Through the Artemis Program, NASA plans to send the first astronauts to the Moon in over fifty years. Before the decade is over, this program aims to establish the infrastructure that will allow for a “sustained program of lunar exploration and development.” The European Space Agency (ESA) also has big plans, which include the creation of a Moon Village that will serve as a spiritual successor to the International Space Station (ISS). China and Roscosmos also came together in June 2021 to announce that they would build the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS) around the lunar south pole.
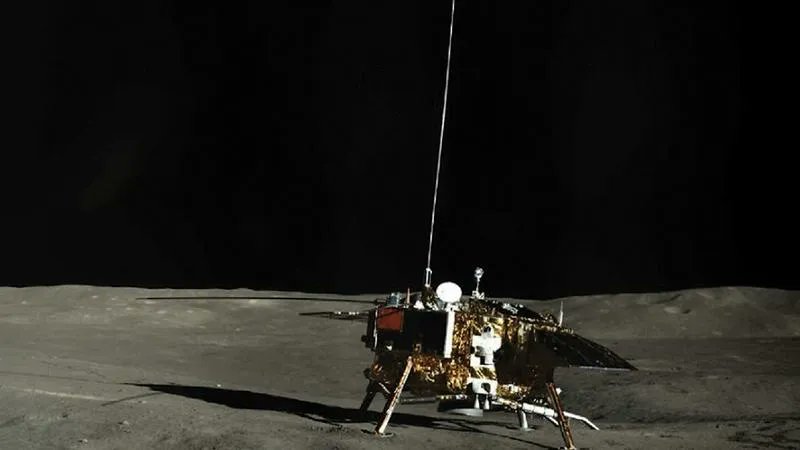
In all cases, space agencies plan to harvest local resources to meet their construction and long-term needs – a process known as In-Situ Resource Utilization (ISRU). Based on samples returned by the fifth mission of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program (Chang’e-5), a team of researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) identified indigenous glass fibers for the first time. According to a paper they authored, these fibers were formed by past impacts in the region and could be an ideal building material for future lunar bases.
Continue reading “Glass Fibers in Lunar Regolith Could Help Build Structures on the Moon”