[/caption]
NASA announced today the winners of the third round of commercial crew development funding, called the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability (CCiCap). This will ultimately allow commercial space companies to be able to provide commercial human spaceflight services for both NASA and other commercial customers. The winners are SpaceX ($440 million), Boeing ($460 million) and Sierra Nevada Corporation ($212.5 million). NASA said these awards will enable a launch of astronauts from U.S. soil in the next five years.
NASA’s Ed Mango said that the differences in the amount each company received was not a difference of two companies getting “full” awards and one getting a half award, but each company negotiated how much work they could get done in the 21-month period that this award covers.
NASA wants to have at least one commercial company able to bring astronauts to and from the International Space Station by 2017, but the three winning companies said they can either meet or beat that deadline, with optimal funding.
During conference calls with reporters, SpaceX’s Elon Musk said his company is shooting for a demonstration flight in mid-2015, with the anticipated Boeing says it can do crewed test flight in late 2016, assuming optimal funding, and Sierra Nevada said they will likely start their operations in 2016 or 2017.
Musk said the cost of getting to first crewed SpaceX flight to ISS would be about $1 billion. The first orbital demo crewed flight probably wouldn’t go to the space station, but would on a subsequent flight, about a year later.
SpaceX is well ahead of the other two companies because of their work – and success – with the unmanned Dragon capsule, which traveled to and from the ISS earlier this year, and was the first commercial spacecraft to be berthed to the Station. For the most part, SpaceX has paid their own way during the development of Dragon and their crewed version, the 7-passenger DragonRider, spending about $300 million of their own money in addition to about $75 million from NASA.
The plans for DragonRider have it making its return landing in the ocean, but SpaceX has completed the development of the SuperDraco thruster, which will mainly be used as a launch abort system but also allow for powered landings on land.
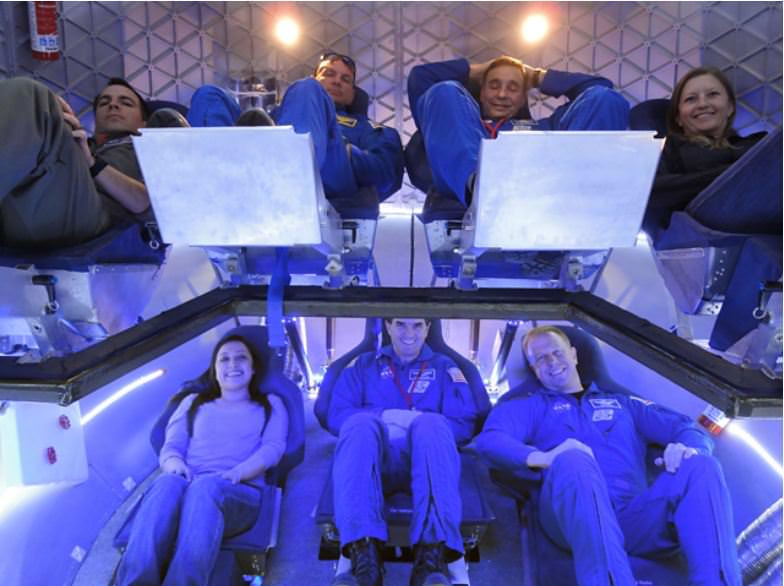
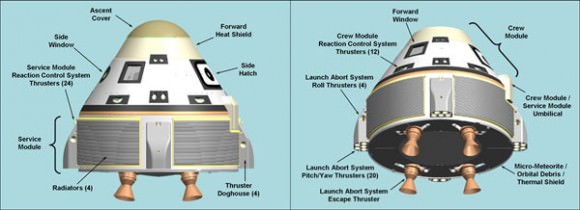
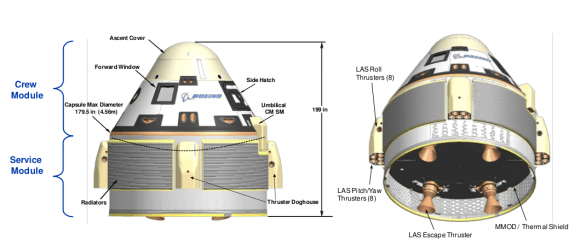
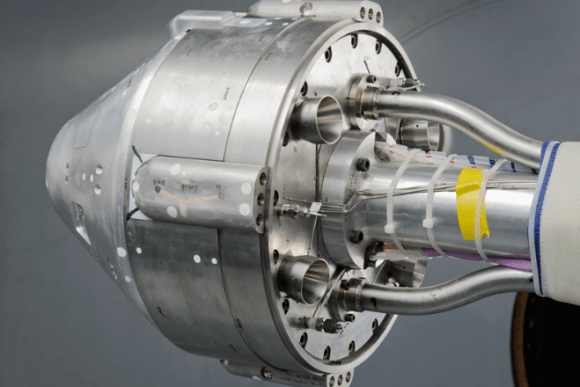
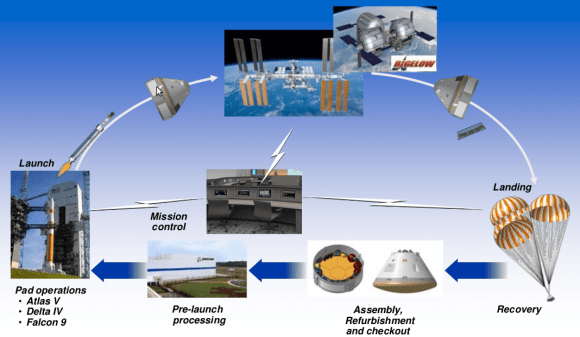
Boeing’s CST-100 capsule, also capable of carrying a crew of seven, has met many milestones, such as drop tests and parachute tests. Like Dragon, the spacecraft will initially land in the ocean, but the company hopes to allow for land-based landings later on. It will launch on an Atlas V rocket.
Sierra Nevada’s Dream Chaser spacecraft, perhaps the most fascinating of the trio of commercial spacecraft, looks like a mini-space shuttle, and comes from the line of NASA experimental vehicles, the HL-20. It can serve as both a transport vehicle and a rescue vehicle from the ISS, and has the capability to land at almost any commercial airport within six hours of leaving the ISS. Dream Chaser will also launch on an Atlas V.

“Today, we are announcing another critical step toward launching our astronauts from U.S. soil on space systems built by American companies,” NASA Administrator Charles Bolden said at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. “We have selected three companies that will help keep us on track to end the outsourcing of human spaceflight and create high-paying jobs in Florida and elsewhere across the country.”
The Commercial Crew Program is a competitive program where commercial companies develop and build vehicles to meet NASA’s requirements, and when fixed milestones are met, NASA provides funding.
NASA says the objective of the CCP is to facilitate the development of a U.S. commercial crew space transportation capability with the goal of achieving safe, reliable and cost-effective access to and from the International Space Station and low Earth orbit.
“For 50 years American industry has helped NASA push boundaries, enabling us to live, work and learn in the unique environment of microgravity and low Earth orbit,” said William Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate. “The benefits to humanity from these endeavors are incalculable. We’re counting on the creativity of industry to provide the next generation of transportation to low Earth orbit and expand human presence, making space accessible and open for business.”
Of course, NASA is also working to develop the Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle (MPCV) and the Space Launch System (SLS), a crew capsule and heavy-lift rocket to provide transportation to distant destinations like the Moon, asteroids or ultimately Mars.
For more details on the program see: http://www.nasa.gov/offices/c3po/home/