[/caption]
The term ‘yardangs’ almost sounds like a fictional word from a Barsoomian tale of creatures living on Mars. However, this is a real word, a geologists’ term for narrow, wind-eroded ridges. These are common land features in the desert regions of Earth, eolian features created by wind and dust. With Mars’ dusty soil and frequent winds, these landforms are common on the Red Planet, too. The abrasive dust is blown by wind, impacting on the bedrock, slowly removing parts of the surface, like a sand-blaster. If the winds blow in the same direction for a long enough period, ‘wind-lanes’ are made. These features are called yardangs.
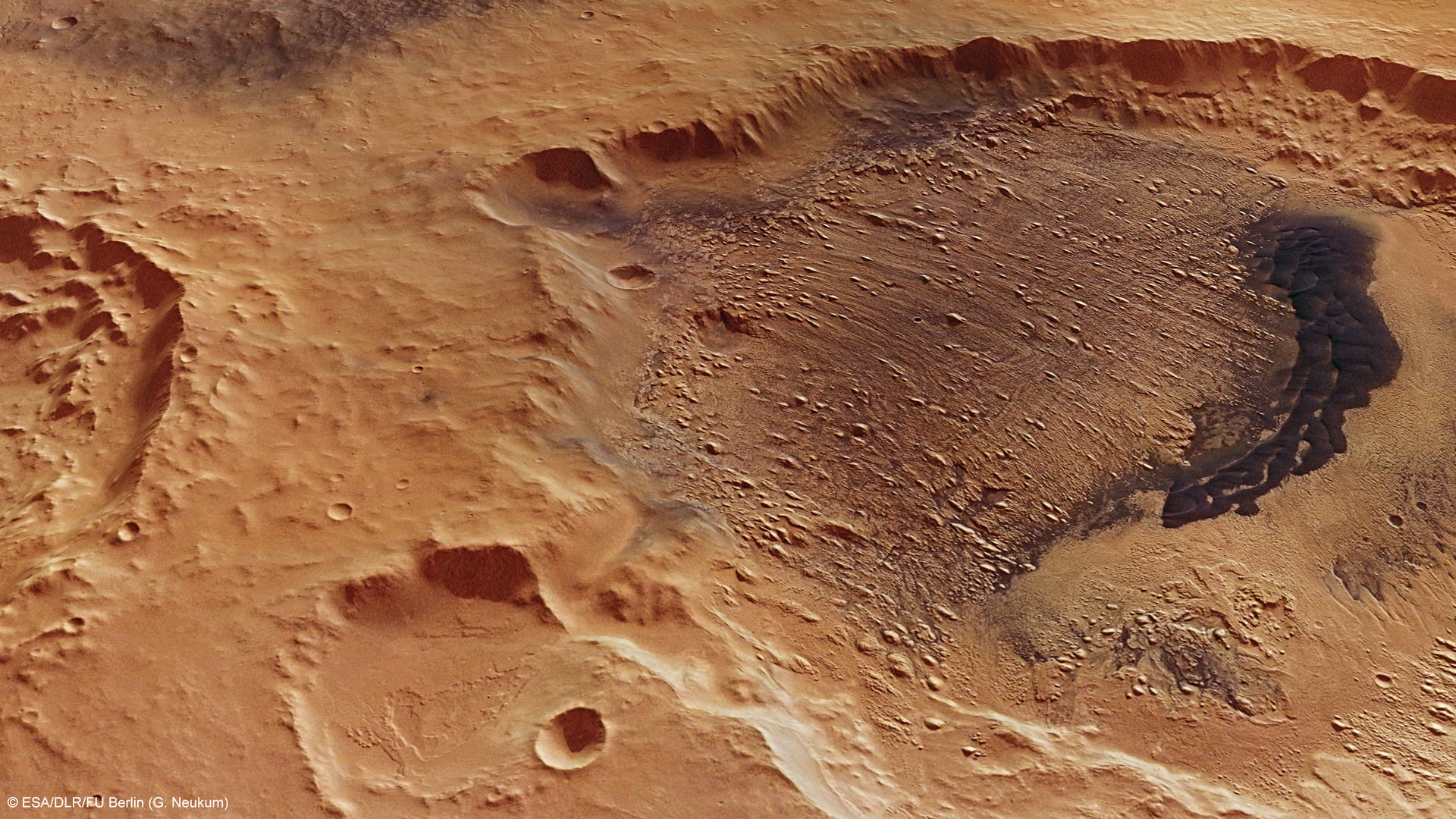
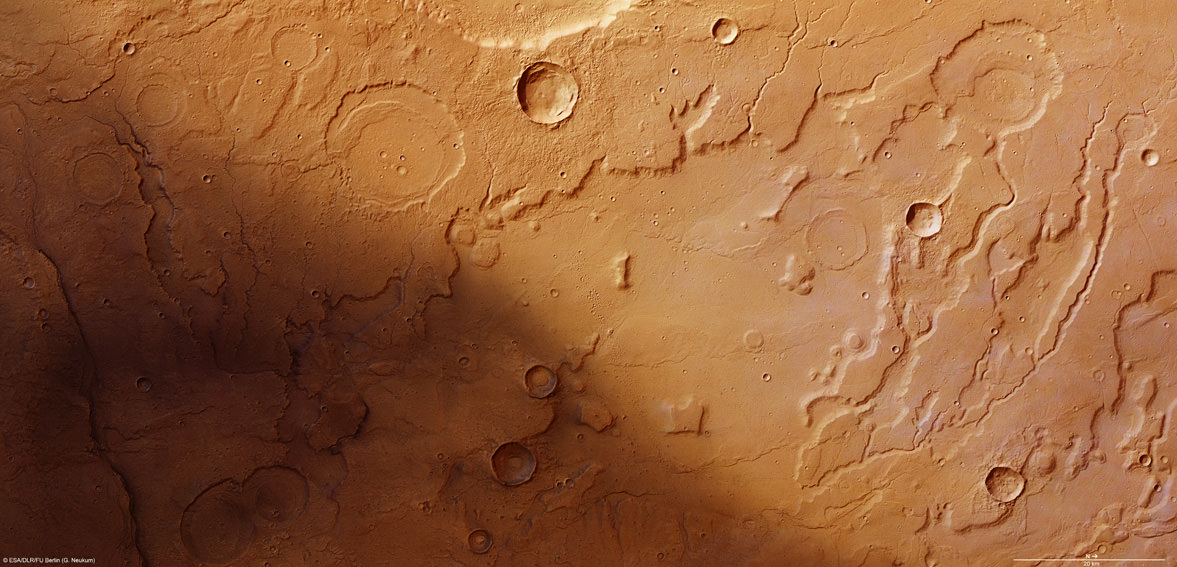
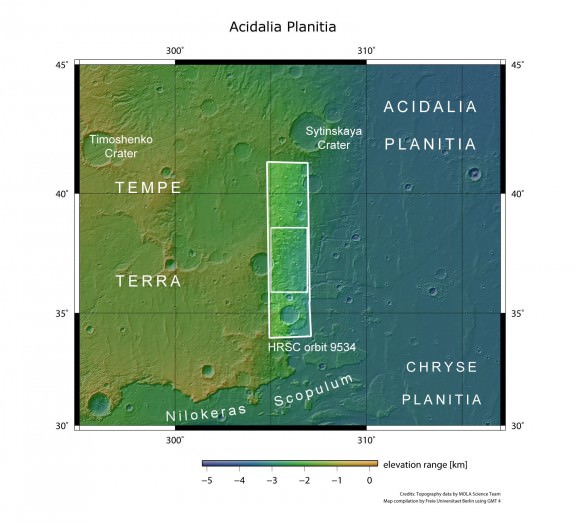
These latest images from the Mars Express mission show yardangs on the floor of Danielson crater, and scientists think this crater may provide evidence that the planet underwent significant periodic fluctuations in its climate due to changes in its rotation axis.
On June 19, 2011, Mars Express took a look at the region pictured here — Arabia Terra region of Mars — imaging Danielson and the smaller Kalocsa crater with its high-resolution stereo camera.
In the case of Danielson crater, scientists think the sediments were cemented in by water, possibly from an ancient deep groundwater reservoir, before being eroded by the wind.

The orientation of the yardangs leads scientists to theorize that strong north–northeasterly winds (from the lower right in the image) both deposited the original sediments and then caused their subsequent erosion in a later drier period of Martian history.
A 30 km-long field of darker dunes can be seen bisecting the yardangs and is thought to have formed at a later epoch.
Some scientists believe that this indicates periodic fluctuations in the climate of Mars, triggered by regular changes in the planet’s axis of rotation. The different layers would have been laid down during different epochs.
But Kalocsa crater shows a completely different topography, with no layered sediments. This is thought to be due to the higher altitude of its floor, with the crater not tapping in to the suspected underlying ancient water reservoir.
However, another hypothesis is that this crater is younger than its neighbor, created when water was not present anymore.
Dang.
Source: ESA