Venus’ terminator – the transitional region between day and night — may fuel an unusually cold region in the atmosphere. Credit: ESA/MPS, Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany
The hottest planet in the Solar System has a surprisingly cold region high in the planet’s atmosphere, according to new findings by the Venus Express spacecraft. While surface temperatures on this hot and hostile planet tops out at 735 Kelvin, or 462 degrees Celsius, ESA scientists say that a layer in the atmosphere about 125 km up has temperatures of around –175 degrees C, and may be cold enough for carbon dioxide to freeze out as ice or snow.
This means this curious cold layer is much colder than any part of Earth’s atmosphere even though Venus is known for its dense, blistering atmosphere and is much closer to the Sun. Additionally, the cold layer appears to be affected by the transitioning between day and night on Venus.
Scientists made the discovery by watching as light from the Sun filtered through the atmosphere to reveal the concentration of carbon dioxide gas molecules at various altitudes along the terminator – the dividing line between the day and night sides of the planet.
Then they combined data about the carbon dioxide concentration with data on atmospheric pressure at each height. The scientists could then calculate the corresponding temperatures.
“Since the temperature at some heights dips below the freezing temperature of carbon dioxide, we suspect that carbon dioxide ice might form there,” said Arnaud Mahieux of the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy and lead author of the paper reporting the results in the Journal of Geophysical Research.
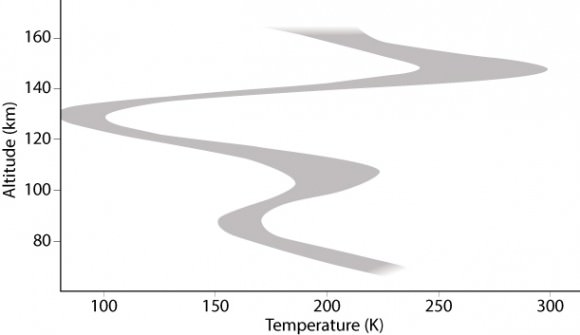
The temperature profile along the terminator for altitudes of 70–160 km above the surface of Venus. Credit: ESA/AOES–A.V. Bernus
Source: ESA
Clouds of small carbon dioxide ice or snow particles should be very reflective, perhaps leading to brighter than normal sunlight layers in the atmosphere.
“However, although Venus Express indeed occasionally observes very bright regions in the Venusian atmosphere that could be explained by ice, they could also be caused by other atmospheric disturbances, so we need to be cautious,” said Mahieux.
The study also found that the cold layer at the terminator is sandwiched between two comparatively warmer layers.
“The temperature profiles on the hot dayside and cool night side at altitudes above 120 km are extremely different, so at the terminator we are in a regime of transition with effects coming from both sides.
“The night side may be playing a greater role at one given altitude and the dayside might be playing a larger role at other altitudes.”
Similar temperature profiles along the terminator have been derived from other Venus Express datasets, including measurements taken during the transit of Venus earlier this year.
Models are able to predict the observed profiles, but further confirmation will be provided by examining the role played by other atmospheric species, such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen and oxygen, which are more dominant than carbon dioxide at high altitudes.
“The finding is very new and we still need to think about and understand what the implications will be,” says Håkan Svedhem, ESA’s Venus Express project scientist. “But it is special, as we do not see a similar temperature profile along the terminator in the atmospheres of Earth or Mars, which have different chemical compositions and temperature conditions.”




 Although Lunar Lander will be an unmanned robotic explorer, the mission will be a forerunner to future human exploration of the Moon as well as Mars. Lunar Lander will use advanced technologies for autonomous landing and will be able to determine the best location for touchdown on its own, utilizing lasers to avoid obstacles on the Moon’s surface.
Although Lunar Lander will be an unmanned robotic explorer, the mission will be a forerunner to future human exploration of the Moon as well as Mars. Lunar Lander will use advanced technologies for autonomous landing and will be able to determine the best location for touchdown on its own, utilizing lasers to avoid obstacles on the Moon’s surface.