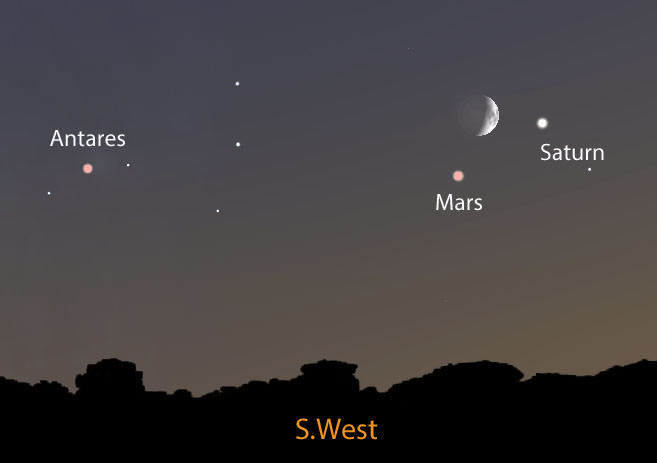
Check it out. Look southwest at dusk tonight and you’ll see three of the solar system’s coolest personalities gathering for a late dinner. Saturn, Mars and the waxing crescent moon will sup in Libra ahead of the fiery red star Antares in Scorpius. All together, a wonderful display of out-of-this-world worlds.

If you have binoculars, take a closer look at the thick lunar crescent. Several prominent lunar seas, visible to the naked eye as dark patches, show up more clearly and have distinctly different outlines even at minimal magnification. Each is a plain of once-molten lava that oozed from cracks in the moon’s crust after major asteroid strikes 3-3.5 billion years ago.
Larger craters also come into view at 10x including the remarkable trio of Theophilus, Cyrillus and Catharina, each of which spans about 60 miles (96 km) across. Even in 3-inch telescope, you’ll see that Theophilus partly overlaps Cyrillus, a clear indicator that the impact that excavated the crater happened after Cyrillus formed.
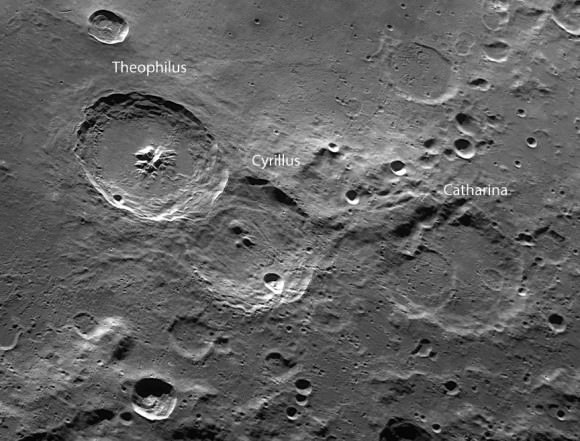

Notice that the rim Theophilus crater is still relatively crisp and fresh compared to the older, more battered outlines of its neighbors. Yet another sign of its relative youth.
Astronomers count craters on moons and planets to arrive at relative ages of their surfaces. Few craters indicate a youthful landscape, while many overlapping ones point to an ancient terrain little changed since the days when asteroids bombarded all the newly forming planets and moons. Once samples of the moon were returned from the Apollo missions and age-dated, scientists could then assign absolute ages to particular landforms. When it comes to planets like Mars, crater counts are combined with estimates of a landscape’s age along with information about the rate of impact cratering over the history of the solar system. Although we have a number of Martian meteorites with well-determined ages, we don’t know from where on Mars they originated.
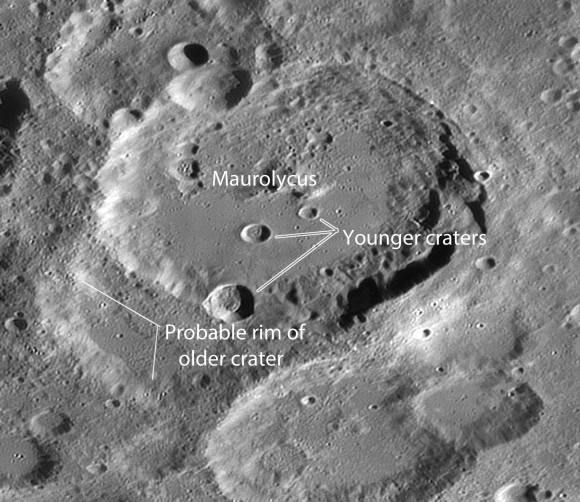

Another crater visible in 10x binoculars tonight is Maurolycus (more-oh-LYE-kus), a great depression 71 miles (114 km) across located in the moon’s southern hemisphere in a region rich with overlapping craters. Low-angled sunlight highlighting the crater’s rim will make it pop near the moon’s terminator, the dividing line between lunar day and night.
Like Theophilus, Maurolycus overlaps a more ancient, unnamed crater best seen in a small telescope. Notice that Maurolycus is no spring chicken either; its floor bears the scares of more recent impacts.
Putting it all into context, despite their varying relative ages, most of the moon’s craters are ancient, punched out by asteroid and comet bombardment more than 3.8 billion years ago. To look at the moon is to see a fossil record of a time when the solar system was a terrifyingly untidy place. Asteroids beat down incessantly on the young planets and moons.
Despite the occasional asteroid scare and meteorite fall, we live in relative peace now. Think what early life had to endure to survive to the present. Deep inside, our DNA still connects us to the terror of that time.