When NASA astronaut Mike Hopkins steps into space for the first time this week, he will wear a spacesuit that previously sprung a water leak and forced Italian astronaut Luca Parmitano back to station in July, NASA officials said Wednesday (Dec. 18).
While at first glance this sounds like an extra bit of drama as Hopkins and Rick Mastracchio make contingency spacewalks Dec. 21, 23 and 25 to kickstart a shut-down cooling loop, NASA officials say the suit is ready to go for another trip outside because astronauts (under NASA’s direction) have made a bunch of changes to the unit.
Repurposing spacesuit parts, a new pad will be added to the back of all NASA spacesuit helmets to soak up water, should one leak again. Astronauts also velcroed a pipe into each suit — a sort of snorkel — that in the worst case, would give an astronaut with a water leak an alternate route for drawing in air.
Also, the Expedition 38 crew swapped out a fan pump separator that likely malfunctioned and caused the spacesuit leak. The cause is still under investigation, but NASA believes that a problem in the water chemistry caused contamination that plugged a tiny hole inside the water separation part of the unit. This allowed the water to escape, enter the air loop and get into the helmet.
Finally, there are new procedures in place for the astronauts themselves. They will monitor the helmet pad for fluid. NASA additionally plotted out its spacewalk procedures — which include the use of a Canadian robotic arm on station — to make sure the astronauts are always within reasonable reach of an airlock.

So here’s why the spacewalks are happening: a week ago (Dec. 11), a flow control valve inside of a pump — the pump is located outside of the station — stopped regulating ammonia temperatures inside of an external cooling loop. The loop is required to, as the name implies, cool down space station electronics. The loop got too cold, it shut down automatically, and NASA took science experiments and redundant systems offline to deal with the problem. (The main problem is NASA can’t run a heat exchanger on Node 2, which affects experiments in the U.S. Columbus laboratory and Japanese Experiment Module. No completed research has been lost to date, however.)
After figuring out that it couldn’t control the valve again, NASA shifted its attention to an isolation valve upstream. That valve is only designed to be in two positions — opened or closed — but the hardware vendor said it could be used at spots in between to regulate the ammonia flow. So software engineers created a patch to make this happen, and uploaded it to station.
Throw in another element, however: the station is about to enter what’s called an annual “high beta” period, when orbital dynamics mean the sun will be shining on it for longer periods of time than usual. (Read more technical details here.) When the angle exceeds 60 degrees, for safety reasons NASA suspends all cargo flights to station as well as spacewalks. This year, it will happen between about Dec. 30, 2013 and Jan. 9, 2014.

So if NASA spent time playing with the valve and found out it couldn’t work in the long run, a couple of problems could happen. First, it would be harder to do a spacewalk to fix it.
Also, the agency was weighing whether to allow Orbital Sciences to fly a Cygnus cargo flight this month, and felt that they could run into a problem where the spacecraft was ready to go, but NASA needed more time to fix the problem. So that’s why the spacewalk is happening.
Here’s a diagram of the pump that Mastracchio and Hopkins plan to replace:
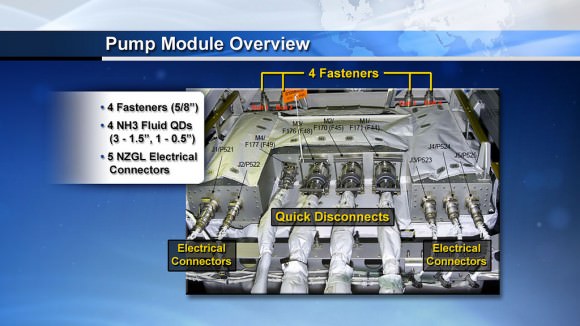
The “nominal” plan is for three spacewalks, but it could range anywhere from two to four depending on how things go. To put things simply, here’s how the spacewalks would go:
- EVA 1: The pump with the broken valve would be disconnected and a spare pump (which is some distance away, but reachable using Canadarm2) would be prepped for the swap.
- EVA 2: The pump with the broken valve would be removed and set aside while the spare pump is partially installed (meaning, only the bolts and electrical connections would be put in.)
- EVA 3: The spare pump’s installation would be finished, and the pump with the broken valve would be stowed more permanently outside. NASA thinks that eventually, it could use that first pump again if astronauts installed a new valve on it, but that isn’t a need for the time being.
Flying Canadarm2 would be Japanese astronaut Koichi Wakata, who has operated every type of robotics currently in orbit. Mastracchio has six spacewalks under his belt already, while Hopkins will be on his first go.
If all goes to plan, NASA will not only swap out the pump, but also preserve the option for the Russians to proceed with a planned Dec. 27 spacewalk that is less urgent. In that case, the cosmonauts plan to swap out experiments, put in a foot restraint and install some cameras.
We’ll cover the spacewalks as they happen. They’re scheduled for Dec. 21, 23 and 25 at 7:10 a.m. EST (12:10 p.m. UTC) and should run about 6.5 hours each. Broadcasts will run live on NASA Television.
By the way, the pump with the problem is just three years old — astronauts had to make three spacewalks in 2010 to install it after a more severe failure. NASA characterized this situation as a more unusual failure and said this is not a symptom of an aging station at all.