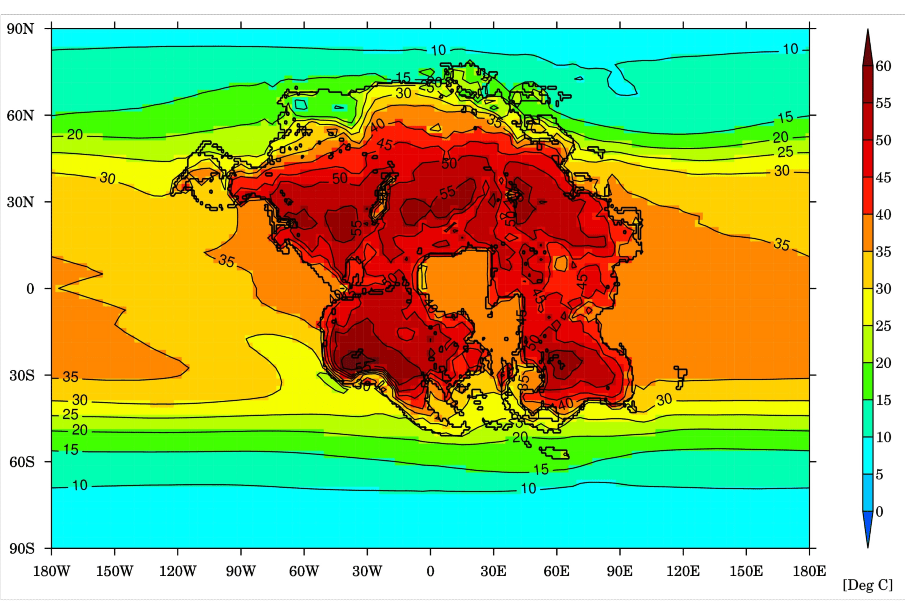
A recent study published in Nature Geoscience uses supercomputer climate models to examine how a supercontinent, dubbed Pangea Ultima (also called Pangea Proxima), that will form 250 million years from now will result in extreme temperatures, making this new supercontinent uninhabitable for life, specifically mammals. This study was conducted by an international team of researchers led by the University of Bristol and holds the potential to help scientists better understand how Earth’s climate could change in the distant future from natural processes, as opposed to climate change.
Continue reading “In 250 Million Years, a Single Supercontinent will Form, Wiping Out Nearly all Mammals”In 250 Million Years, a Single Supercontinent will Form, Wiping Out Nearly all Mammals