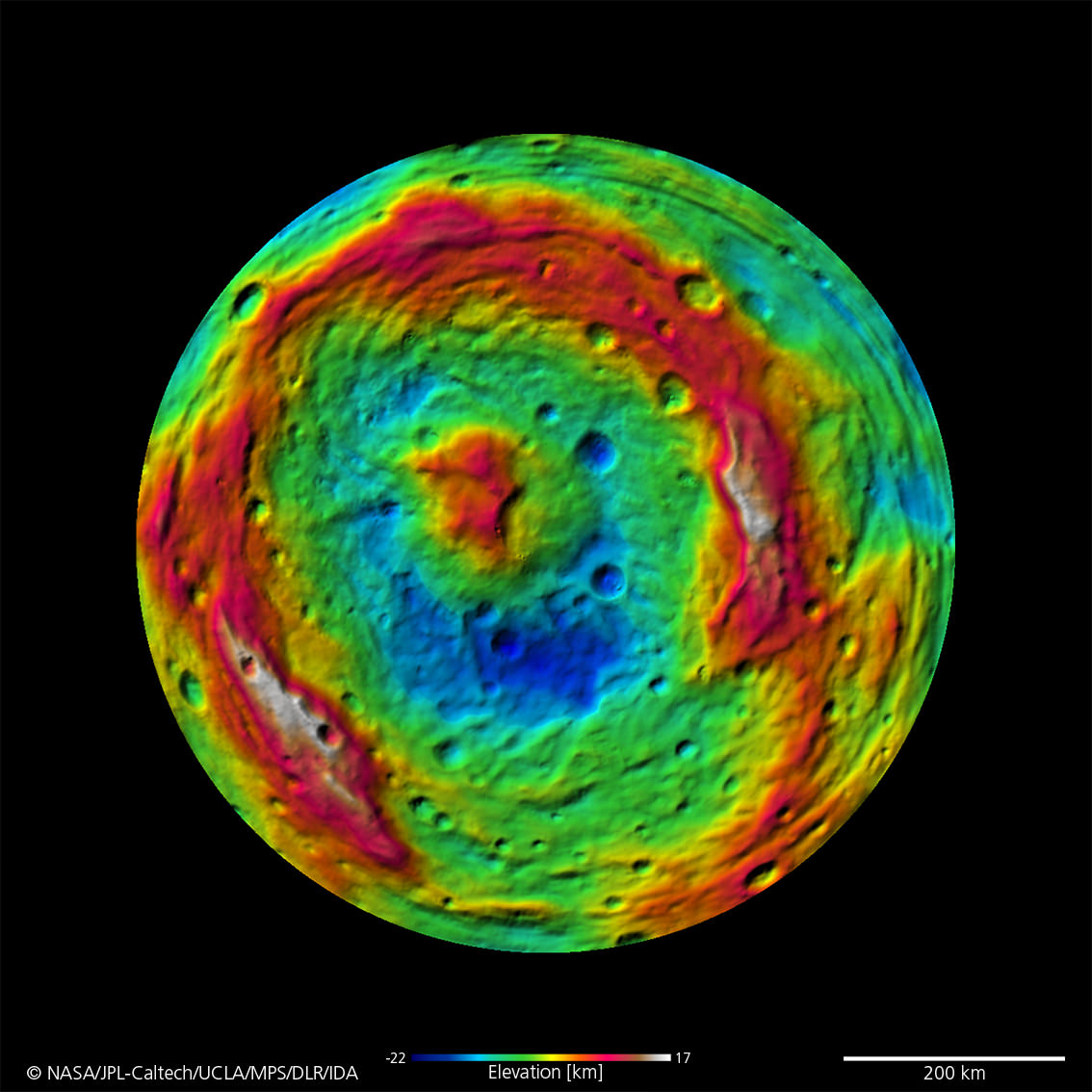
“There is a global dichotomy on Vesta and a fundamental difference between the northern and southern hemispheres”, said Raymond. “The northern hemisphere is older and heavily cratered in contrast to the brighter southern hemisphere where the texture is more smooth and there are lots of sets of grooves. There is a massive mountain at the South Pole. One of the more surprising aspects is the set of deep equatorial troughs.”
“There is also a tremendous and surprising diversity of surface color and morphology. The south is consistent with basaltic lithology and the north with impacts. We are trying to make sense of the data and will integrate that with the high resolution observations we are now collecting.”
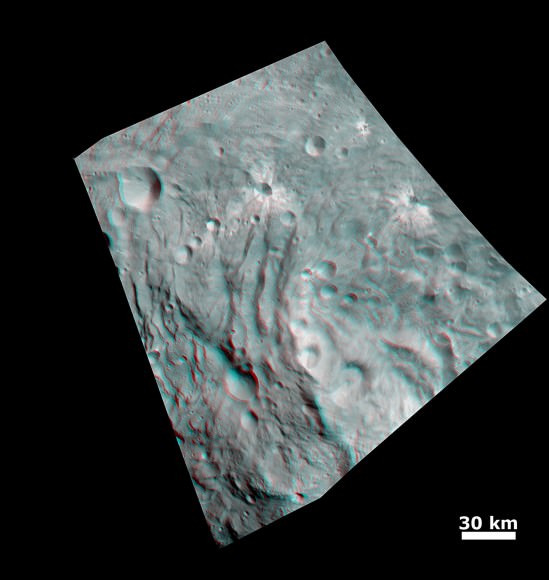
Indeed Vesta’s completely unique and striking dichotomy can be directly traced back to the basins which were formed by ancient cataclysmic impacts resulting in shockwaves that fundamentally altered the surface and caused the formation of the long troughs that ring Vesta at numerous latitudes.
“The troughs extend across 240 degrees of longitude,” said Debra Buczkowski, Dawn participating scientist, of the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University, Laurel, Md. “Their formation can be tied back to the two basins at the South Pole.”
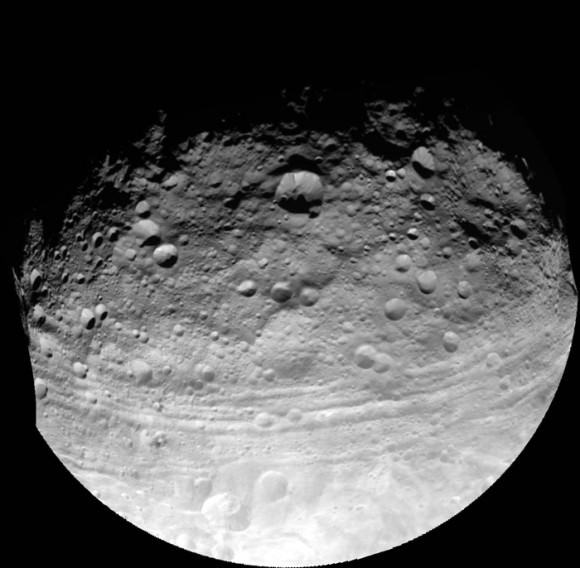

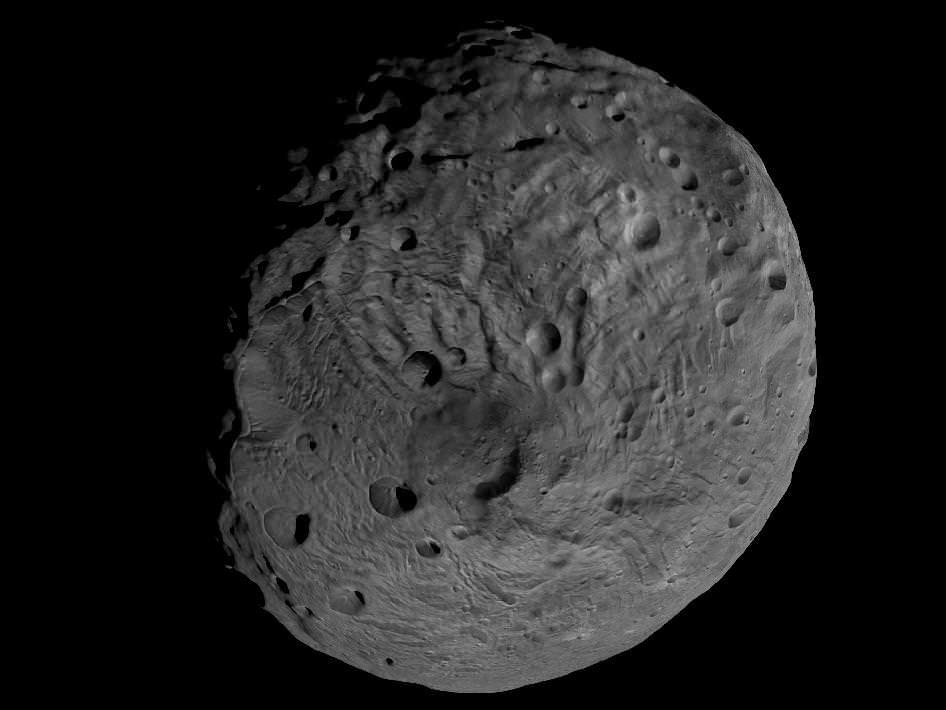
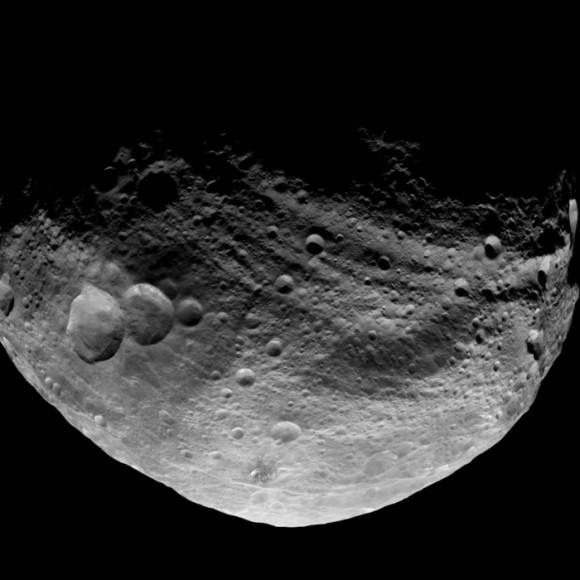
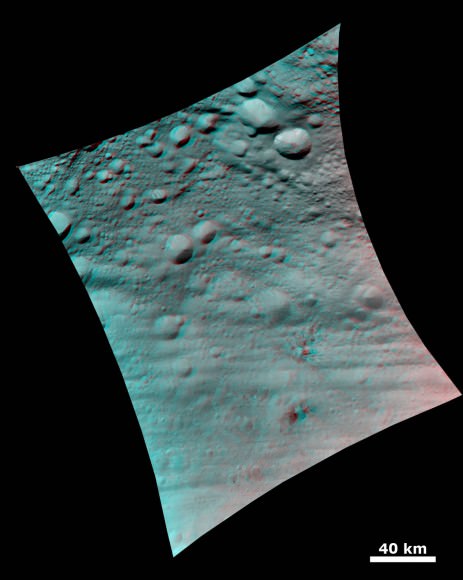
This full view of the giant asteroid Vesta was taken by NASA’s Dawn spacecraft, as part of a rotation characterization sequence on July 24, 2011, at a distance of 3,200 miles (5,200 kilometers). A rotation characterization sequence helps the scientists and engineers by giving an initial overview of the character of the surface as Vesta rotated underneath the spacecraft. This view of Vesta shows impact craters of various sizes and grooves parallel to the equator. The resolution of this image is about 500 meters per pixel. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA
In an exclusive follow up interview with Universe Today, Raymond said “We believe that the troughs formed as a direct result of the impacts,” said “The two sets of troughs are associated with the two large basins [Rheasilvia and Older Basin].”
“The key piece of evidence presented was that the set of troughs in the northern hemisphere, that look older (more degraded) are circumferential to the older impact basin,” Raymond told me.
“The equatorial set are circumferential to Rheasilvia. That Rheasilvia’s age appears in places to be much younger is at odds with the age of the equatorial troughs. An explanation for that could be resurfacing by younger mass wasting features (landslides, slumps). We will be working on clarifying all these relationships in the coming months with the higher resolution HAMO (High Altitude Mapping Orbit) data.”
Dawn has gradually spiraled down closer to Vesta using her exotic ion thrusters and began the HAMO mapping campaign on Sept. 29.
Surface features are dated by crater counting methodology.
“Preliminary crater counting age dates for the equatorial trough region yields a very old age (3.8 Billion years). So there is a discrepancy between the apparent younger age for the Rheasilvia basin and the old age for the troughs. These could be reconciled if Rheasilvia is also 3.8 Billion years old but the surface has been modified by slumping or other processes,” Raymond elaborated.
Time will tell as further data is analyzed.

“Vesta is full of surprises, no more so than at the South Pole,” said Paul Schenk at the GSA briefing. Schenk is a Dawn participating scientist of the Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, Texas.
The ‘Rheasilvia’ basin was initially discovered in images of Vesta taken a decade ago by the Hubble Space Telescope which revealed it as a gaping hole in the southern hemisphere. But it wasn’t until Dawn entered orbit on July 16, 2011 after a nearly four year interplanetary journey that Earthlings got their first close up look at the mysterious polar feature and can now scrutinize it in detail to elucidate its true nature.
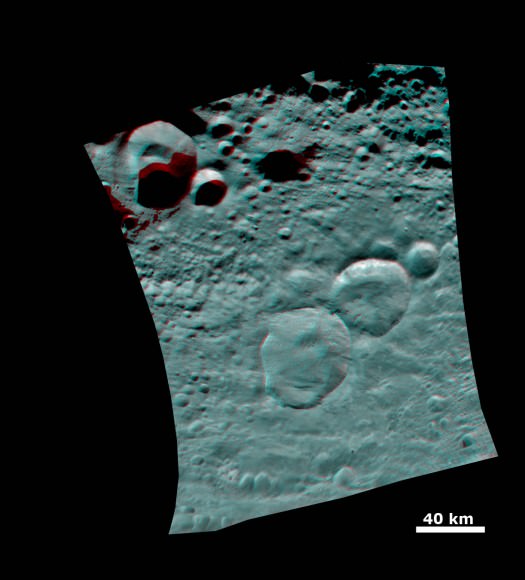
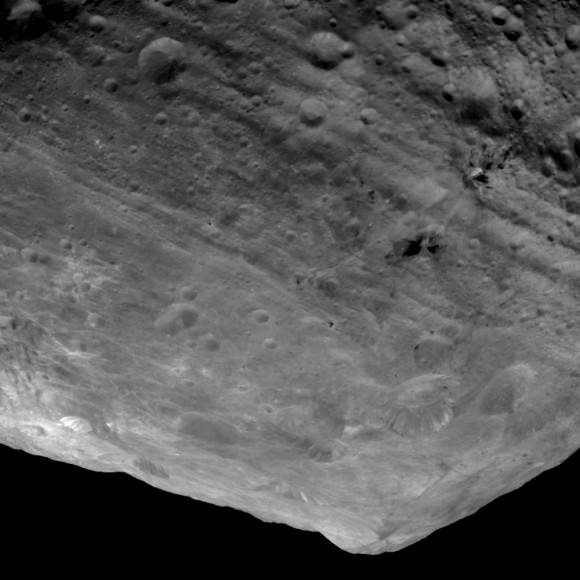
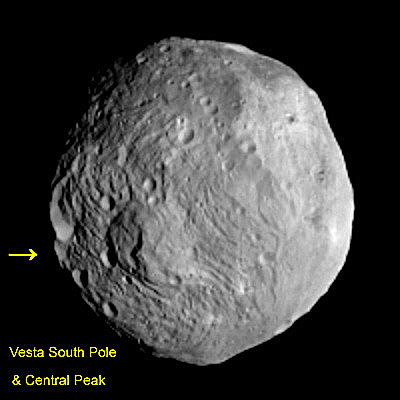
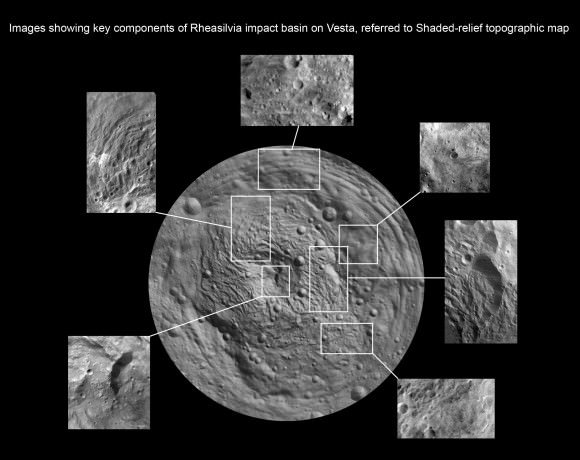
“The South Pole [Rheasilvia] basin is a roughly circular, impact structure and a deep depression dominated by a large central mound,” said Schenk. “It shows sharp scarps, smooth areas, landslide deposits, debris flows. It’s about 475 km in diameter and one of the deepest (ca. 20 -25 km) impact craters in the solar system.”
The central peak is an enormous mountain, about 22 km high and 180 km across- one of the biggest in the solar system. “It’s comparable in some ways to Olympus Mons on Mars,” Schenk stated.
“We were quite surprised to see a second basin in the mapping data outside of Rheasilvia. This was unexpected. It’s called ‘Older Basin’ for now.”
‘Older Basin’ is about 375 km in diameter. They overlap at the place where Rheasilvia has a missing rim.
“These basins are interesting because we believe Vesta is the source of a large number of meteorites, the HED meteorites that have a spread of ages,” Schenk explained.
Multiple large impacts over time may explain the source of the HED (Howardite, Eucrite and Diogenite) meteorites.
“We did expect large impacts on Vesta, likely associated with the late heavy bombardment recognized in the lunar impact record,” Raymond told Universe Today. “The surprising element is that the two apparently largest impacts – keeping in mind that other larger impact basins may be lurking under the regolith – are overlapping.”
Dawn’s VIR spectrometer has detected pyroxene bands covering Vesta’s surface, which is indicative of typical basaltic material, said Federico Tosi, a VIR team member of the Italian Space Agency, Rome. “Vesta has diverse rock types on its surface.”
“VIR measured surface temperatures from 220K to 270 K at the 5 micron wavelength. The illuminated areas are warmer.”
So far there is no clear indication of olivine which would be a marker for seeing Vesta’s mantle, Tossi elaborated.
The VIR spectrometer combines images, spectral information and temperature that will allow researchers to evaluate the nature, composition and evolutionary forces that shaped Vesta’s surface.
The team is absolutely thrilled to see a complicated geologic record that’s been preserved for study with lots of apparent surface layering and surprisingly strong and complex structural features with a large range of color and brightness.
Stay tuned for a year of Vestan delights !
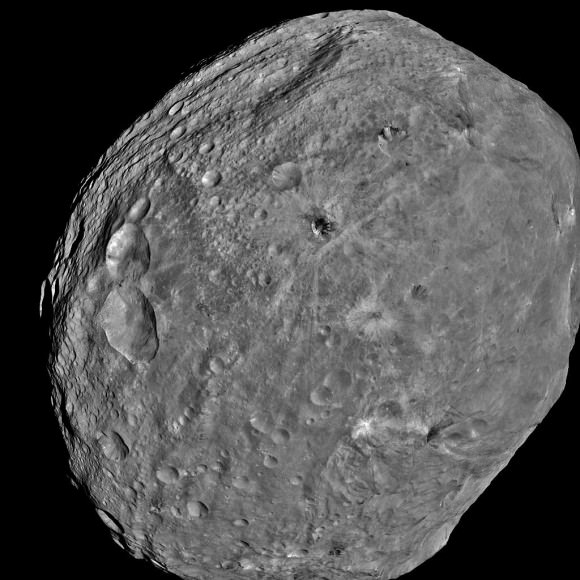

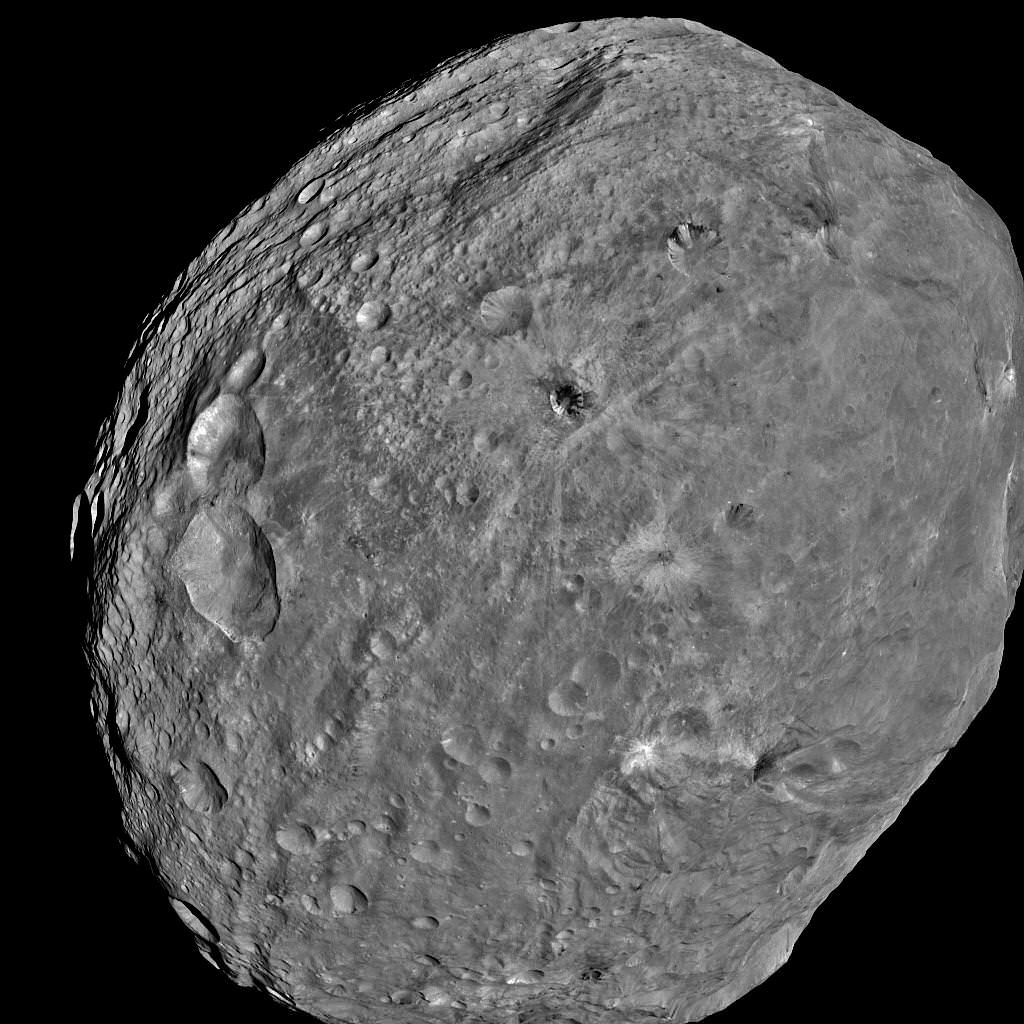
South Pole Rheasilvia basin is at lower right. NASA's Dawn spacecraft obtained this image of the giant asteroid Vesta with its framing camera on July 24, 2011 from a distance of about 3,200 miles (5,200 kilometers). Dawn entered orbit around Vesta on July 16, and will spend a year orbiting the body.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA
Read Ken’s continuing features about Dawn and Vesta starting here:
Amazing New View of the Mt. Everest of Vesta
Dramatic 3 D Imagery Showcases Vesta’s Pockmarked, Mountainous and Groovy Terrain
Rheasilvia – Super Mysterious South Pole Basin at Vesta
Space Spectacular — Rotation Movies of Vesta
3 D Alien Snowman Graces Vesta
NASA Unveils Thrilling First Full Frame Images of Vesta from Dawn
Dawn Spirals Down Closer to Vesta’s South Pole Impact Basin
First Ever Vesta Vistas from Orbit – in 2D and 3D
Dawn Exceeds Wildest Expectations as First Ever Spacecraft to Orbit a Protoplanet – Vesta