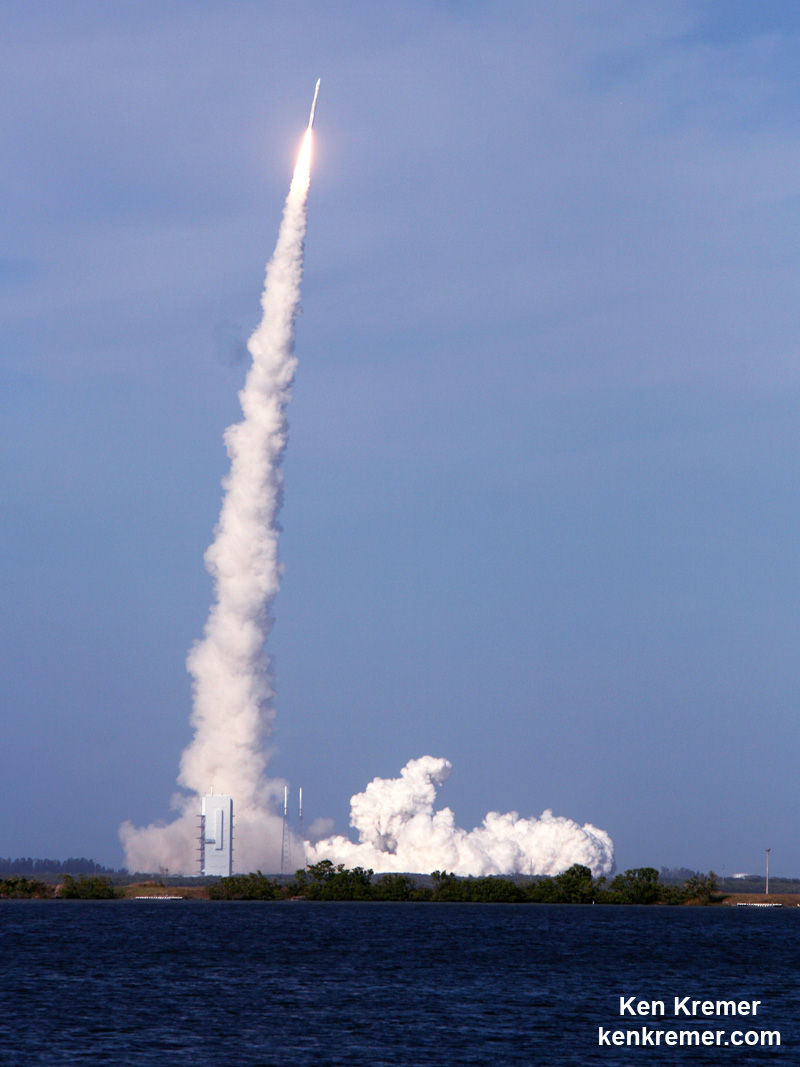
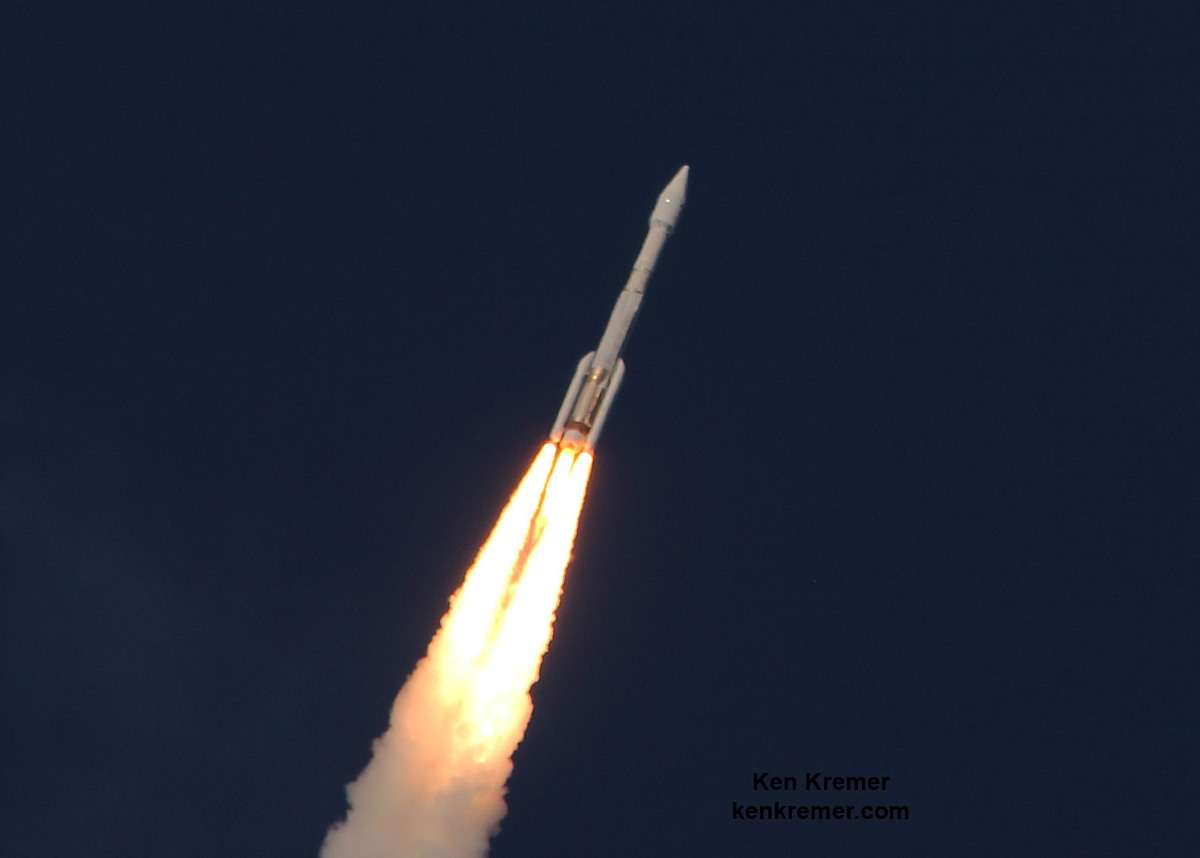
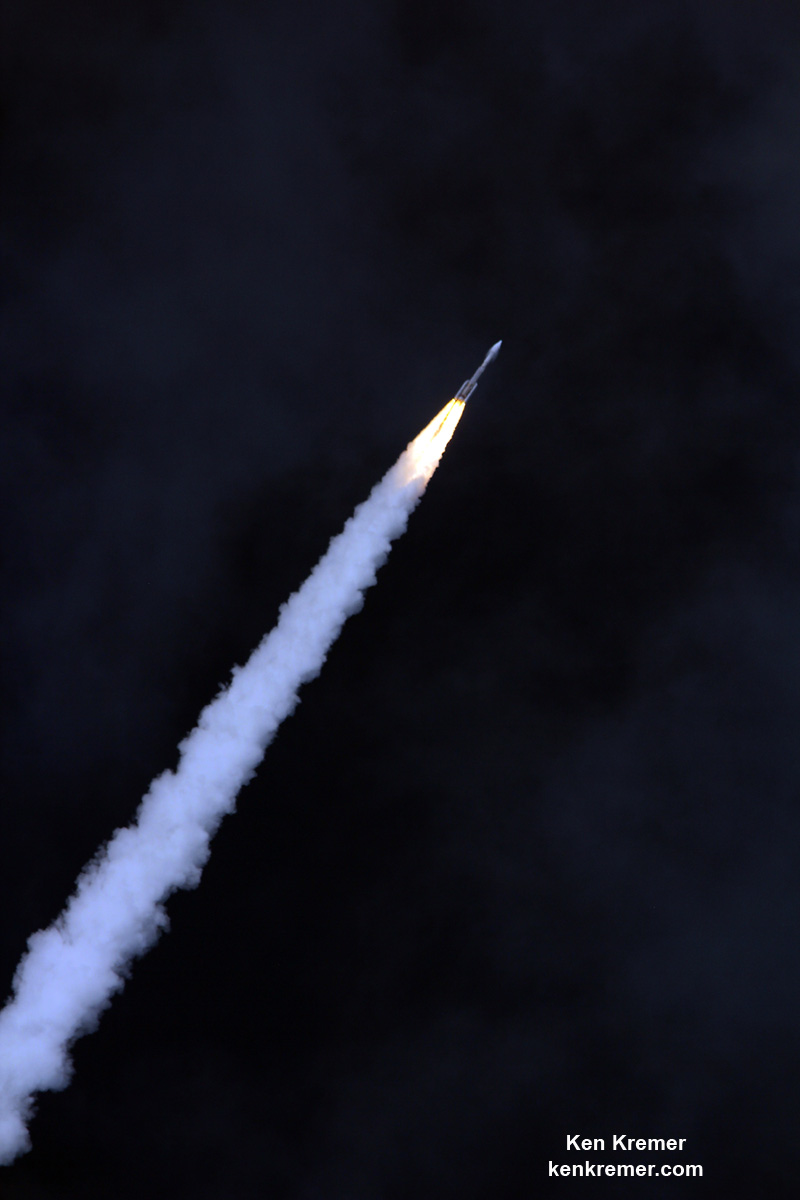
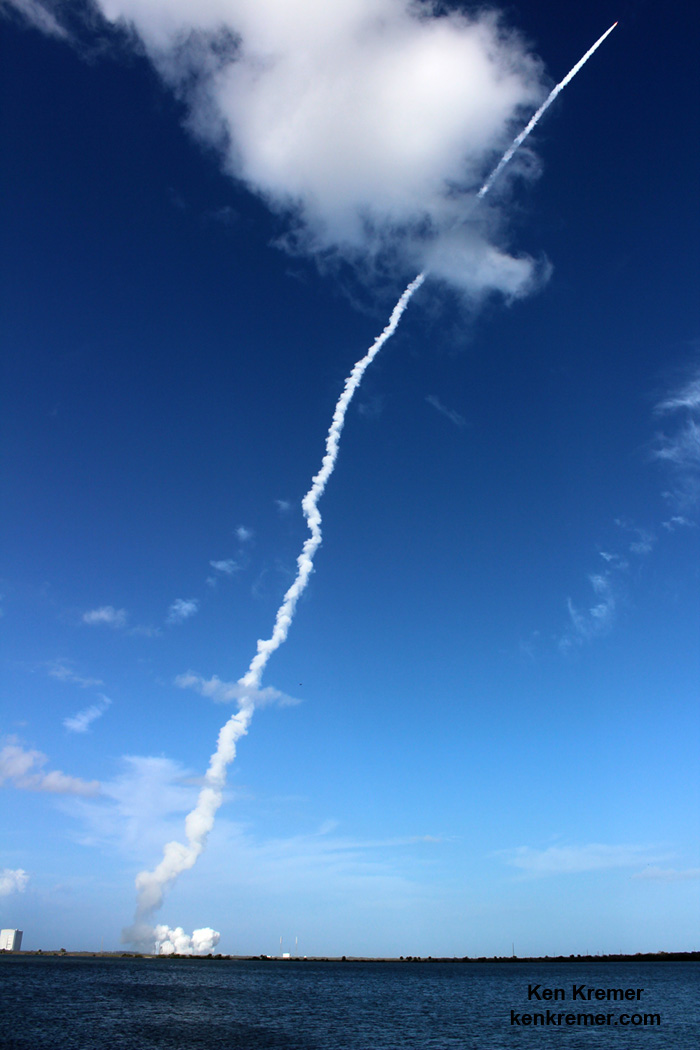
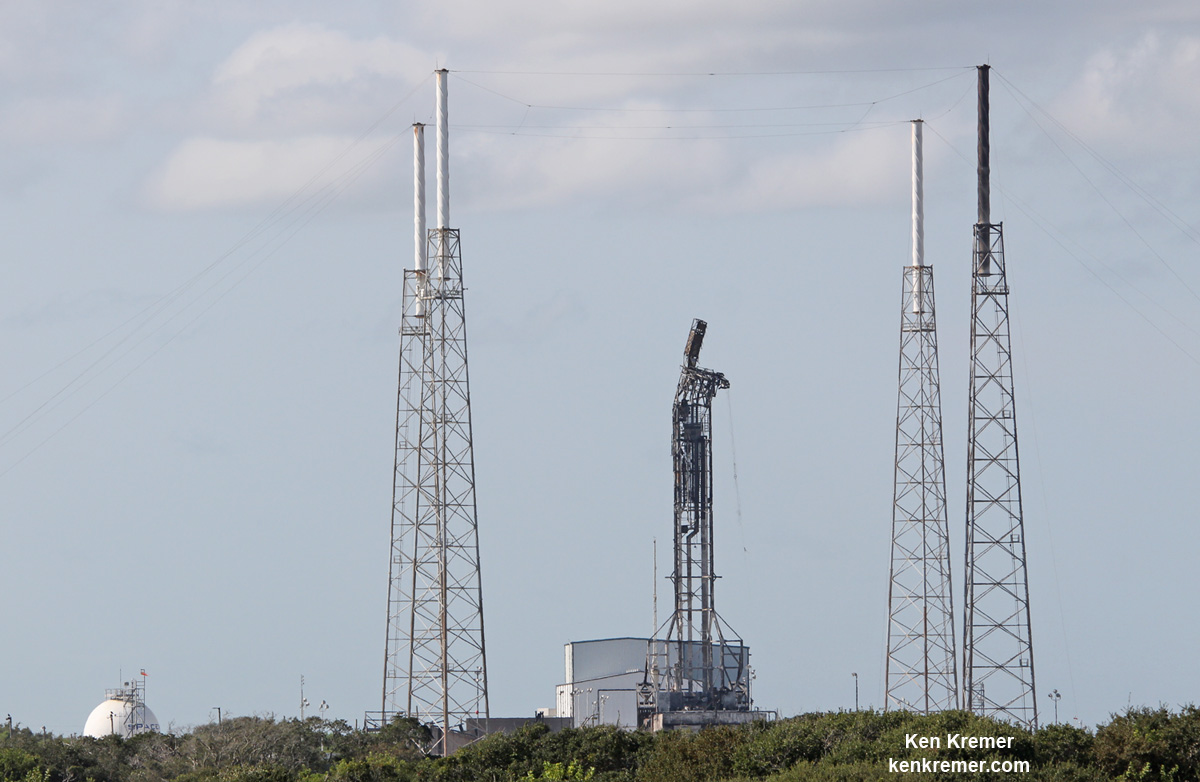
In the face of unrelenting days of very poor weather and a range conflict with another very critical rocket launch, SpaceX is pushing back the return debut of their private Falcon 9 rocket carrying a revolutionary fleet of voice and data commercial communications relay satellites for Iridium to no earlier than next weekend, Jan 14.
Earlier indications of a nearly weeks long launch delay from Monday, Jan. 9 to next Saturday morning, Jan. 14, were officially confirmed today, Jan. 8, by SpaceX and their Iridium Communications customer.
“Launch moving due to high winds and rains at Vandenberg,” SpaceX announced today, Jan. 8.
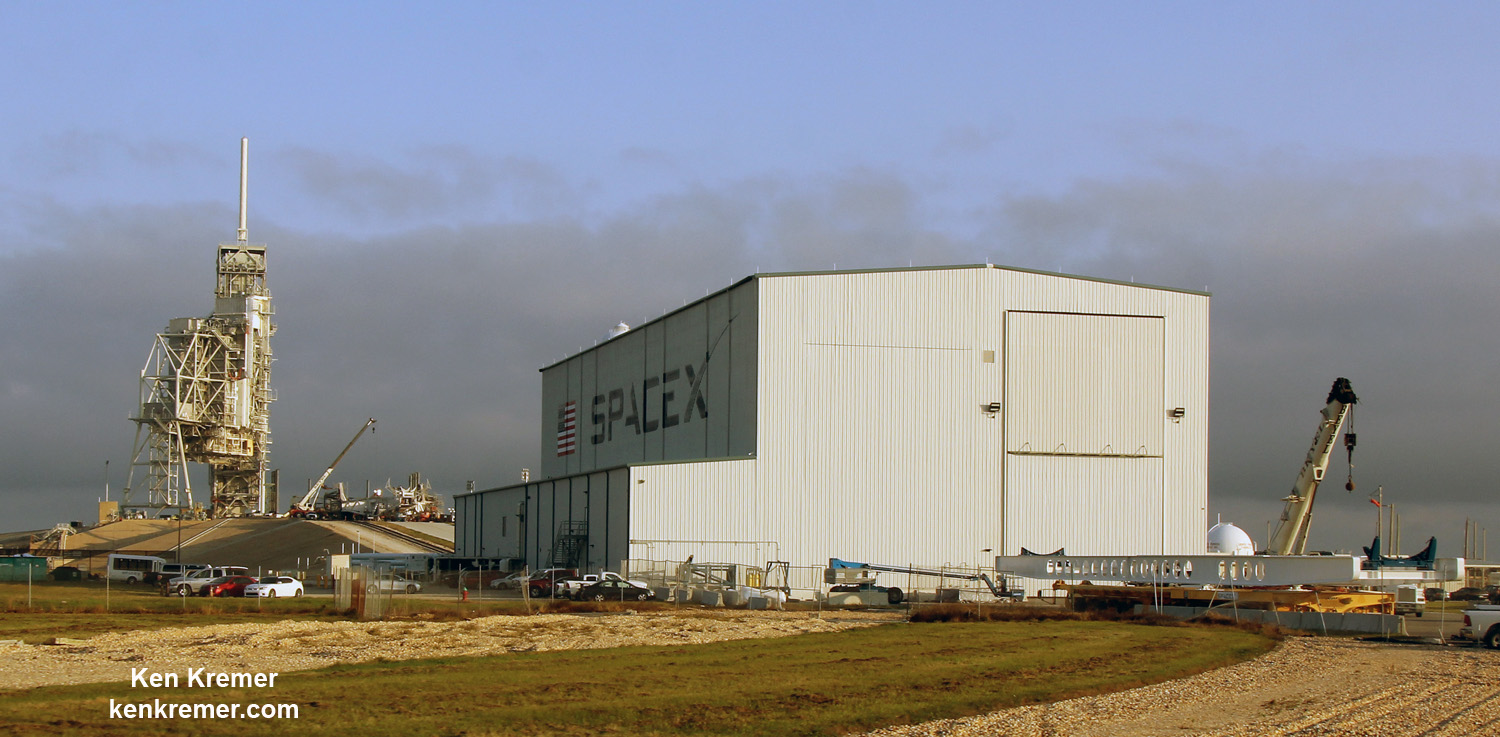
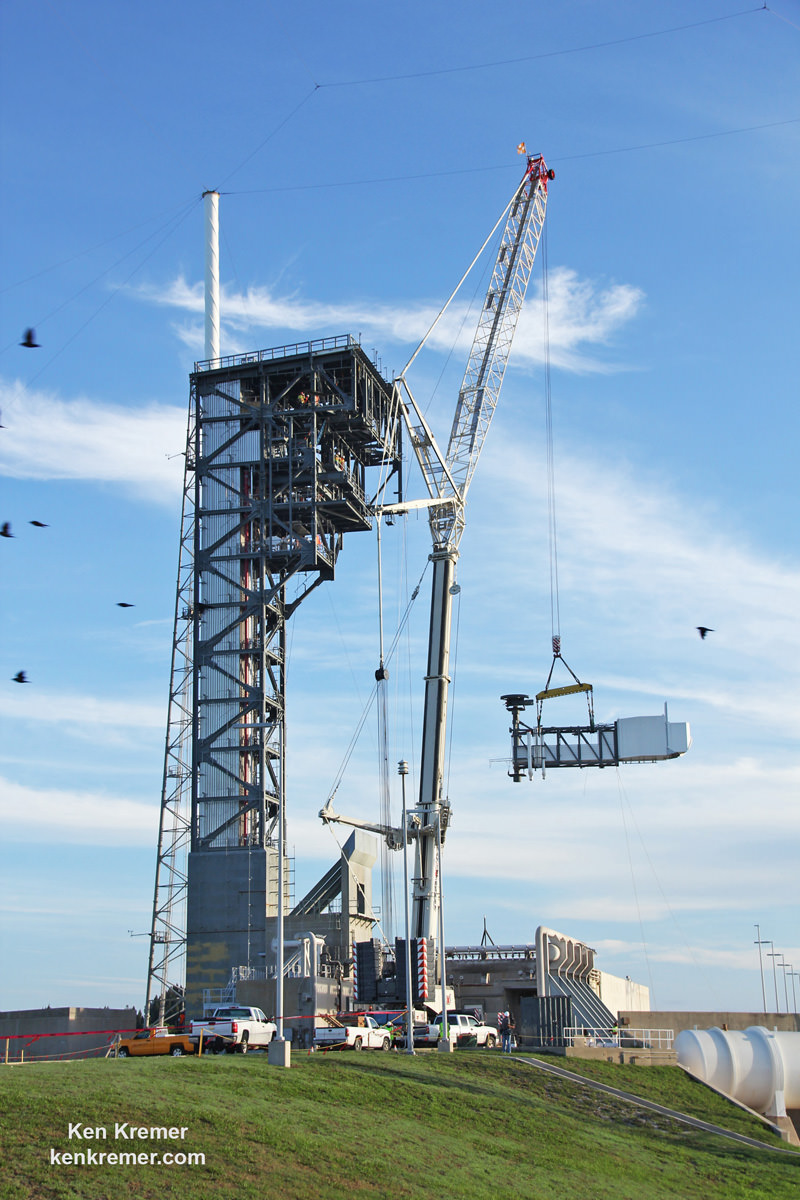
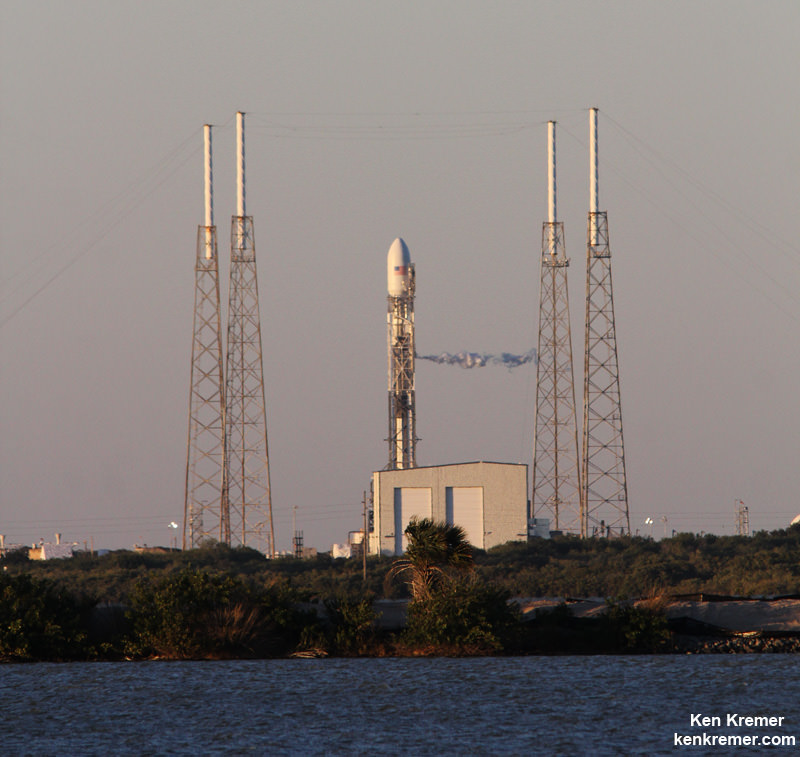
Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 with the payload of 10 identical next generation Iridium NEXT communications satellites had been slated for 10:22 am PST (1:22 pm EST), Jan. 9, 2017 from Space Launch Complex 4E on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
The advanced next satellites will start the process of replacing an aging Iridium fleet in orbit for nearly two decades.
And it was less than 48 hours ago on Friday, Jan. 6, that the FAA finally granted SpaceX a license to launch the ‘Return to Flight’ Falcon 9 mission – as I confirmed with the FAA here.
“The FAA accepted the investigation report on the AMOS-6 mishap and has closed the investigation,” FAA spokesman Hank Price confirmed to Universe Today.
“SpaceX applied for a license to launch the Iridium NEXT satellites from Vandenberg Air Force Base. The FAA has granted a license for that purpose.”
The SpaceX investigation report into the total loss of the Falcon 9 rocket and AMOS-6 payload has not been released at this time. The FAA has oversight responsibility to encourage, facilitate, and promote U.S. commercial space transportation and ensure the protection of public safety.
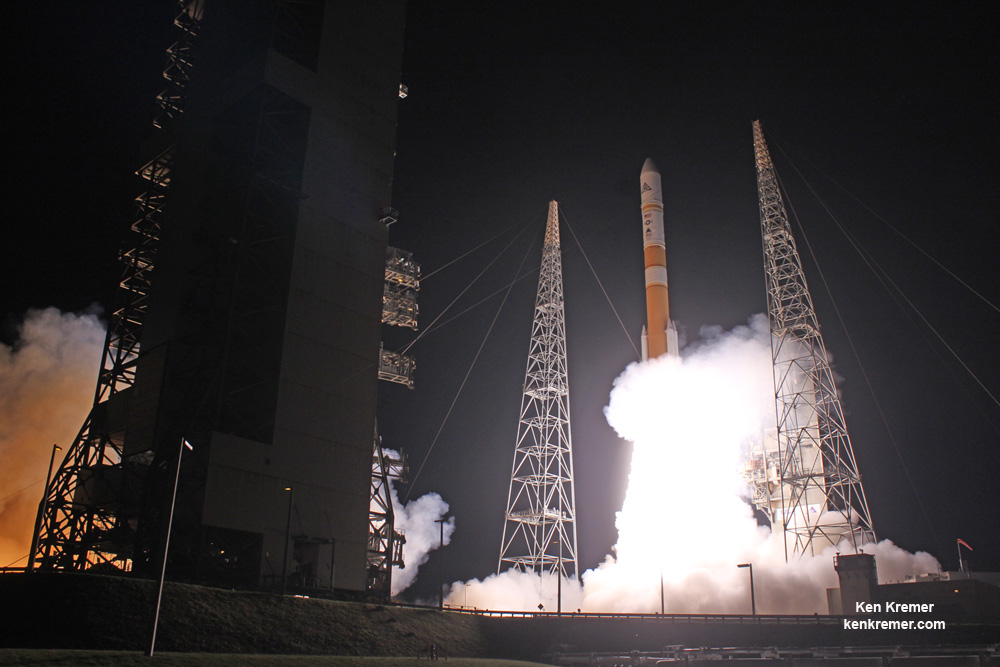
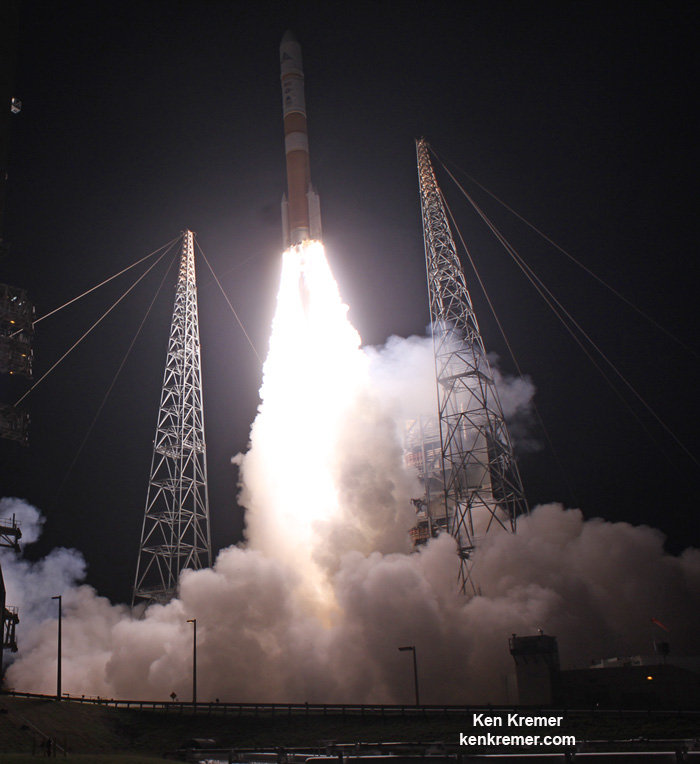
The private rocket – developed by CEO Elon Musk and his company – has been grounded for four months since a catastrophic launch pad explosion last September suddenly destroyed another Falcon 9 and its $200 million Israeli owned satellite during a prelaunch fueling test on the Florida Space Coast.
The Sept. 1, 2016 calamity was the second Falcon 9 failure within 15 months time. Both occurred inside the second stage and called into question the rockets reliability.
The prognosis of a week of bad California weather had been known for some time and finally prompted an official announcement just 24 hours before the hoped for launch.
“With high winds and rain in the forecast at Vandenberg Air Force Base, the first launch of 10 Iridium NEXT satellites is now planned for January 14th at 9:54:34 am PST with a back-up date of January 15th,” Iridium officials elaborated in a statement.
The mission, known as Iridium 1, has an instantaneous launch opportunity at 9:54:34 a.m. PST (12:54:34 p.m. EST).
Next Sunday, Jan. 15 is available as a back-up launch opportunity in case of a delay for any reason including technical and weather related issues.
Furthermore, humorous pleas by Iridium CEO Matt Desch for divine intervention went unheeded !
“Can now confirm: new launch date Jan 14 at 9:54am pst. Bad weather the cause. Anti-rain dances didn’t work – oh well. Cal needs rain?” said Iridium CEO Matt Desch when he threw in the towel this morning by tweet.
Things change fast and furious in the rocket business, and flexibility is the name of the game if you want to survive the frequently changing landscape.

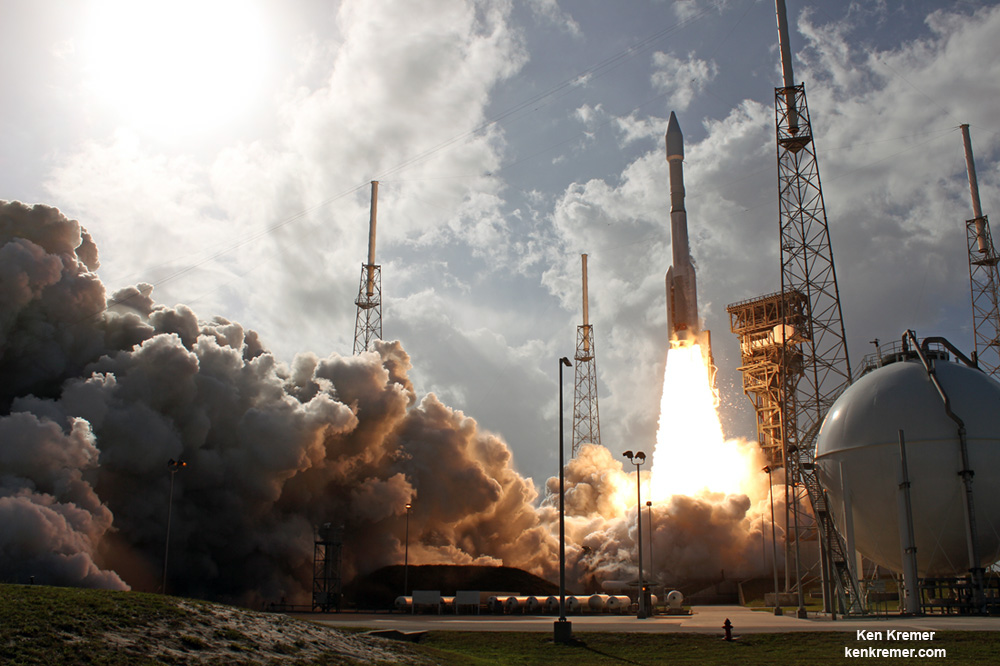
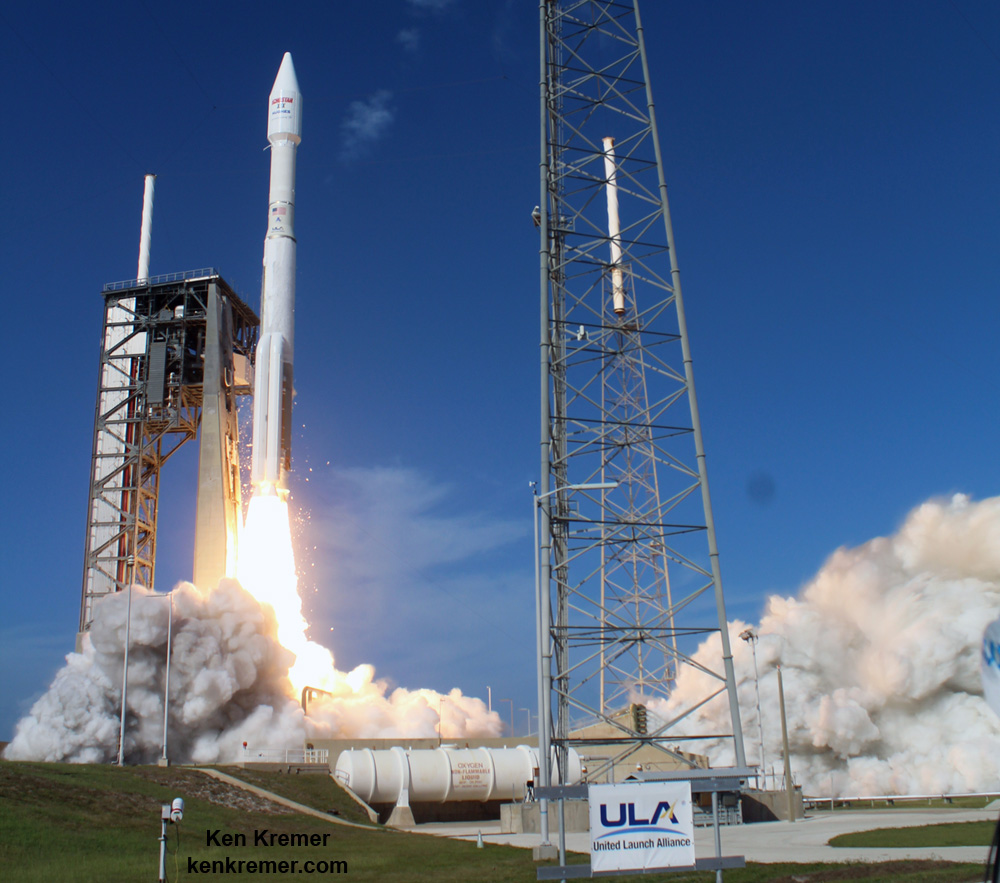
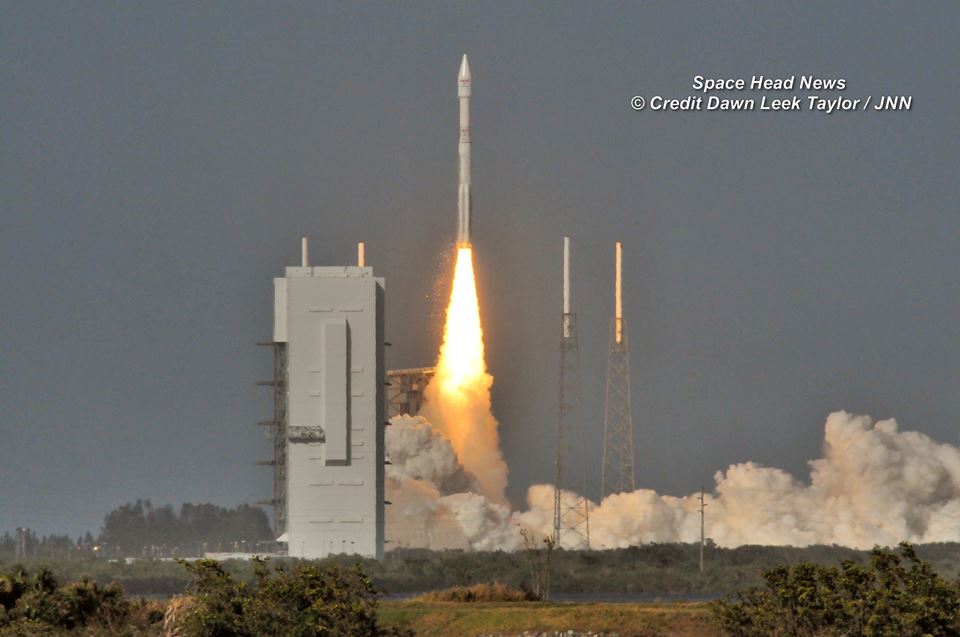
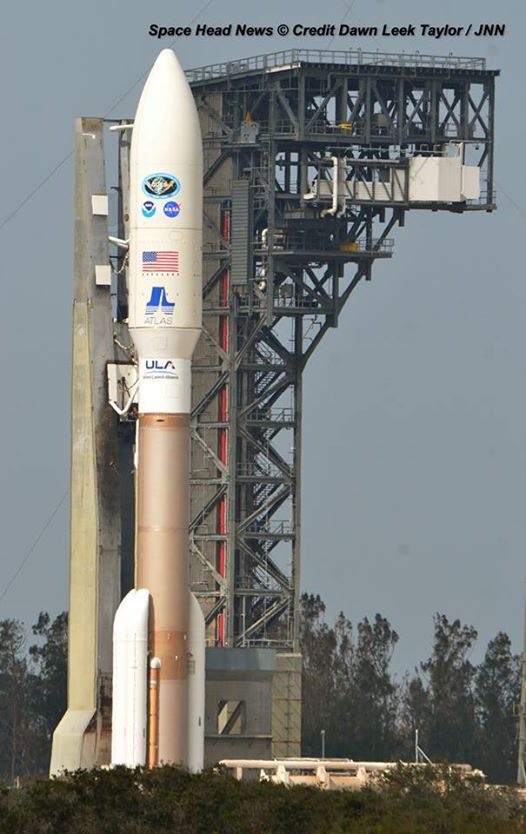
A contributing factor to the delay is a range conflict with an upcoming Atlas rocket launch for the U.S National Reconnaissance Organization (NRO) at Vandenberg AFB.
“Other range conflicts this week results in next available launch date being Jan 14,” SpaceX confirmed.
The United Launch Alliance Atlas V is scheduled to launch the super secret NROL-79 spy satellite for the NRO on Jan. 26.
Prior to the launch, ULA must conduct a wet dress rehearsal (WDR) of the Atlas V by fueling it with propellants to confirm its readiness to launch.
The clandestine NROL-79 intelligence-gathering payload is critical to US national defense. Surly it was manufactured over a time span of several years at an unknown classified cost probably amounting to billions of dollars.
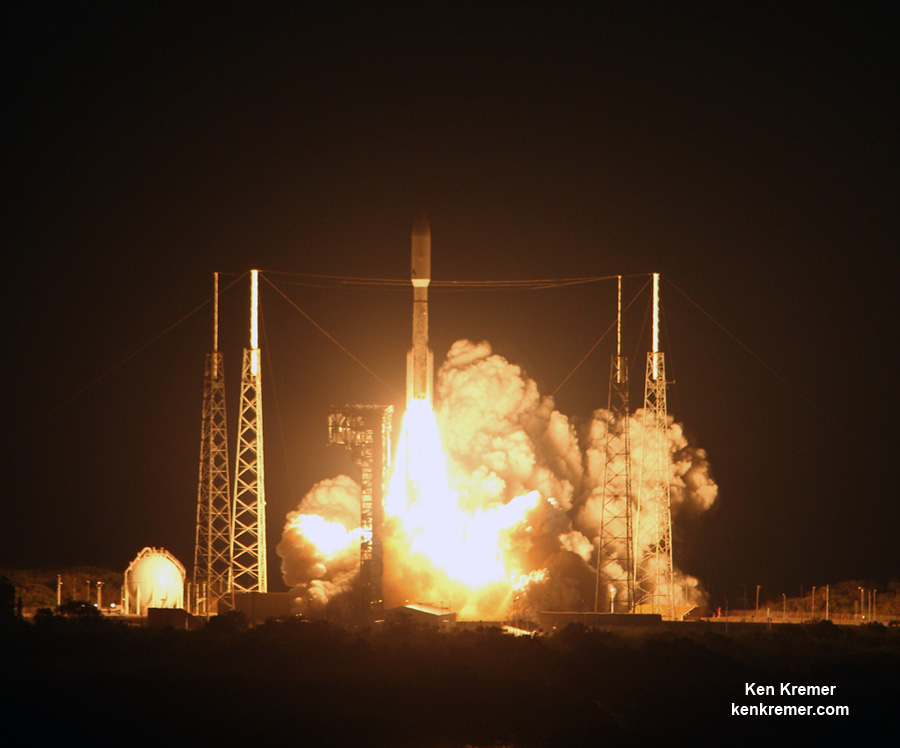
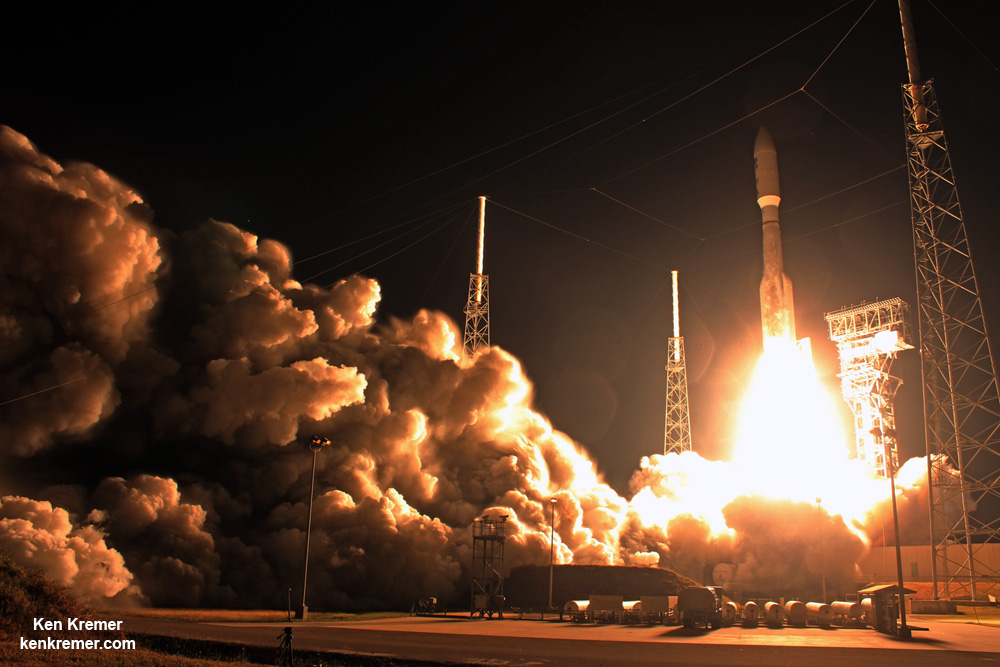
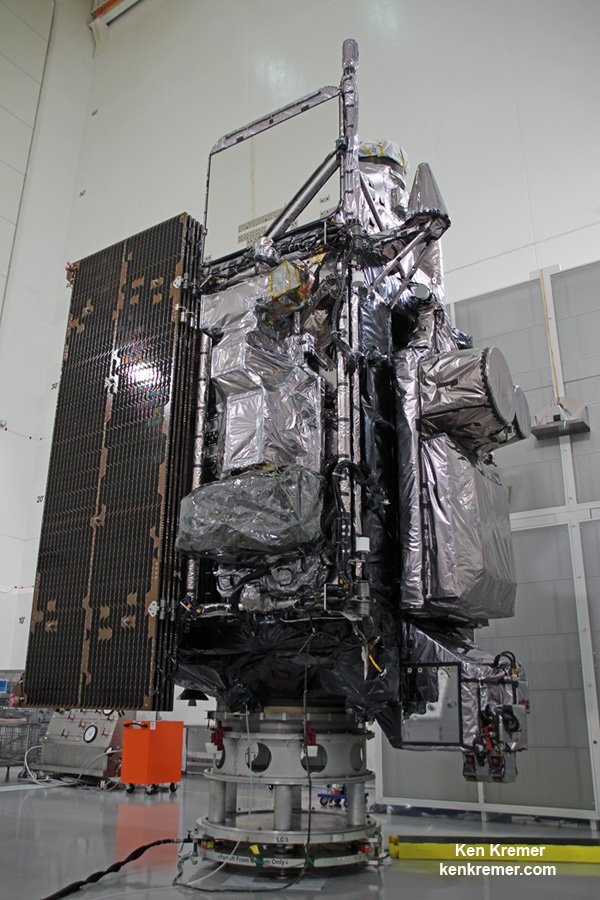
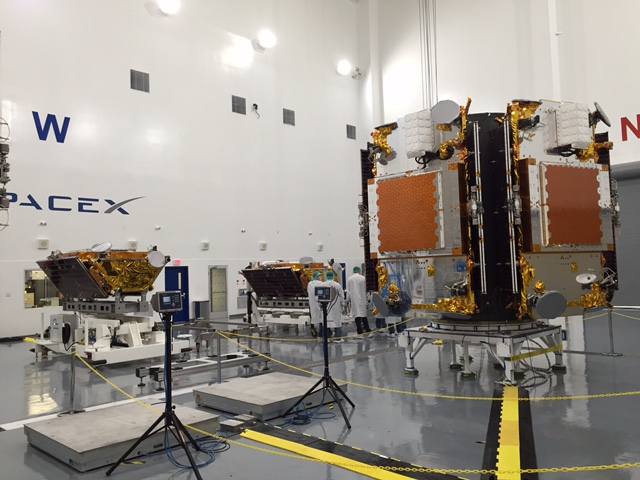
For the Iridium – 1 mission the 229-foot (70-meter) Falcon 9 will carry a fleet of ten Iridium NEXT mobile voice and data relay satellites to orbit from Vandenberg Air Force Base, Ca, for Iridium Communications.
Video Caption: Iridium NEXT: Changing the Paradigm In Space Communications. Credit: Iridium/SpaceX
Iridium 1 is the first of seven planned Falcon 9 launches to establish the Iridium NEXT constellation which will eventually consist of 81 advanced satellites.
The FAA license approved on Jan. 6 covers all seven launches.
“Space Explorations Technologies is authorized to conduct seven launches of Falcon 9 version 1.2 vehicles from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Air Force Base with each flight transporting ten Iridium NEXT payloads to low Earth orbit.
The license also allows SpaceX to land the first stage on a droneship at sea in the Pacific Ocean.
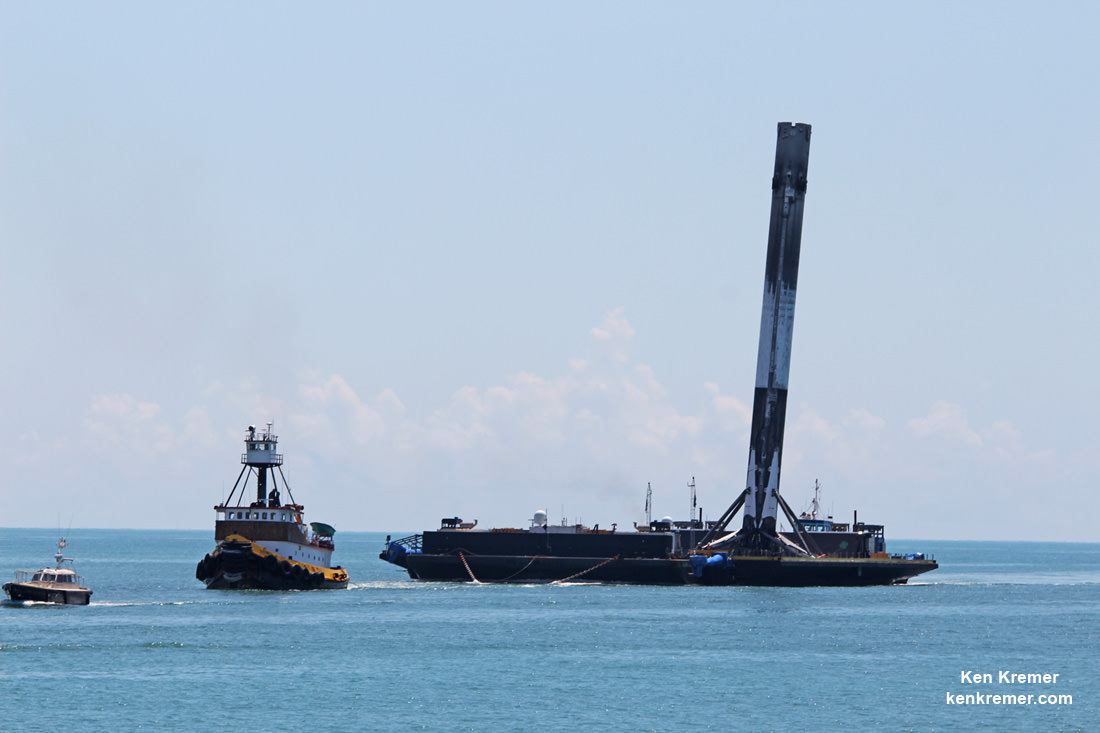

So besides the launch, SpaceX plans to continue its secondary objective of recovering the Falcon 9 first stage via a propulsive soft landing – as done several times previously and witnessed by this author.
The Iridium-1 mission patch featured herein highlights both the launch and landing objectives.
The goal is to eventually recycle and reuse the first stage – and thereby dramatically slash launch costs per Musk’s vision.
This Falcon 9 has been outfitted with four landing lags and grid fins for a controlled landing on a tiny barge prepositioned in the Pacific Ocean several hundred miles off the west coast of California.
Desch says that all seven of his Falcon’s will be new – not reused.
“All our seven F9s are new,” Desch tweeted.
On Jan. 2, SpaceX issued a statement ascribing the Sept. 1, 2016 AMOS-6 launch pad anomaly as being traced to a failure wherein one of three high pressure helium storage tanks located inside the second stage liquid oxygen (LOX) tank of the Falcon 9 rocket suddenly burst. Cold helium is used to pressurize the propellant tanks. They provided some but not many technical details.
The failure apparently originated at a point where the helium tank “buckles” and accumulates oxygen – “leading to ignition” of the highly flammable superchilled oxygen propellant in the second stage when it came into contact with carbon fibers covering the helium tanks – also known as composite overwrapped pressure vessels (COPVs).
“Friction ignition” between the carbon fibers acting as a friction source and super chilled oxygen led to the calamitous explosion, SpaceX concluded was the most likely cause of the disaster.
Watch this space for continuing updates as SpaceX rolls the rocket out from the processing hangar and we watch the saga of the foggy weather forecast with great anticipation !

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.