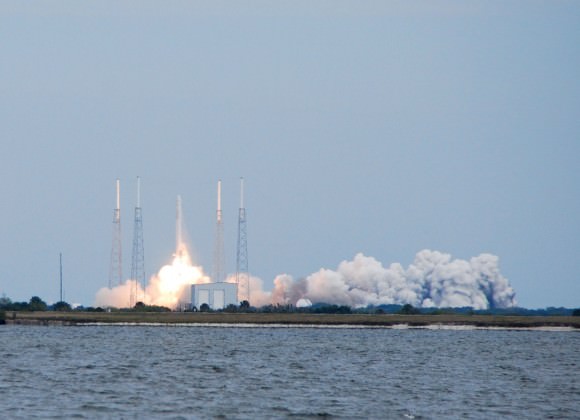
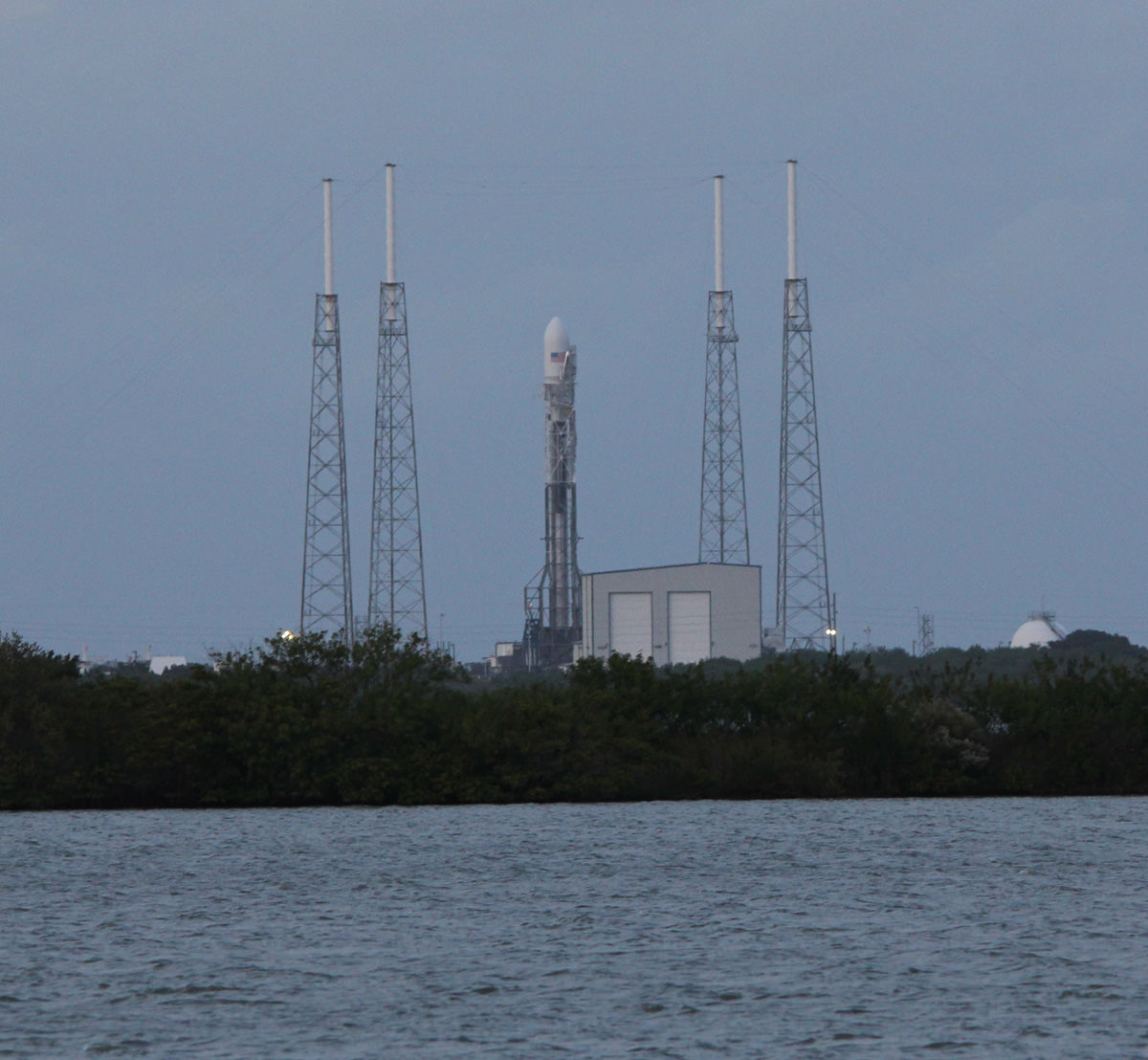
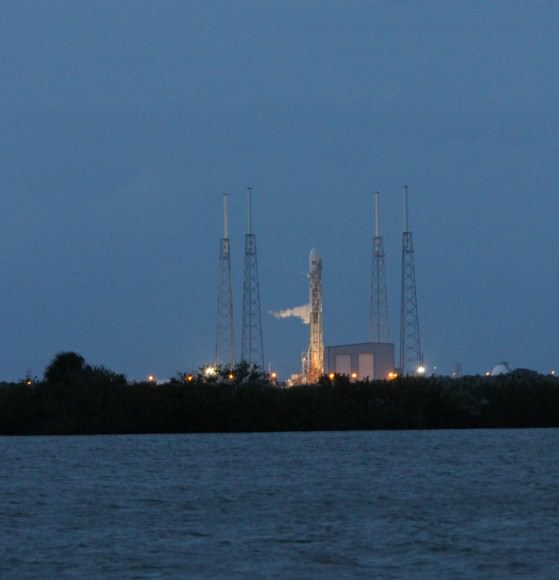
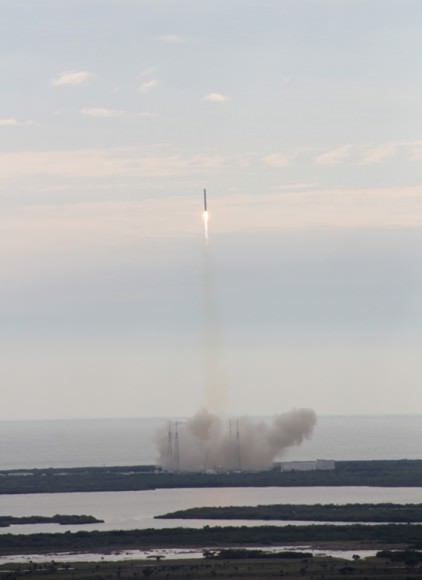
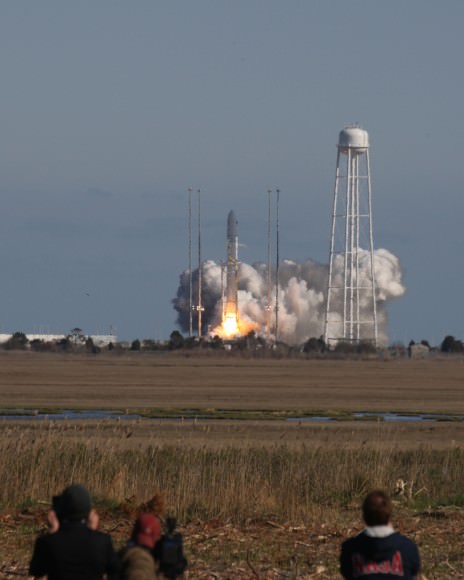
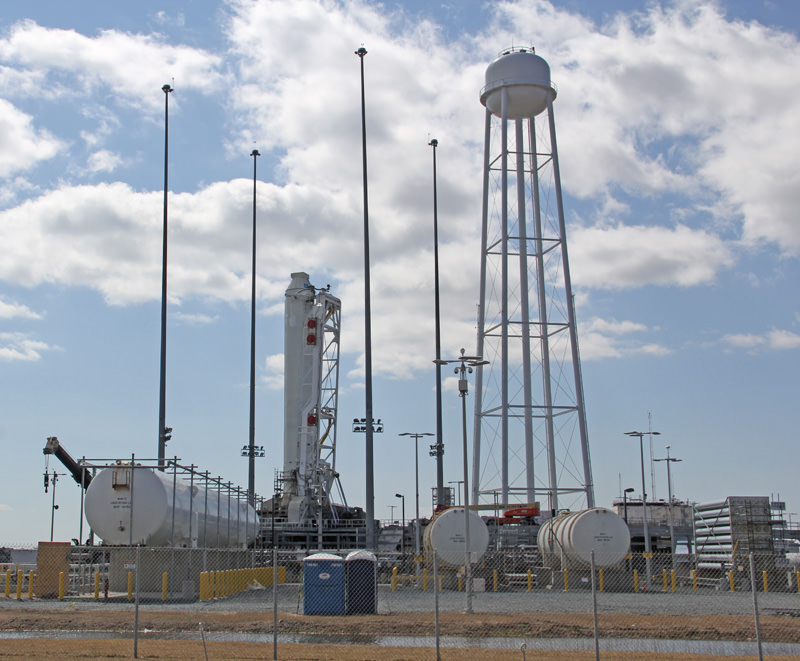
Seaside panoramic view of an Antares rocket and Cygnus cargo spacecraft built by Orbital Sciences at Launch Pad 0A at NASA Wallops Flight Facility on the Virginia Eastern Shore. Blastoff for the ISS is slated for Jan. 7, 2014 at 1:55 p.m. EDT. Credit: Ken Kremer – kenkremer.com
UPDATE – Frigid Weather Delays Antares Launch to Jan. 8[/caption]
The status quo in space flight operations is no more.
Private American rockets are leading the charge of overdue change into the innovative ‘Commercial Space Race’ by blasting 2014 open with a pair of ‘Big Bang fireworks’ just a day apart on Jan. 6 and Jan. 7.
A dynamic duo of US aerospace firms – SpaceX and Orbital Sciences – are each poised to launch their own recently developed private boosters in the first week of the new year and aiming to dramatically cut costs.
And to top that off, the rockets are thundering aloft from two different spaceports located some 800 miles apart along the US East coast – weather permitting of course given the monster snow storm and frigid arctic air – akin to Mars – bearing down at this very moment on the big populations centers of the Atlantic coast region.
UPDATE ALERT – Antares Launch just postponed to Wed, Jan 8 at 1:32 p.m.due to extremely cold weather forecast. Back up day is Jan. 9
Both companies are revolutionizing access to space for both government entities as well as commercial companies doing lucrative business in space.
The implications of vastly reducing expenses for space travel and space commerce are far reaching and imperative – especially in the face of static and declining budgets mandated by politicians worldwide.
Except for China, which just landed its first rover on the Moon, is investing mightily in space and science and reaping strong economic growth.
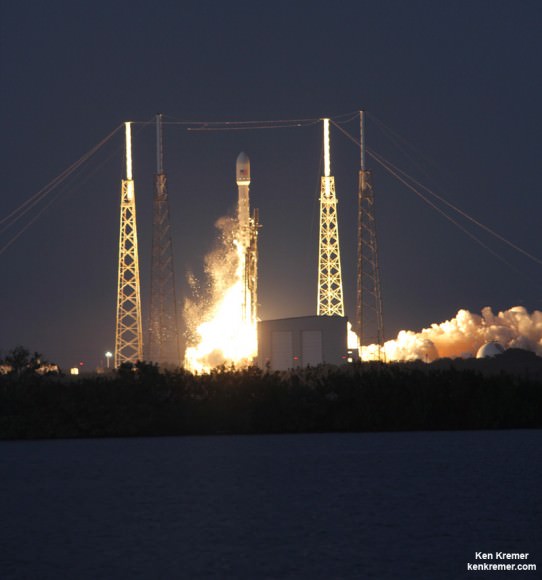

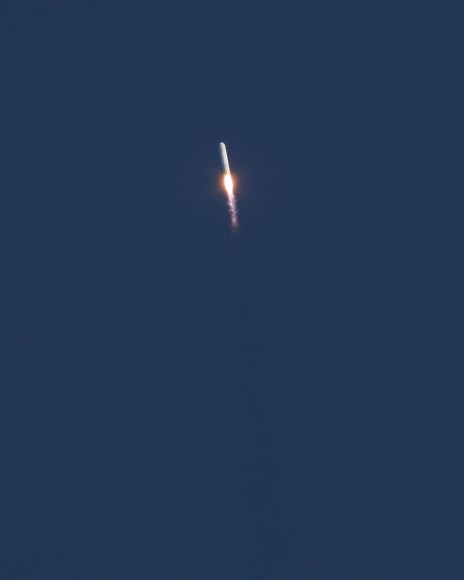
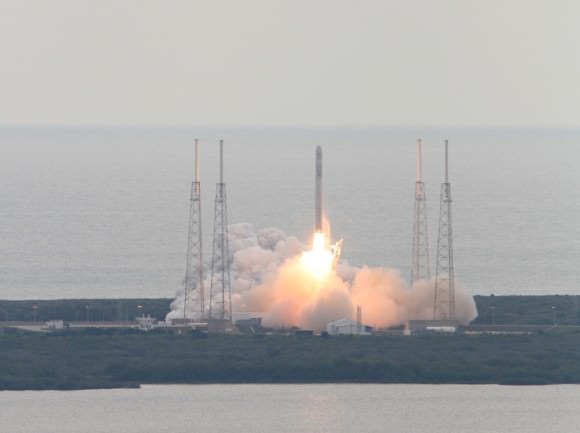
SpaceX is first on deck with their next generation Falcon 9 rocket poised to soar on Monday, Jan. 6, with a highly valuable international payload – the Thiacom-6 commercial broadcasting satellite.
Note: This launch has just been postponed from Jan. 3 according to a brief statement I received from the USAF 45th Space Wing. Apparently due to concerns with the rocket – better safe than sorry.
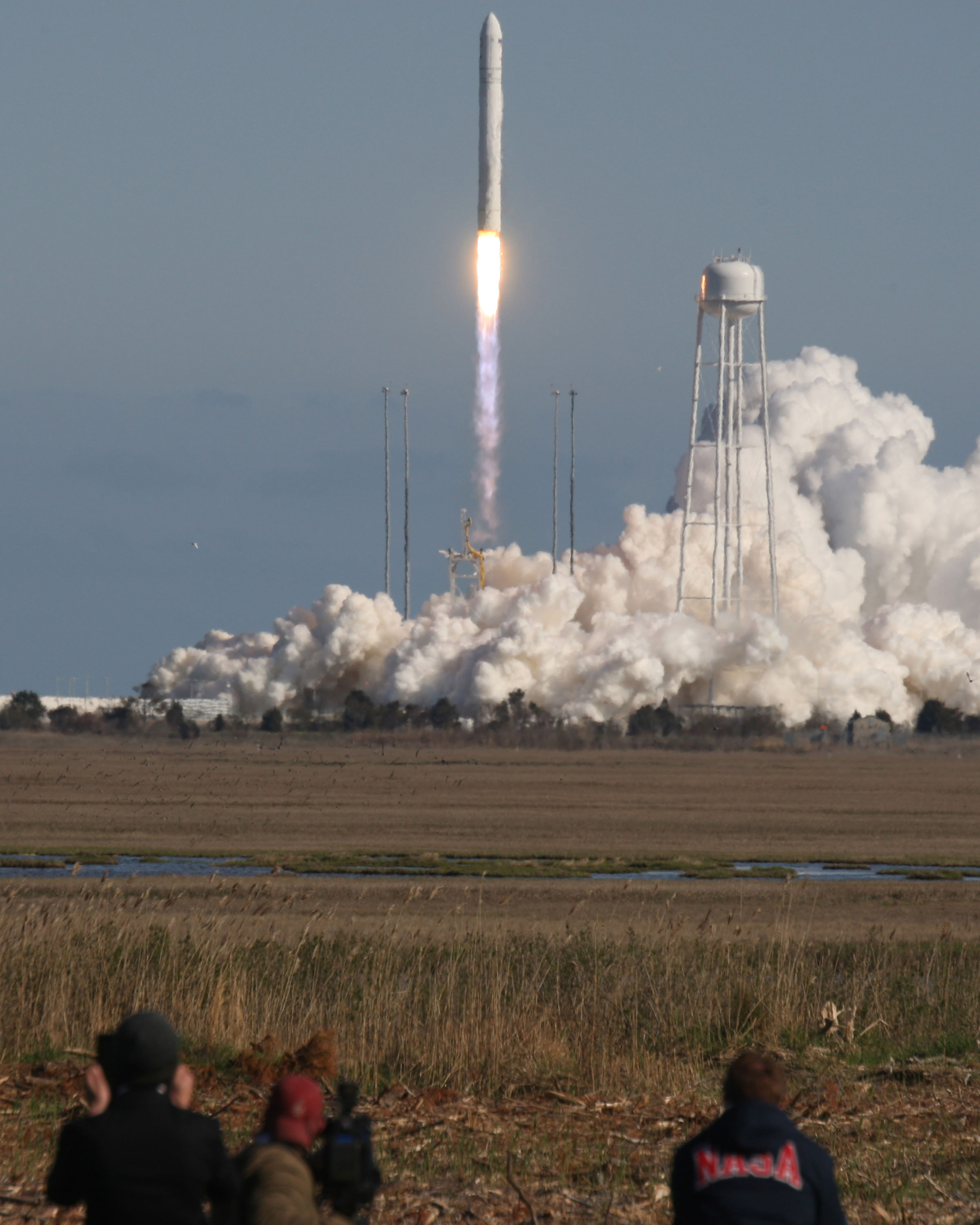
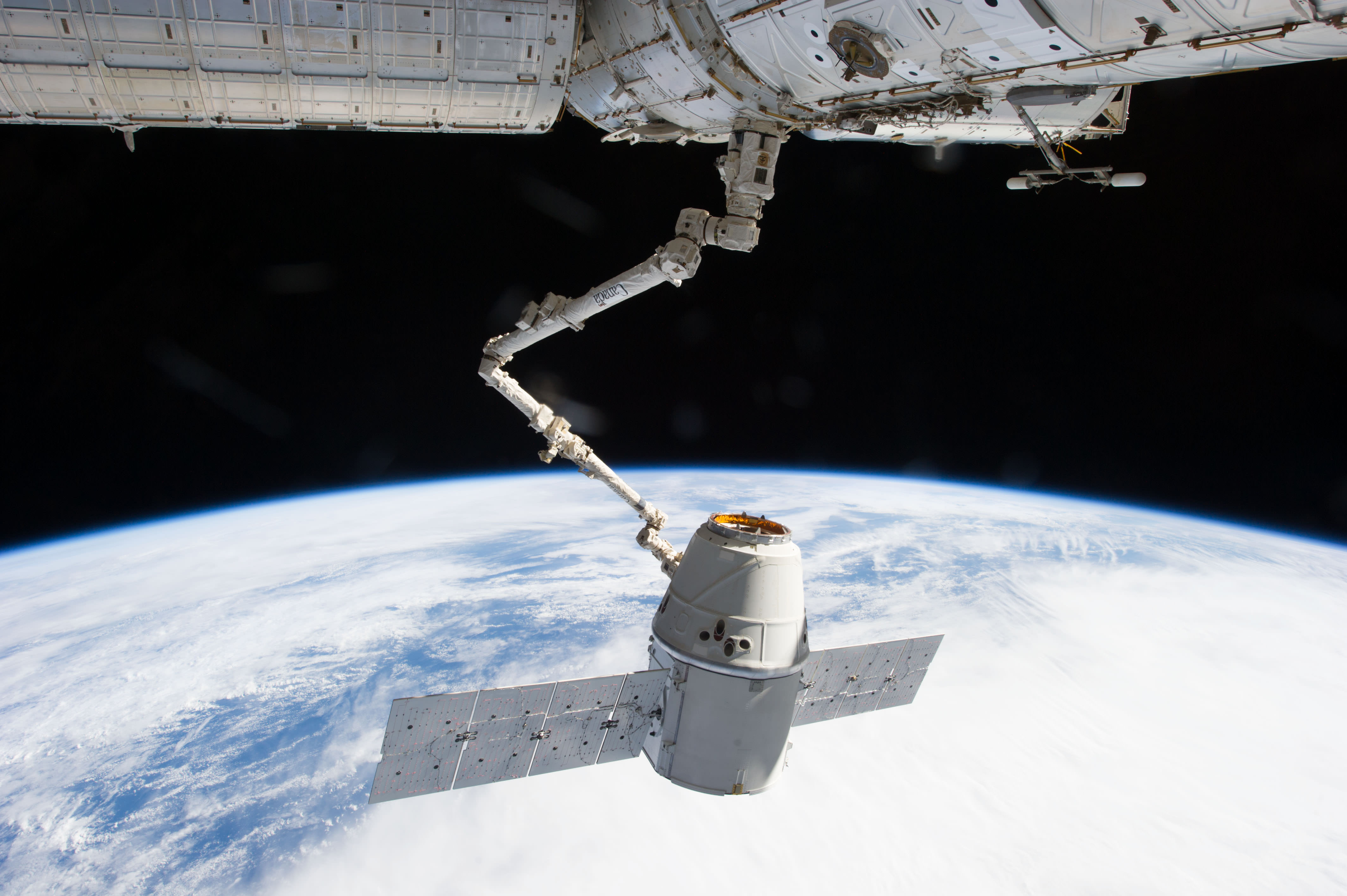
Orbital Sciences follows up quickly on Tuesday, Jan. 7, with their two stage Antares rocket carrying the firm’s own Cygnus cargo vessel on its first operational commercial resupply mission for NASA – that’s bound for the International Space Station (ISS).
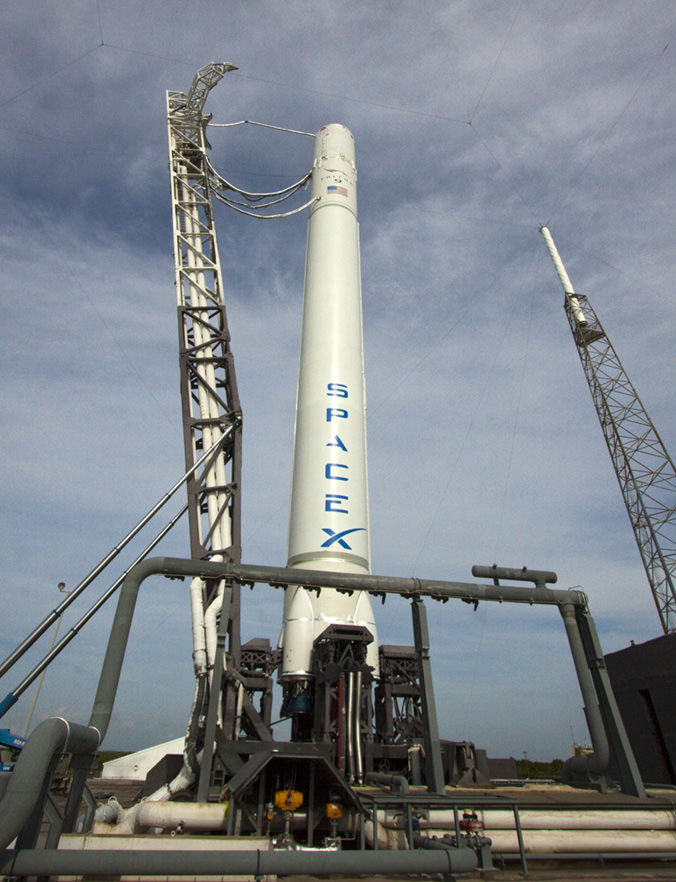
The upgraded SpaceX Falcon 9 v1.1 two stage rocket is slated to launch from complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, likely at dusk.
The original Jan. 3 Falcon 9 evening time launch had been scheduled for 5:50 p.m. Thaicom-6 will be placed into an elliptical supersynchronous transfer orbit.
The commercial space race sometimes makes for strange bedfellows. The Thaicom-6 satellite was built by Orbital Sciences.
This marks only the 2nd launch of the newly upgraded Falcon 9 from Florida. Read my eyewitness reports about the thunderous maiden liftoff barely a month ago on Dec. 3, 2013 with the SES-8 commercial telecom satellite – starting here.
The new Falcon 9 is the key to achieving SpaceX’s future launch manifest of some 50 payloads worth billions of dollars.
The next gen Falcon 9 will also launch the human rated SpaceX Dragon to the ISS. But first the Dragon and Falcon 9 must successfully achieve a pair of abort tests planned for 2014. Read my new article and discussion with SpaceX CEO Elon Musk – here.
The Jan. 7 Antares liftoff is currently scheduled for 1:55 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 0A at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) at NASA Wallops Island, Virginia.

The Antares launch comes on the heels of the completely successful demonstration flight to the space station by Orbital Sciences in September 2013.
This flight was originally scheduled for mid-December 2013 in prime time but was postponed due to the urgent repairs required to get the ISS cooling system back in full operation.
And although it’s now moved to daylight by reason of orbital mechanics, the liftoff could still easily be visible to millions of residents along a wide swath of the US East Coast spanning from North Carolina to New York City – weather permitting.
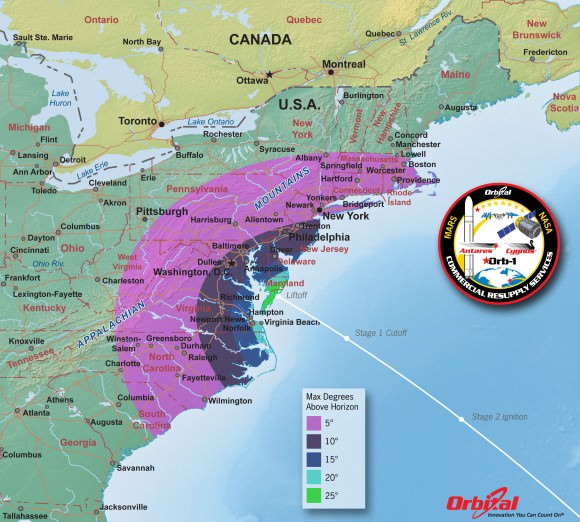
The Antares daytime launch will be visible to millions of spectators across a wide area of the Eastern US -weather permitting. This map shows the maximum elevation (degrees above the horizon) that the Antares rocket will reach during the Jan 7, 2014 launch depending on your location along the US east coast. Credit: Orbital Sciences
I’ll be covering the Antares launch, dubbed Orb-1, from on site at NASA Wallops – watch for my continuing reports.
The Cygnus logistics vessel will carry a total of 2,780 pounds of supplies to the station, including vital science experiments to expand the research capability of the Expedition 38 crew members aboard the orbiting laboratory, crew provisions, spare parts and experiment hardware, says NASA.
Also packed aboard the Antares/Cygnus flight are a batch of student experiments involving life sciences topics ranging from amoeba reproduction to calcium in the bones to salamanders.
“The 23 experiments flying next week [on Antares/Cygnus] are the culmination of 8,700 students engaged in real experiment design, and 1,800 proposals received by student teams,” Dr. Jeff Goldstein told Universe Today. Goldstein is the Center Director for the National Center for Earth and Space Science Education (NCESSE),which is sponsoring and organizing the student experiments.
This rocket volley is but the opening salvo of shots heard reverberating round the world that will surely “rock” the space industry to its core by cutting the steep cost of access to space.
“This is really rocking the industry. Everybody has to look out,” said Martin Halliwell, SES chief technical officer during a recent media briefing with Elon Musk, including Universe Today.
Both the SpaceX Falcon 9/Dragon and Orbital Sciences Antares/Cygnus vehicles were developed from the start with seed money from NASA in a public-private partnership.
The goal was to restore America’s cargo and crew capabilities to low Earth orbit and the ISS that was totally lost following the forced retirement of NASA’s Space Shuttles.
After a slow start, both Orbital Sciences and SpaceX have succeeded in bringing their new rockets and delivery vehicles safely on line.
SpaceX next Dragon cargo launch to the ISS is currently scheduled for Feb. 22, said SpaceX spokeswoman Emily Shanklin to Universe Today.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, commercial space, Chang’e-3, LADEE, Mars and more news.
…………….
Learn more about SpaceX, Orbital Sciences Antares Jan. 8 launch, Curiosity, Orion, MAVEN, MOM, Mars rovers and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations
Jan 7-9: “Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launch from Virginia on Jan. 8” & “Space mission updates”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, evening