Greetings, fellow SkyWatchers! Are you ready for some spooky targets this week? Then follow along as we take a look at the “Little Eyes”, the “Skull Nebula” and a star that’s as red as a drop of blood! If the weather permits, we’ll also be enjoying the Taruid Meteor Shower! Time to dust off those optics and meet me in the backyard…
Monday, October 29 – October’s Full Moon is known as the “Hunter’s Moon” or the “Blood Moon,” its name came from a time when hunters would stalk the fields by Luna’s cold light in search of prey before the winter season began. Pick a place at sunset to watch it rise – a place having a stationary point with which you can gauge its progress. Make note of the time when the first rim appears and then watch how quickly it gains altitude! How long does it take before it rises above your marker?
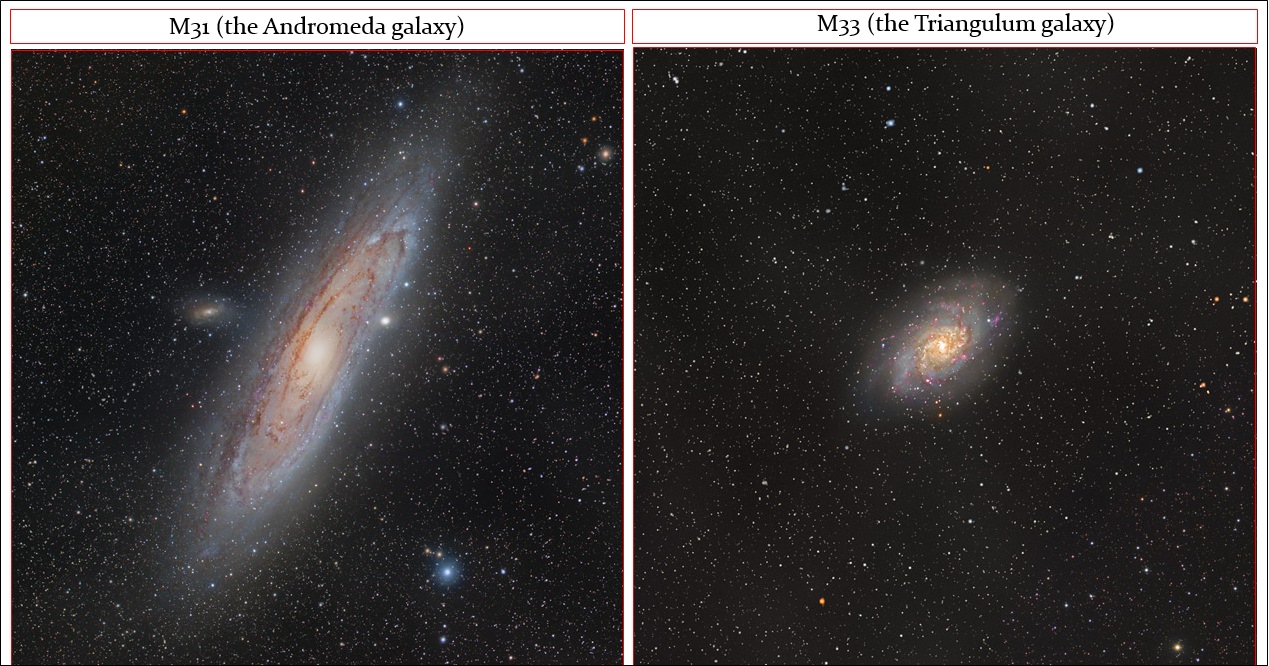
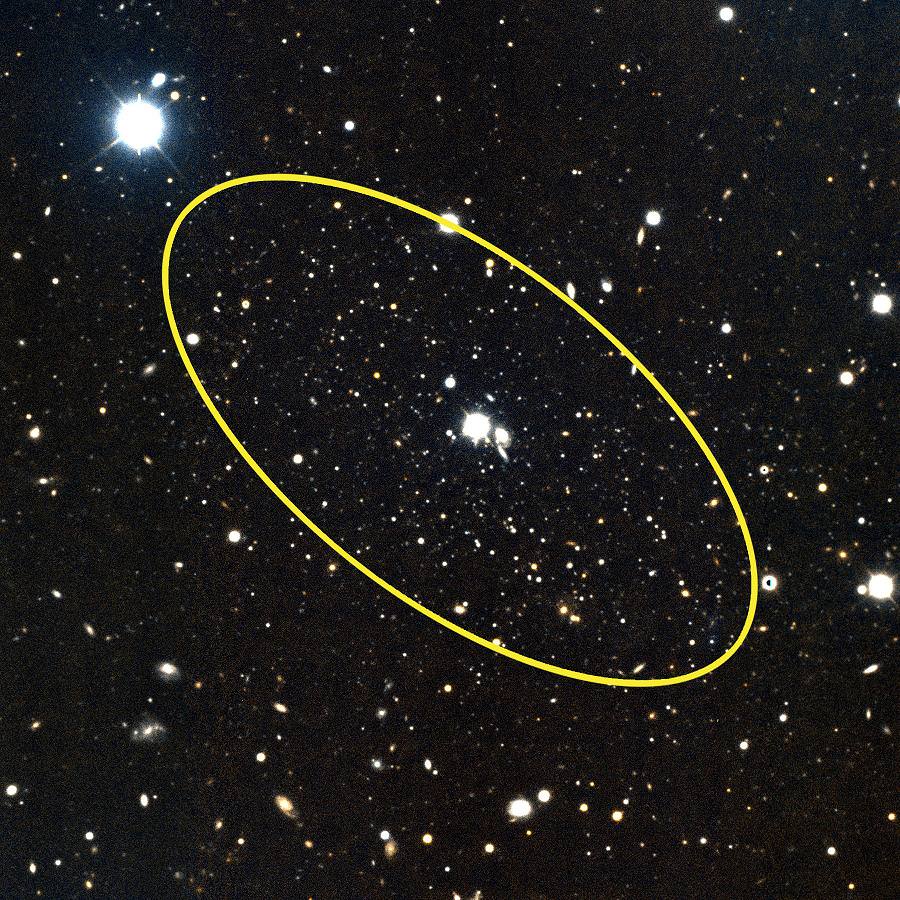
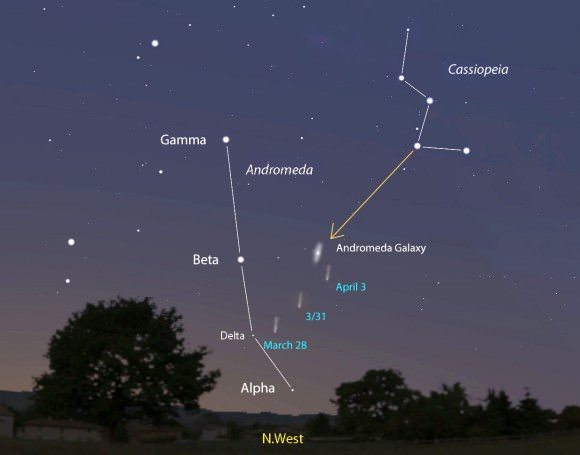
On this night in 1749, the French astronomer Le Gentil was at the eyepiece of an 18? focal length telescope. His object of choice was the Andromeda Galaxy, which he believed to be a nebula. Little did he know at the time that his descriptive notes also included M32, a satellite galaxy of M31. It was the first small galaxy discovered, and it would be another 175 years before these were recognized as such by Edwin Hubble.
Even though it’s very bright tonight, take the time to view the Andromeda Galaxy for yourself. Located just about a degree west of Nu Andromeda, this ghost set against the starry night was known as far back as 905 AD, and was referred to as the “Little Cloud.” Located about 2.2 million light-years from our solar system, this expansive member of our Local Galaxy Group has delighted observers of all ages throughout the years. No matter if you view with just your eyes, a pair of binoculars or a large telescope, M31 still remains one of the most spectacular galaxies in the night.
Tuesday, October 30 – Tonight let’s have a look at the big, fat Moon as we return again with binoculars to identify the maria once again. Take the time to repeat the names to yourself and to study a map. One of the keys to successfully learning to identify craters is by starting with large, easily recognized features. Even though the Moon is very bright when full, try using colored or Moon filters with your telescope to have a look at the many surface features which throw amazing patterns across its surface. If you have none, a pair of sunglasses will suffice.
Look for things you might not ordinarily notice – such as the huge streak which emanates from crater Menelaus. Look at the pattern projected from Proclus – or the intense little dot of little-known Pytheas north of Copernicus. It’s hard to miss the blinding beacon of Aristarchus! Check the southeastern limb where the edge of Furnerius lights up the landscape…or how a nothing crater like Censorinus shines on the southeast shore of Tranquillitatis, while Dionysus echoes it on the southwest. Could you believe Manlius just north of central could be such a perfect ring – or that Anaxagoras would look like a northern polar cap? On the eastern limb we see the bright splash ray patterns surrounding ancient Furnerius – yet the rays themselves emanate from the much younger crater Furnerius A. All over the visible side, we see small points light up: a testament to the Moon’s violent past written in its scarred lines. Take a look now at the western limb…for the sunrise is about to advance around it.
Wednesday, October 31 – Happy Halloween! Many cultures around the world celebrate this day with a custom known as “Trick or Treat.” Tonight instead of tricking your little ghouls and goblins, why not treat them to a sweet view through your telescope or binoculars? What Halloween would be complete without a witch?! Easily found from a modestly dark site with the unaided eye, the Pleiades can be spotted well above the northeastern horizon within a couple of hours of nightfall. To average skies, many of the 7 bright components will resolve easily without the use of optical aid, but to telescopes and binoculars? M45 (Right Ascension: 03 : 47.0 – Declination: +24 : 07) is stunning…
First let’s explore a bit of history. The recognition of the Pleiades dates back to antiquity and its stars are known by many names in many cultures. The Greeks and Romans referred to them as the “Starry Seven,” the “Net of Stars,” “The Seven Virgins,” “The Daughters of Pleione,” and even “The Children of Atlas.” The Egyptians referred to them as “The Stars of Athyr,” the Germans as “Siebengestiren” (the Seven Stars), the Russians as “Baba” after Baba Yaga, the witch who flew through the skies on her fiery broom. The Japanese call them “Subaru,” Norsemen saw them as packs of dogs and the Tonganese as “Matarii” (the Little Eyes). American Indians viewed the Pleiades as seven maidens placed high upon a tower to protect them from the claws of giant bears, and even Tolkien immortalized the stargroup in “The Hobbit” as “Remmirath.” The Pleiades have even been mentioned in the Bible! So, you see, no matter where we look in our “starry” history, this cluster of seven bright stars has been part of it. But, let’s have some Halloween fun!
The date of the Pleiades culmination (its highest point in the sky) has been celebrated through its rich history by being marked with various festivals and ancient rites – but there is one particular rite that really fits this occasion! What could be more spooky on this date than to imagine a group of Druids celebrating the Pleiades’ midnight “high” with Black Sabbath? This night of “unholy revelry” is still observed in the modern world as “All Hallow’s Eve” or more commonly as Halloween. Although the actual date of the Pleiades midnight culmination is now on November 21 instead of October 31, why break with tradition? Thanks to its nebulous regions, M45 looks wonderfully like a “ghost” haunting the starry skies.
Treat yourself and your loved ones to the “scariest” object in the night. Binoculars give an incredible view of the entire region, revealing far more stars than are visible with the naked eye. Small telescopes at lowest power will enjoy M45?s rich, icy-blue stars and fog-like nebulosity. Larger telescopes and higher power reveal many pairs of double stars buried within its silver folds. No matter what you choose, the Pleiades definitely rock!
Thursday, November 1 – On this day in 1977, Charles Kowal made a wild discovery – Chiron. This represented the first discovery of a multitude of tiny, icy bodies that lie in the outer reaches of our solar system. Collectively known as Centaurs, they reside in unstable orbits between Jupiter and Neptune and are almost certainly “refugees”” from the Kuiper Belt.
Tonight let’s go for something small, but white-hot as we head for a dwarf star and planetary nebula, NGC 246. You’ll find it just a bit more than a fistwidth north-northeast of Beta Ceti (RA 00 47 03.34 Dec -11 52 18.9).
First discovered by Sir William Herschel and cataloged as object V.25, this 8th magnitude planetary nebula has a wonderful patchy, diffuse structure that envelops four stars. Around 1600 light-years away, the nebulosity you can see around the exterior edges was once the outer atmosphere of a star much like our own Sun. At the center of the nebula lies the responsible star – the fainter member of a binary system. While it is now in the process of becoming a white dwarf, we can still enjoy the product of this expanding shell of gas that is often called the “Skull Nebula.”
Friday, November 2 – Celestial scenery alert! If you’re up when the Moon rises, be sure to look for the close pairing of Jupiter and the Moon – they’re only about a fingerwidth apart! For a few viewers in the southernmost Africa region, this is an occultation event, so be sure to check resources for websites like IOTA which will give you times for locations in your area. What a great photographic opportunity… Clear skies!
Today celebrates the birth of an astronomy legend – Harlow Shapely. Born in 1885, the American-born Shapley paved the way in determining distances to stars, clusters, and the center of our Milky Way galaxy. Among his many achievements, Shapely was also the Harvard College Observatory director for many years. Today in 1917 also represents the night first light was seen through the Mt. Wilson 100? telescope.
Of course, Dr. Shapley spent his fair share of time on the Hooker telescope as well. One of his many points of study was globular clusters, their distance, and their relationship to the halo structure of our galaxy. Tonight let’s have a look at a very unusual little globular located about a fistwidth south-southeast of Beta Ceti and just a couple of degrees north-northwest of Alpha Sculptor (RA 00:52:47.5 Dec -26:35:24), as we have a look at NGC 288.
Discovered by William Herschel on October 27, 1785, and cataloged by him as H VI.20, the class X globular cluster blew apart scientific thinking in the late 1980?s as a study of perimeter globulars showed it to be more than 3 million years older than similar globulars – thanks to the color magnitude diagrams of Hertzsprung and Russell. By identifying both its blue and red branches, it was shown that many of NGC 288?s stars are being stripped away by tidal forces and contributing to the formation of the Milky Way’s halo structure. In 1997, three additional variable stars were discovered in this cluster.
At magnitude 8, this small globular is easy for southern observers, but faint for northern ones. If you are using binoculars, be sure to look for the equally bright spiral galaxy NGC 253 to the globular’s north.
Saturday, November 3 – On this day in 1955, one of the few documented cases of a person being hit by a meteorite occurred. What are the odds on that? In 1957 the Russian space program launched its first “live” astronaut into space – Laika. Carried on board Sputnik 2, our canine hero was the first living creature to reach orbit. The speedily developed Sputnik 2 was designed with sensors to transmit the ambient pressure, breathing patterns and heartbeat of its passenger, and also had a television camera on board to monitor its occupant. The craft also studied ultraviolet and x-ray radiation to further assess the impact of space flight upon live occupants. Unfortunately, the technology of the time offered no way to return Laika to Earth, so she perished in space. On April 14, 1958, Laika and Sputnik 2 returned to Earth in a fiery re-entry after 2,570 orbits.
Since we’ve got the scope out, let’s go have another look at that galaxy we spied last night!
Discovered by Caroline Herschel on September 23, 1783, NGC 253 (RA 00 47.6 Dec -25 17) is the brightest member of a concentration of galaxies known as the Sculptor Group, near to our own local group and the brightest of all outside it. Cataloged as both H V.1 and Bennett 4, this 7th magnitude beauty is also known as Caldwell 65, and due to both its brightness and oblique angle is often called the “Silver Dollar Galaxy.” As part of the SAC 110 best NGCs, you can even spot this one if you don’t live in the Southern Hemisphere. At around 10 million light-years away, this very dusty, star-forming Seyfert galaxy rocks in even a modest telescope!
Sunday, November 4 – This morning will be the peak of the Southern Taurid meteor shower. Already making headlines around the world for producing fireballs, the Taurids will be best visible in the early morning hours, but the Moon will interfere. The radiant for this shower is, of course, the constellation of Taurus and red giant Aldeberan, but did you know the Taurids are divided into two streams?
It is surmised that the original parent comet shattered as it passed our Sun around 20,000 to 30,000 years ago. The larger “chunk” continued orbiting and is known as periodic comet Encke. The remaining debris field turned into smaller asteroids, meteors and larger fragments that often pass through our atmosphere creating the astounding “fireballs” known as bolides. Although the fall rate for this particular shower is rather low at 7 per hour, these slow traveling meteors (27 km or 17 miles per second) are usually very bright and appear to almost “trundle” across the sky. With the chances high all week of seeing a bolide, this makes a bit of quiet contemplation under the stars worthy of a morning walk. Be sure to look at how close Saturn is to the Moon!
For unaided eye or binocular observers – or those who just wish something a bit “different” tonight – have a look at 19 Pisces. You’ll find it as the easternmost star in the small “circlet” just south of the Great Square of Pegasus.
Also known as TX, you’ll find this one quite delightful for its strong red color. TX is a cool giant star which varies slightly in magnitude on an irregular basis. This carbon star is located anywhere from 400 to 1000 light-years away and rivals even R Leporis’ crimson beauty.
Until next week? Wishing you clear skies!