[/caption]
When it comes to space, the first thing most people think of is NASA. Or Russia and the European Space Agency, or even more recently, countries like China and Japan. In the public eye, Canada has tended to be a bit farther down on the list. There is the Canadian Space Agency, but it is better known for developing space and satellite technologies, not awe-inspiring launches to the Moon or other planets, which naturally tend to get the most attention.
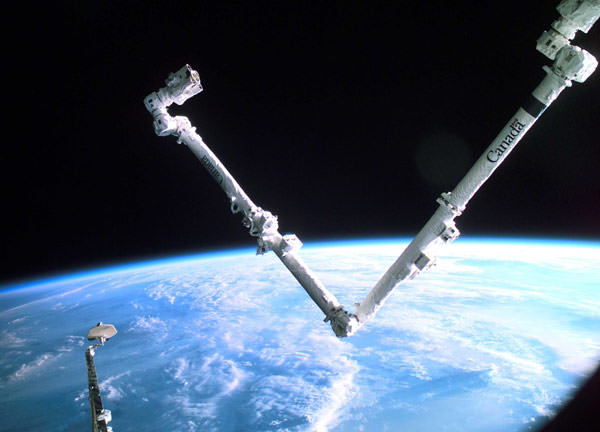
Canada has its own astronauts, too, but they go into orbit on the Space Shuttle or Russian rockets. Canada’s role in space should not, however, be underestimated. It was, for example, the first country to have a domestic communications satellite in geostationary orbit, Anik A1, in 1972. There is also the well-known Canadarm used on the Space Shuttle and Canadarm2 on the International Space Station, as well as the space robot Dextre on the ISS. Canada has also contributed technology to various robotic planetary missions as well.
But even in these times of budget constraints, new ventures are being planned, including a mission to place two video cameras on the International Space Station late next year, via a Russian mission.
The cameras will provide near real-time video broadcasting continuously in high-definition. The cameras are being developed by Urthecast, a Vancouver-based firm, which is investing $10 million in the project.
Like their American counterparts now, the investment and development of space technology is coming increasingly from the private sector instead of the government. In 1996, the Canadian government contributed 32% to domestic space revenue; in 2010, it was only 18% and it is estimated to drop again over the next three years.
Because of smaller budgets, the CSA focuses on assisting with larger missions from other countries instead of developing its own launch vehicles. According to Mark Burbidge, head of industrial policy at the CSA, the Canadian Space Agency doesn’t have the money for such projects. “That got our astronauts up there,” he says, referring to the Canadarm.
Another area that Canada may be able to contribute to is space tourism, a prime example of private companies becoming involved in the space business. Companies like SpaceX, Virgin Galactic and Bigelow Airspace are changing the way that people will go into near-orbit and low-Earth orbit. No dependence solely on government dollars to finance their objectives such as tourist space flights, small orbiting hotels or launching commercial satellites.
At this stage, government funding is still often required, especially for smaller firms, but the future looks promising. Space companies are becoming gradually less reliant on the government for revenue growth. The investment return tends to be primarily a scientific one, according to Dr. Jean de Lafontaine, founder of space services company NGC Aerospace in Quebec, making space tourism more of an ideal option for private companies.
This would seem to be an optimum arrangement, allowing companies to compete in orbital missions and tourism, while government agencies like NASA, ESA, etc. are better able to invest in larger-scale planetary missions and other costly space projects (noting however that some commercial companies also have their eyes on the Moon and Mars).
Canada may not have its own rockets or grandiose space missions, not yet anyway, but it will continue to make important contributions to space exploration. And as a Canadian, I am very pleased about that!