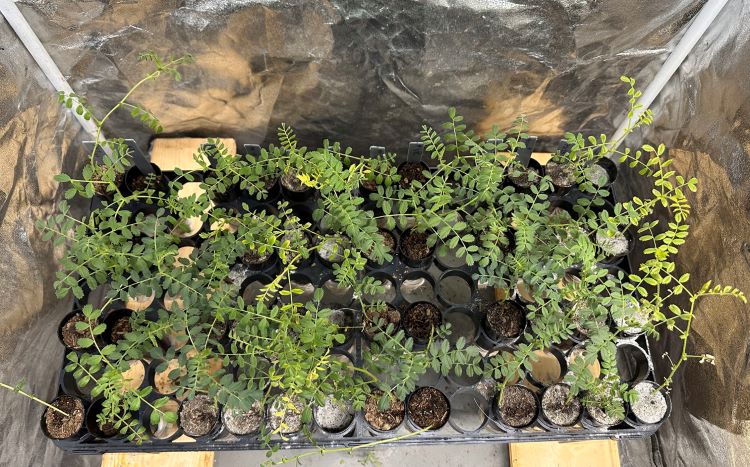
A recent preprint investigates how chickpeas have been successfully grown in lunar regolith simulants (LRS), marking the first time such a guideline has been established not only for chickpeas, but also for growing food for long-term human space missions. This study was conducted by researchers from Texas A&M University and Brown University and holds the potential to develop more efficient methods in growing foods using extraterrestrial resources, specifically with NASA’s Artemis program slated to return humans to the lunar surface in the next few years.
Continue reading “Chickpeas Grown in Lunar Regolith Are Stressed but Reach Maturity”Chickpeas Grown in Lunar Regolith Are Stressed but Reach Maturity