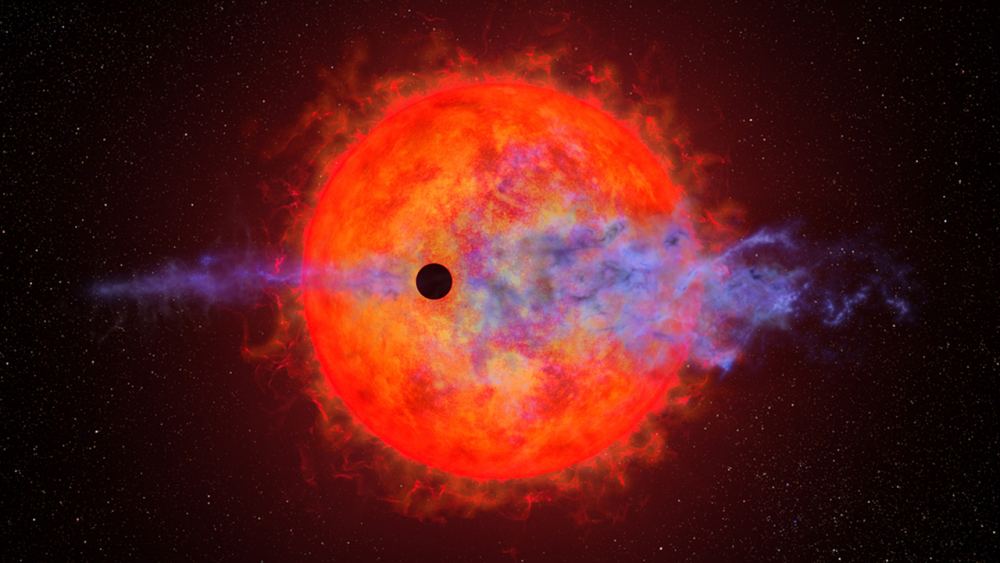
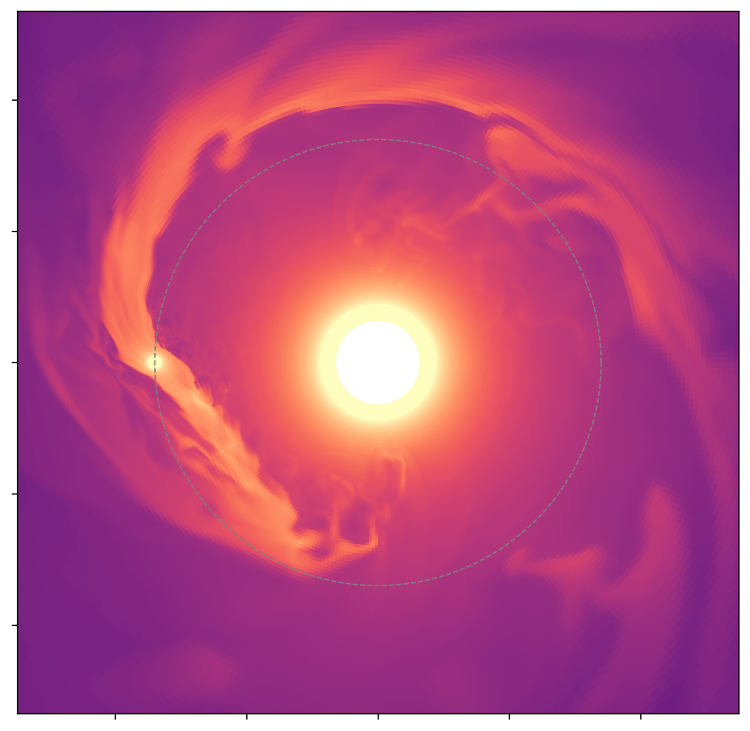
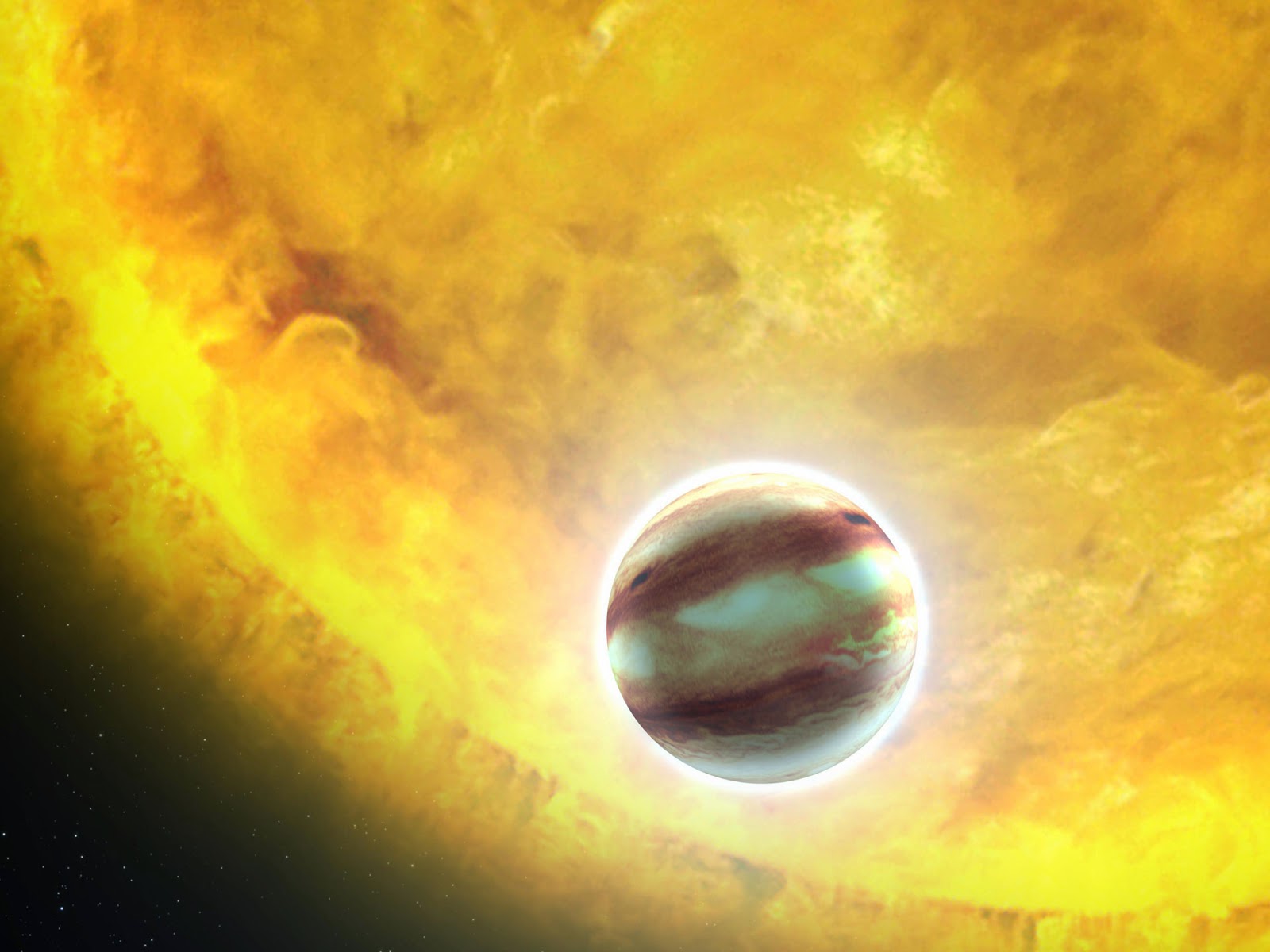
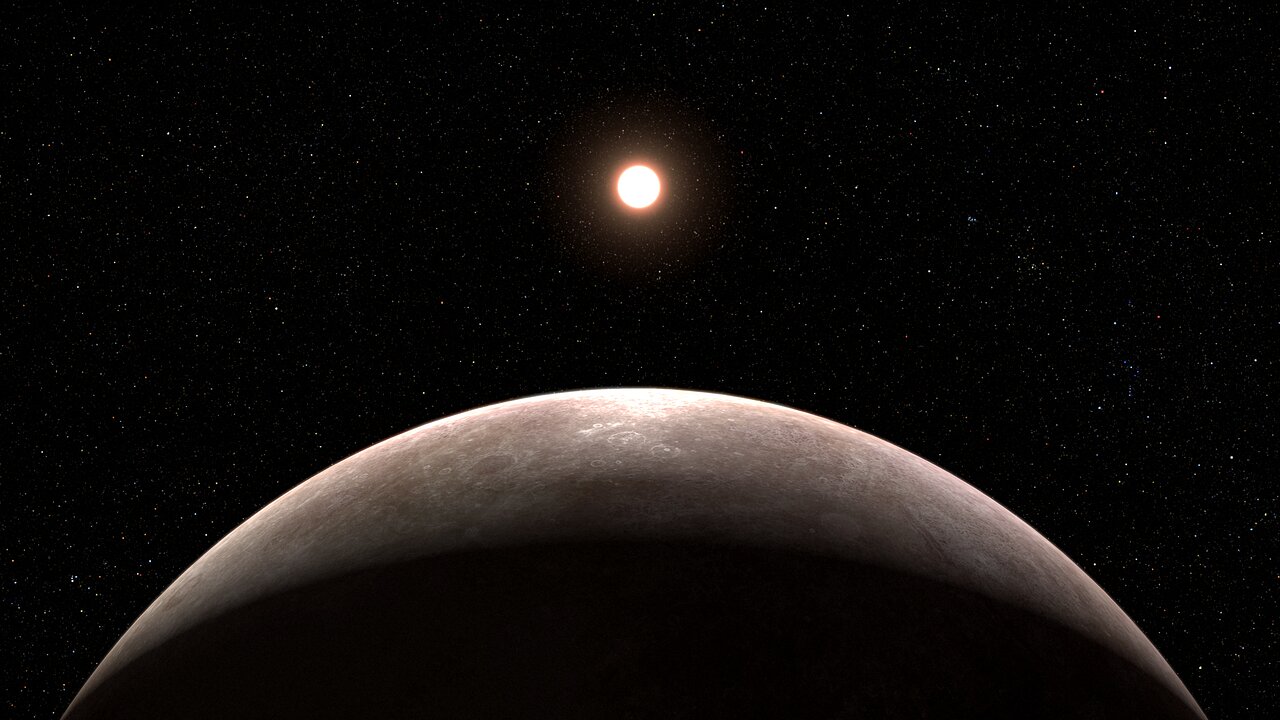
What do you get when a hot young world orbits a wildly unstable young red dwarf? For AU Microsopii b, the answer is: flares from the star tearing away the atmosphere. That catastrophic loss happens in fits and starts, “hiccuping” out its atmosphere at one point and then losing practically none the next.
Continue reading “Astronomers are Watching a Planet Get its Atmosphere Blasted Away into Space”Astronomers are Watching a Planet Get its Atmosphere Blasted Away into Space