NASA Administrator Charles Bolden discusses future of NASA human spaceflight during exploration forum at NASA Headquarters, Washington, DC. Credit: Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com
Story updated[/caption]
NASA GODDARD SPACE FLIGHT CENTER, MD – Why is NASA’s Commercial Crew Program to develop private human transport ships to low Earth orbit important?
That’s the question I posed to NASA Administrator Charles Bolden when we met for an exclusive interview at NASA Goddard.
The Commercial Crew Program (CCP) is the critical enabler “for establishing a viable orbital infrastructure” in the 2020s, NASA Administrator Charles Bolden told Universe Today in an exclusive one-on-one interview at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
Bolden, a Space Shuttle commander who flew four time to space, says NASA wants one of the new American-made private crewed spaceships under development by SpaceX, Boeing and Sierra Nevada – with NASA funding – to be ready to ferry US astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS) and back to Earth by late 2017. Flights for other commercial orbital space ventures would follow later and into the next decade.
Since the shutdown of NASA’s space shuttle program following the final flight by STS-135 in 2011 (commanded by Chris Ferguson), America has been 100% dependent on the Russians to fly our astronauts to the space station and back.
“Commercial crew is critical. We need to have our own capability to get our crews to space,” Bolden told me, during a visit to the NASA Goddard cleanroom with the agency’s groundbreaking Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) science probes.

Administrator Bolden foresees a huge shift in how the US will conduct space operations in low earth orbit (LEO) just a decade from now. The future LEO architecture will be dominated not by NASA and the ISS but rather by commercial entrepreneurs and endeavors in the 2020s.
“There are going to be other commercial stations or other laboratories,” Bolden excitedly told me.
And the cash strapped Commercial Crew effort to build new astronaut transporters is the absolutely essential enabler to get that exploration task done, he says.
“Commercial Crew is critical to establishing the low Earth orbit infrastructure that is required for exploration.”
“We have got to have a way to get our crews to space.”
“You know people try to separate stuff that NASA does into nice little neat packages. But it’s not that way anymore.”
Bolden and NASA are already looking beyond the ISS in planning how to use the new commercial crew spaceships being developed by SpaceX, Boeing and Sierra Nevada in a public- partnership with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
“Everything we do [at NASA] is integrated. We have to have commercial crew [for] a viable low Earth orbit infrastructure – a place where we can do testing – for example with what’s going on at the ISS today.”
“And in the out years you are going to be doing the same type of work.”
“But it’s not going to be on the ISS.”
“After 2024 or maybe 2028, if we extend it again, you are going to see the people on commercial vehicles. There are going to be other stations or other laboratories.”
“But there won’t be NASA operated laboratories. They will be commercially viable and operating laboratories.”

Private NewSpace ventures represent a revolutionary departure from current space exploration thinking. But none of these revolutionary commercial operations will happen if we don’t have reliable and cost effective human access to orbit from American soil with American rockets on American spaceships.
“We need to have our own capability to get our crews to space – first of all. That’s why commercial crew is really, really, really important,” Bolden emphasized.
The ongoing crises in Ukraine makes development of a new US crew transporter to end our total reliance on Russian spaceships even more urgent.
“Right now we use the Russian Soyuz. It is a very reliable way to get our crews to space. Our partnership with Roscosmos is as strong as it’s ever been.”
“So we just keep watching what’s going on in other places in the world, but we continue to work with Roscosmos the way we always have,” Bolden stated.
The latest example is this week’s successful launch of the new three man Russian-US- German Expedition 40 crew to the ISS on a Soyuz.
Of course, the speed at which the US develops the private human spaceships is totally dependent on the funding level for the Commercial Crew program.
Unfortunately, progress in getting the space taxis actually built and flying has been significantly slowed because the Obama Administration CCP funding requests for the past few years of roughly about $800 million have been cut in half by a reluctant US Congress. Thus forcing NASA to delay the first manned orbital test flights by at least 18 months from 2015 to 2017.
And every forced postponement to CCP costs US taxpayers another $70 million payment per crew seat to the Russians. As a result of the congressional CCP cuts more than 1 Billion US Dollars have been shipped to Russia instead of on building our own US crew transports – leaving American aerospace workers unemployed and American manufacturing facilities shuttered.
I asked Bolden to assess NASA’s new funding request for the coming fiscal year 2015 currently working its way through Congress.
“It’s looking better. It’s never good. But now it’s looking much better,” Bolden replied.
“If you look at the House markup that’s a very positive indication that the budget for commercial crew is going to be pretty good.”
The pace of progress in getting our crews back to orbit basically can be summed up in a nutshell.
“No Bucks, No Buck Rogers,” Chris Ferguson, who now leads Boeing’s crew effort, told me in a separate exclusive interview for Universe Today.

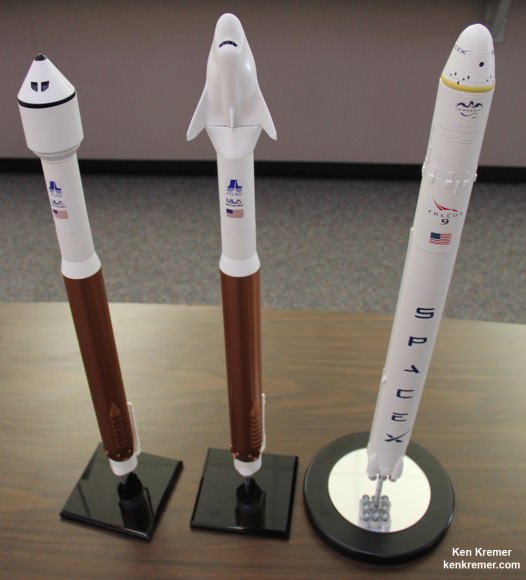
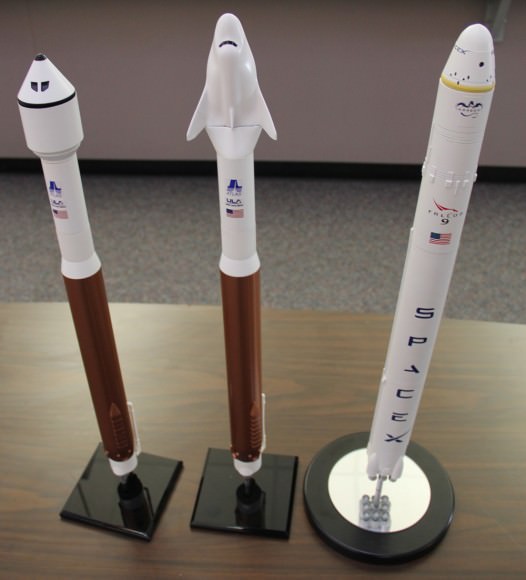
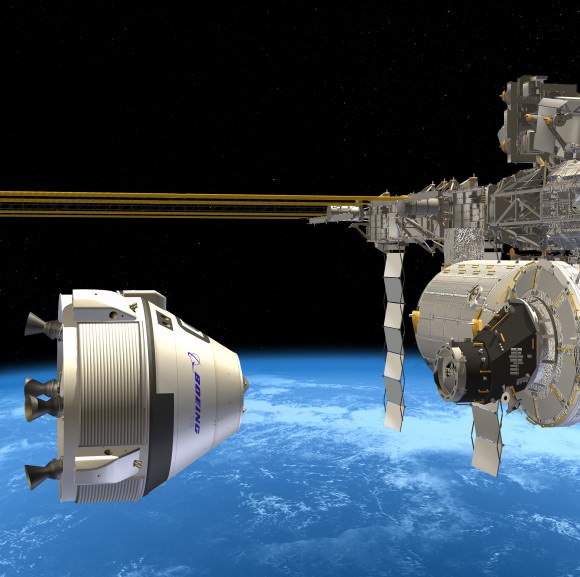
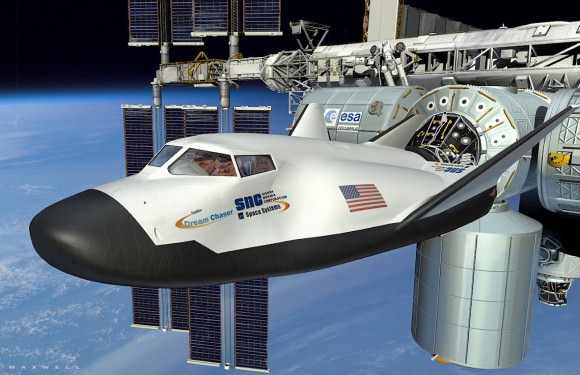
The Boeing CST-100, Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser and SpaceX Dragon ‘space taxis’ are all vying for funding in the next round of contracts to be awarded by NASA around late summer 2014 known as Commercial Crew Transportation Capability (CCtCap).
All three company’s have been making excellent progress in meeting their NASA mandated milestones in the current contract period known as Commercial Crew Integrated Capability initiative (CCiCAP) under the auspices of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
Altogether they have received more than $1 Billion in NASA funding under the current CCiCAP initiative. Boeing and SpaceX were awarded contracts worth $460 million and $440 million, respectively. Sierra Nevada was given what amounts to half an award worth $212.5 million.
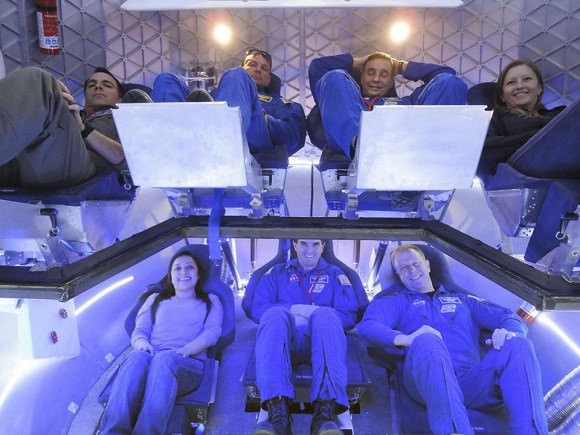
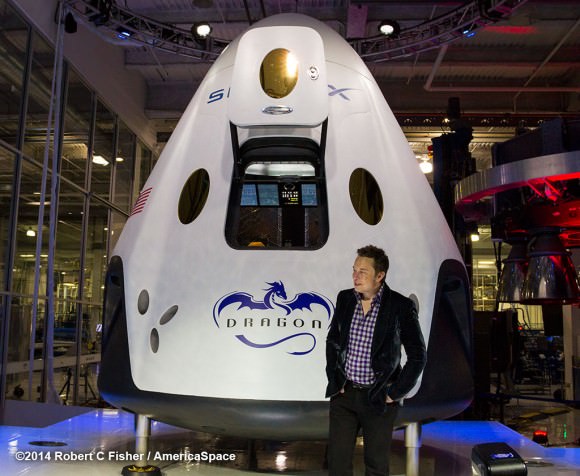
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk just publicly unveiled his manned Dragon V2 spaceship on May 29.
Boeing’s Chris Ferguson told me that assembly of the CST-100 test article starts soon at the Kennedy Space Center.
NASA officials have told me that one or more of the three competitors will be chosen later this year in the next phase under CCtCAP to build the next generation spaceship to ferry astronauts to and from the ISS by 2017.
In order to certify the fitness and safety of the new crew transporters, the CCtCAP contracts will specify that “each awardee conduct at least one crewed flight test to verify their spacecraft can dock to the space station and all its systems perform as expected.”
Concurrently, NASA is developing the manned Orion crew vehicle for deep space exploration. The state-of-the-art capsule will carry astronauts back to the Moon and beyond on journeys to Asteroids and one day to Mars.
“We need to have our own capability to get our crews to space. Commercial Crew is critical to establishing the low Earth orbit infrastructure that is required for exploration,” that’s the bottom line message from my interview with NASA Administrator Bolden.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing SpaceX, Boeing, Sierra Nevada, Orbital Sciences, commercial space, Orion, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more planetary and human spaceflight news.