[/caption]
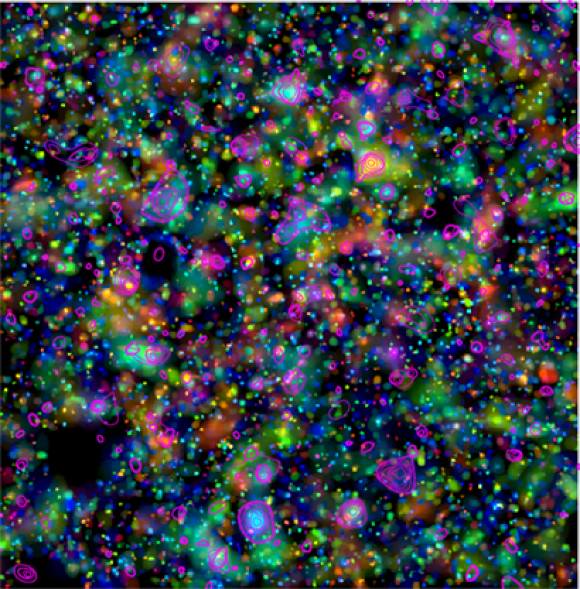
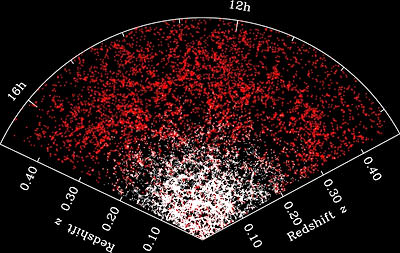
Need more evidence that the expansion of the Universe is accelerating? Just look to the Hubble Space Telescope. An international team of astronomers has indeed confirmed that the expansion of the universe is accelerating. The team, led by Tim Schrabback of the Leiden Observatory, conducted an intensive study of over 446,000 galaxies within the COSMOS (Cosmological Evolution Survey) field, the result of the largest survey ever conducted with Hubble. In making the COSMOS survey, Hubble photographed 575 slightly overlapping views of the same part of the Universe using the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) onboard the orbiting telescope. It took nearly 1,000 hours of observations.
In addition to the Hubble data, researchers used redshift data from ground-based telescopes to assign distances to 194,000 of the galaxies surveyed (out to a redshift of 5). “The sheer number of galaxies included in this type of analysis is unprecedented, but more important is the wealth of information we could obtain about the invisible structures in the Universe from this exceptional dataset,” said co-author Patrick Simon from Edinburgh University.
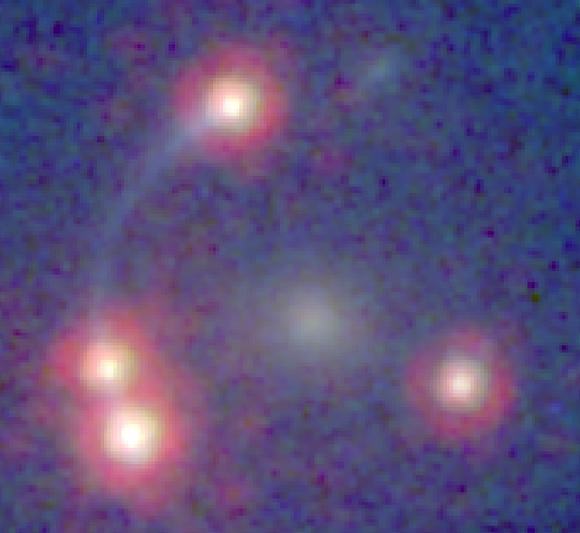
In particular, the astronomers could “weigh” the large-scale matter distribution in space over large distances. To do this, they made use of the fact that this information is encoded in the distorted shapes of distant galaxies, a phenomenon referred to as weak gravitational lensing. Using complex algorithms, the team led by Schrabback has improved the standard method and obtained galaxy shape measurements to an unprecedented precision. The results of the study will be published in an upcoming issue of Astronomy and Astrophysics.
The meticulousness and scale of this study enables an independent confirmation that the expansion of the Universe is accelerated by an additional, mysterious component named dark energy. A handful of other such independent confirmations exist. Scientists need to know how the formation of clumps of matter evolved in the history of the Universe to determine how the gravitational force, which holds matter together, and dark energy, which pulls it apart by accelerating the expansion of the Universe, have affected them. “Dark energy affects our measurements for two reasons. First, when it is present, galaxy clusters grow more slowly, and secondly, it changes the way the Universe expands, leading to more distant — and more efficiently lensed — galaxies. Our analysis is sensitive to both effects,” says co-author Benjamin Joachimi from the University of Bonn. “Our study also provides an additional confirmation for Einstein’s theory of general relativity, which predicts how the lensing signal depends on redshift,” adds co-investigator Martin Kilbinger from the Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris and the Excellence Cluster Universe.
The large number of galaxies included in this study, along with information on their redshifts is leading to a clearer map of how, exactly, part of the Universe is laid out; it helps us see its galactic inhabitants and how they are distributed. “With more accurate information about the distances to the galaxies, we can measure the distribution of the matter between them and us more accurately,” notes co-investigator Jan Hartlap from the University of Bonn. “Before, most of the studies were done in 2D, like taking a chest X-ray. Our study is more like a 3D reconstruction of the skeleton from a CT scan. On top of that, we are able to watch the skeleton of dark matter mature from the Universe’s youth to the present,” comments William High from Harvard University, another co-author.
The astronomers specifically chose the COSMOS survey because it is thought to be a representative sample of the Universe. With thorough studies such as the one led by Schrabback, astronomers will one day be able to apply their technique to wider areas of the sky, forming a clearer picture of what is truly out there.
Source: EurekAlert
Paper: Schrabback et al., ‘Evidence for the accelerated expansion of the Universe from weak lensing tomography with COSMOS’, Astronomy and Astrophysics, March 2010,