In the movie “Avatar”, we could tell at a glance that the alien moon Pandora was teeming with alien life. Here on Earth though, the most abundant life is not the plants and animals that we are familiar with. The most abundant life is simple and microscopic. There are 50 million bacterial organisms in a single gram of soil, and the world wide bacterial biomass exceeds that of all plants and animals. Microbes can grow in extreme environments of temperature, salinity, acidity, radiation, and pressure. The most likely form in which we will encounter life elsewhere in our solar system is microbial.
Astrobiologists need strategies for inferring the presence of alien microbial life or its fossilized remains. They need strategies for inferring the presence of alien life on the distant planets of other stars, which are too far away to explore with spacecraft in the foreseeable future. To do these things, they long for a definition of life, that would make it possible to reliably distinguish life from non-life.
Unfortunately, as we saw in the first installment of this series, despite enormous growth in our knowledge of living things, philosophers and scientists have been unable to produce such a definition. Astrobiologists get by as best they can with definitions that are partial, and that have exceptions. Their search is geared to the features of life on Earth, the only life we currently know.
In the first installment, we saw how the composition of terrestrial life influences the search for extraterrestrial life. Astrobiologists search for environments that once contained or currently contain liquid water, and that contain complex molecules based on carbon. Many scientists, however, view the essential features of life as having to do with its capacities instead of its composition.
In 1994, a NASA committee adopted a definition of life as a “self-sustaining chemical system capable of Darwinian evolution”, based on a suggestion by Carl Sagan. This definition contains two features, metabolism and evolution, that are typically mentioned in definitions of life.
Metabolism is the set of chemical processes by which living things actively use energy to maintain themselves, grow, and develop. According to the second law of thermodynamics, a system that doesn’t interact with its external environment will become more disorganized and uniform with time. Living things build and maintain their improbable, highly organized state because they harness sources of energy in their external environment to power their metabolism.
Plants and some bacteria use the energy of sunlight to manufacture larger organic molecules out of simpler subunits. These molecules store chemical energy that can later be extracted by other chemical reactions to power their metabolism. Animals and some bacteria consume plants or other animals as food. They break down complex organic molecules in their food into simpler ones, to extract their stored chemical energy. Some bacteria can use the energy contained in chemicals derived from non-living sources in the process of chemosynthesis.
In a 2014 article in Astrobiology, Lucas John Mix, a Harvard evolutionary biologist, referred to the metabolic definition of life as Haldane Life after the pioneering physiologist J. B. S. Haldane. The Haldane life definition has its problems. Tornadoes and vorticies like Jupiter’s Great Red Spot use environmental energy to sustain their orderly structure, but aren’t alive. Fire uses energy from its environment to sustain itself and grow, but isn’t alive either.
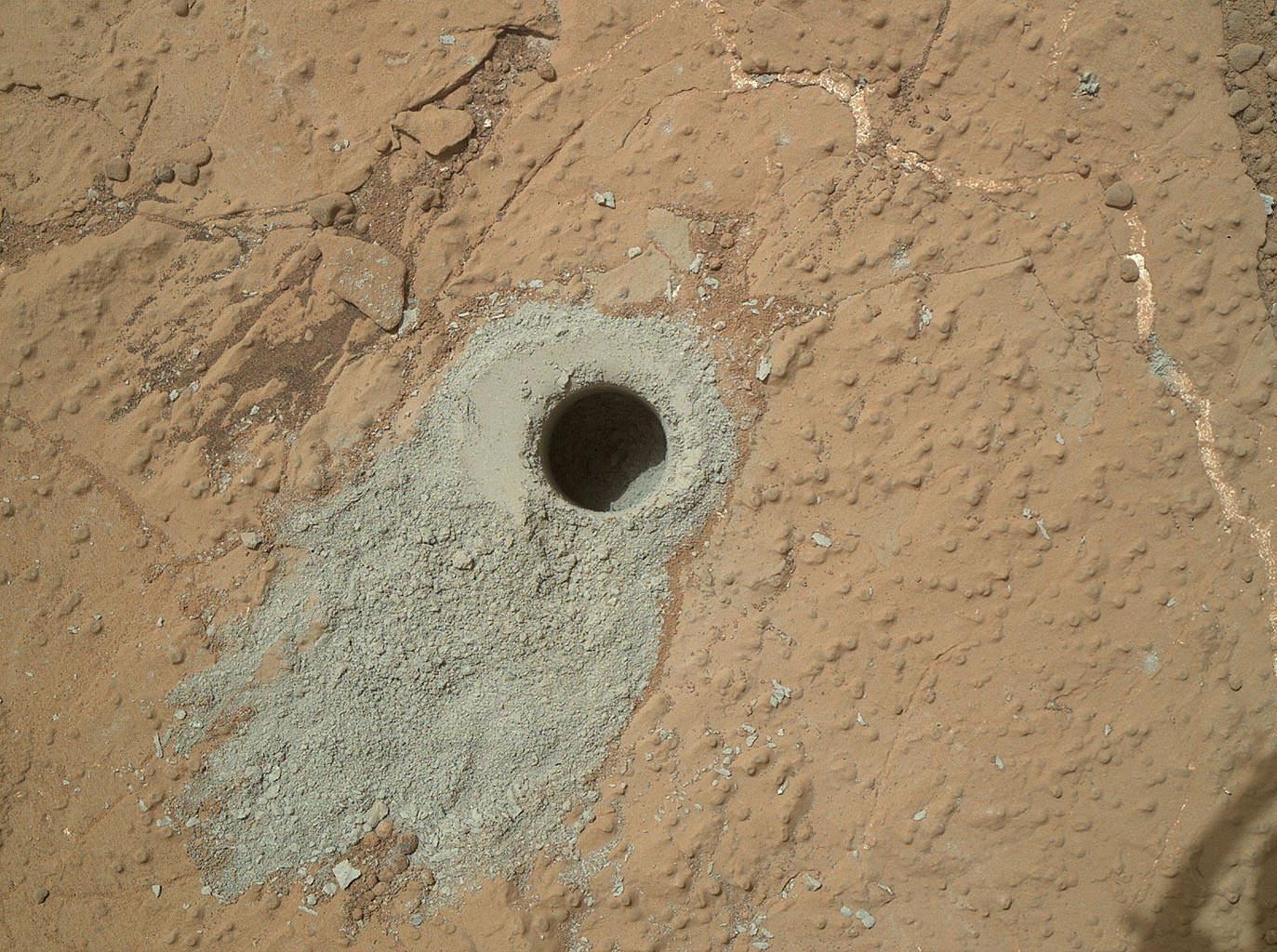
Despite its shortcomings, astrobiologists have used Haldane definition to devise experiments. The Viking Mars landers made the only attempt so far to directly test for extraterrestrial life, by detecting the supposed metabolic activities of Martian microbes. They assumed that Martian metabolism is chemically similar to its terrestrial counterpart.
One experiment sought to detect the metabolic breakdown of nutrients into simpler molecules to extract their energy. A second aimed to detect oxygen as a waste product of photosynthesis. A third tried to show the manufacture of complex organic molecules out of simpler subunits, which also occurs during photosynthesis. All three experiments seemed to give positive results, but many researchers believe that the detailed findings can be explained without biology, by chemical oxidizing agents in the soil.
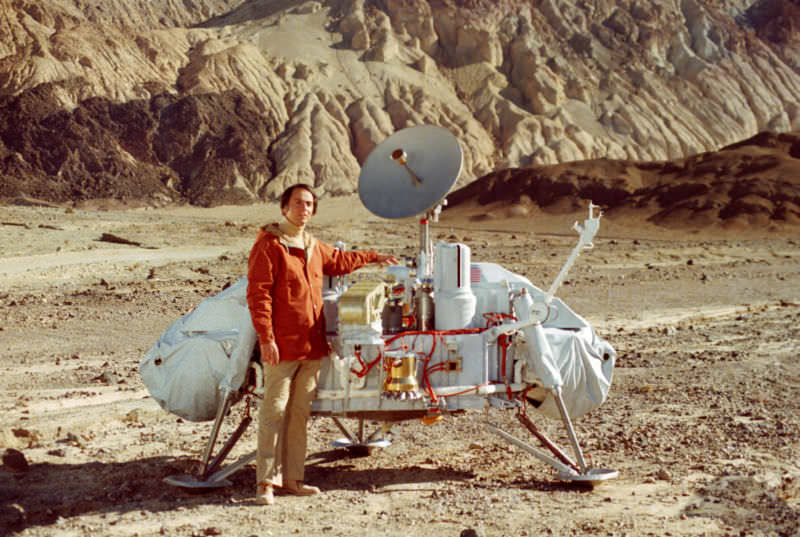

Credits: NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Caltech
Some of the Viking results remain controversial to this day. At the time, many researchers felt that the failure to find organic materials in Martian soil ruled out a biological interpretation of the metabolic results. The more recent finding that Martian soil actually does contain organic molecules that might have been destroyed by perchlorates during the Viking analysis, and that liquid water was once abundant on the surface of Mars lend new plausibility to the claim that Viking may have actually succeeded in detecting life. By themselves, though, the Viking results didn’t prove that life exists on Mars nor rule it out.
The metabolic activities of life may also leave their mark on the composition of planetary atmospheres. In 2003, the European Mars Express spacecraft detected traces of methane in the Martian atmosphere. In December 2014, a team of NASA scientists reported that the Curiosity Mars rover had confirmed this finding by detected atmospheric methane from the Martian surface.
Most of the methane in Earth’s atmosphere is released by living organisms or their remains. Subterranean bacterial ecosystems that use chemosynthesis as a source of energy are common, and they produce methane as a metabolic waste product. Unfortunately, there are also non-biological geochemical processes that can produce methane. So, once more, Martian methane is frustratingly ambiguous as a sign of life.
Extrasolar planets orbiting other stars are far too distant to visit with spacecraft in the foreseeable future. Astrobiologists still hope to use the Haldane definition to search for life on them. With near future space telescopes, astronomers hope to learn the composition of the atmospheres of these planets by analyzing the spectrum of light wavelengths reflected or transmitted by their atmospheres. The James Webb Space Telescope scheduled for launch in 2018, will be the first to be useful in this project. Astrobiologists want to search for atmospheric biomarkers; gases that are metabolic waste products of living organisms.
Once more, this quest is guided by the only example of a life-bearing planet we currently have; Earth. About 21% of our home planet’s atmosphere is oxygen. This is surprising because oxygen is a highly reactive gas that tends to enter into chemical combinations with other substances. Free oxygen should quickly vanish from our air. It remains present because the loss is constantly being replaced by plants and bacteria that release it as a metabolic waste product of photosynthesis.
Traces of methane are present in Earth’s atmosphere because of chemosynthetic bacteria. Since methane and oxygen react with one another, neither would stay around for long unless living organisms were constantly replenishing the supply. Earth’s atmosphere also contains traces of other gases that are metabolic byproducts.
In general, living things use energy to maintain Earth’s atmosphere in a state far from the thermodynamic equilibrium it would reach without life. Astrobiologists would suspect any planet with an atmosphere in a similar state of harboring life. But, as for the other cases, it would be hard to completely rule out non-biological possibilities.
Besides metabolism, the NASA committee identified evolution as a fundamental ability of living things. For an evolutionary process to occur there must be a group of systems, where each one is capable of reliably reproducing itself. Despite the general reliability of reproduction, there must also be occasional random copying errors in the reproductive process so that the systems come to have differing traits. Finally, the systems must differ in their ability to survive and reproduce based on the benefits or liabilities of their distinctive traits in their environment. When this process is repeated over and over again down the generations, the traits of the systems will become better adapted to their environment. Very complex traits can sometimes evolve in a step-by-step fashion.
Mix named this the Darwin life definition, after the nineteenth century naturalist Charles Darwin, who formulated the theory of evolution. Like the Haldane definition, the Darwin life definition has important shortcomings. It has trouble including everything that we might think of as alive. Mules, for example, can’t reproduce, and so, by this definition, don’t count as being alive.
Despite such shortcomings, the Darwin life definition is critically important, both for scientists studying the origin of life and astrobiologists. The modern version of Darwin’s theory can explain how diverse and complex forms of life can evolve from some initial simple form. A theory of the origin of life is needed to explain how the initial simple form acquired the capacity to evolve in the first place.
The chemical systems or life forms found on other planets or moons in our solar system might be so simple that they are close to the boundary between life and non-life that the Darwin definition establishes. The definition might turn out to be vital to astrobiologists trying to decide whether a chemical system they have found really qualifies as a life form. Biologists still don’t know how life originated. If astrobiologists can find systems near the Darwin boundary, their findings may be pivotally important to understanding the origin of life.
Can astrobiologists use the Darwin definition to find and study extraterrestrial life? It’s unlikely that a visiting spacecraft could detect to process of evolution itself. But, it might be capable of detecting the molecular structures that living organisms need in order to take part in an evolutionary process. Philosopher Mark Bedau has proposed that a minimal system capable of undergoing evolution would need to have three things: 1) a chemical metabolic process, 2) a container, like a cell membrane, to establish the boundaries of the system, and 3) a chemical “program” capable of directing the metabolic activities.
Here on Earth, the chemical program is based on the genetic molecule DNA. Many origin-of-life theorists think that the genetic molecule of the earliest terrestrial life forms may have been the simpler molecule ribonucleic acid (RNA). The genetic program is important to an evolutionary process because it makes the reproductive copying process stable, with only occasional errors.
Both DNA and RNA are biopolymers; long chainlike molecules with many repeating subunits. The specific sequence of nucleotide base subunits in these molecules encodes the genetic information they carry. So that the molecule can encode all possible sequences of genetic information it must be possible for the subunits to occur in any order.
Steven Benner, a computational genomics researcher, believes that we may be able to develop spacecraft experiments to detect alien genetic biopolymers. He notes that DNA and RNA are very unusual biopolymers because changing the sequence in which their subunits occur doesn’t change their chemical properties. It is this unusual property that allows these molecules to be stable carriers of any possible genetic code sequence.
DNA and RNA are both polyelectrolytes; molecules with regularly repeating areas of negative electrical charge. Benner believes that this is what accounts for their remarkable stability. He thinks that any alien genetic biopolymer would also need to be a polyelectrolyte, and that chemical tests could be devised by which a spacecraft might detect such polyelectrolyte molecules. Finding the alien counterpart of DNA is a very exciting prospect, and another piece to the puzzle of identifying alien life.
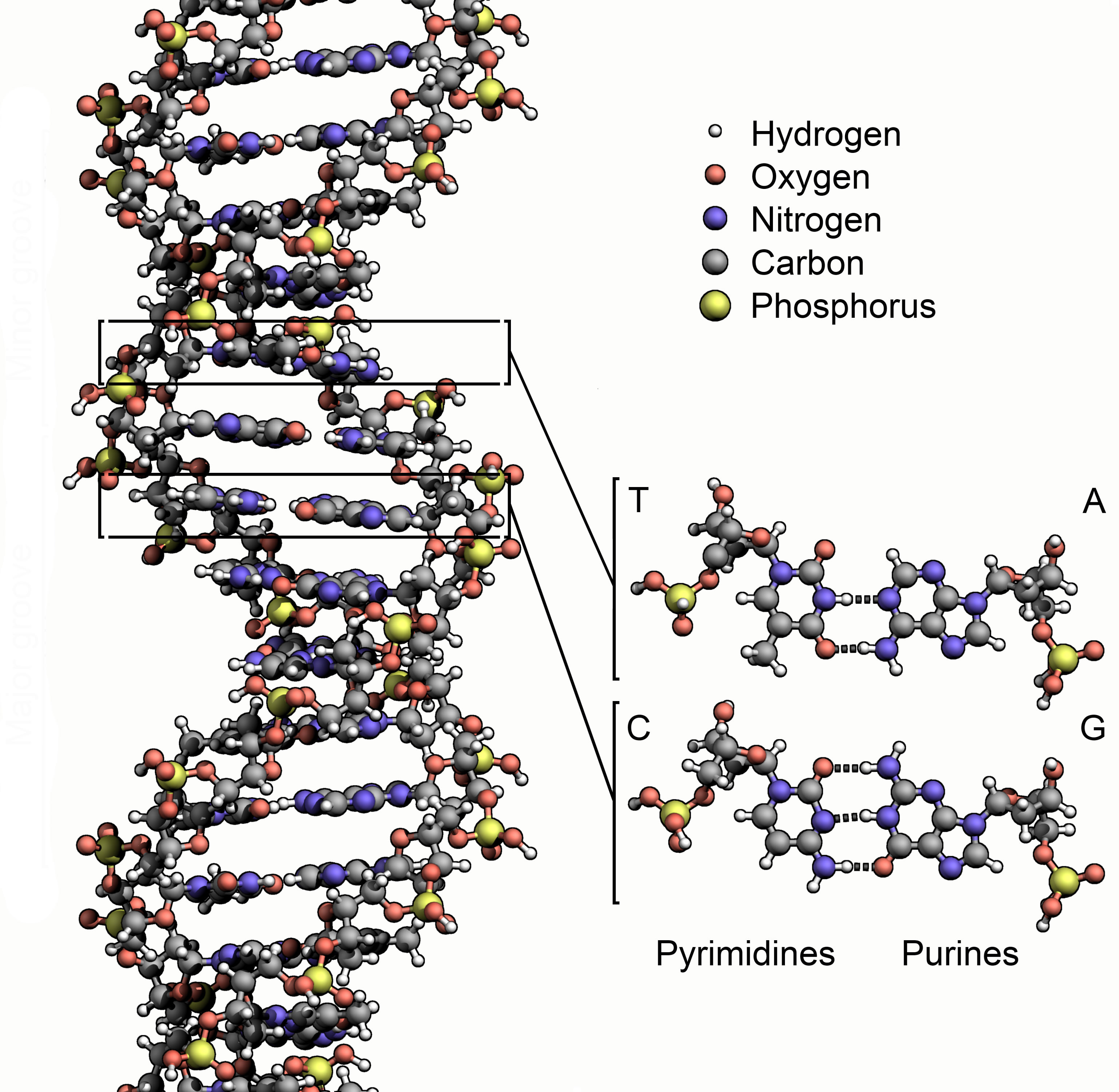
Credit: Zephyris
In 1996 President Clinton, made a dramatic announcement of the possible discovery of life on Mars. Clinton’s speech was motivated by the findings of David McKay’s team with the Alan Hills meteorite. In fact, the McKay findings turned out to be just one piece to the larger puzzle of possible Martian life. Unless an alien someday ambles past our waiting cameras, the question of whether or not extraterrestrial life exists is unlikely to be settled by a single experiment or a sudden dramatic breakthrough. Philosophers and scientists don’t have a single, sure-fire definition of life. Astrobiologists consequently don’t have a single sure-fire test that will settle the issue. If simple forms of life do exist on Mars, or elsewhere in the solar system, it now seems likely that that fact will emerge gradually, based on many converging lines of evidence. We won’t really know what we’re looking for until we find it.
References and further reading:
P. S. Anderson (2011) Could Curiosity Determine if Viking Found Life on Mars?, Universe Today.
S. K. Atreya, P. R. Mahaffy, A-S. Wong, (2007), Methane and related trace species on Mars: Origin, loss, implications for life, and habitability, Planetary and Space Science, 55:358-369.
M. A. Bedau (2010), An Aristotelian account of minimal chemical life, Astrobiology, 10(10): 1011-1020.
S. A. Benner (2010), Defining life, Astrobiology, 10(10):1021-1030.
E. Machery (2012), Why I stopped worrying about the definition of life…and why you should as well, Synthese, 185:145-164.
G. M. Marion, C. H. Fritsen, H. Eicken, M. C. Payne, (2003) The search for life on Europa: Limiting environmental factors, potential habitats, and Earth analogs. Astrobiology 3(4):785-811.
L. J. Mix (2015), Defending definitions of life, Astrobiology, 15(1) posted on-line in advance of publication.
P. E. Patton (2014) Moons of Confusion: Why Finding Extraterrestrial Life may be Harder than we Thought, Universe Today.
T. Reyes (2014) NASA’s Curiosity Rover detects Methane, Organics on Mars, Universe Today.
S. Seeger, M. Schrenk, and W. Bains (2012), An astrophysical view of Earth-based biosignature gases. Astrobiology, 12(1): 61-82.
S. Tirard, M. Morange, and A. Lazcano, (2010), The definition of life: A brief history of an elusive scientific endeavor, Astrobiology, 10(10):1003-1009.
C. R. Webster, and numerous other members of the MSL Science team, (2014) Mars methane detection and variability at Gale crater, Science, Science express early content.
Did Viking Mars landers find life’s building blocks? Missing piece inspires new look at puzzle. Science Daily Featured Research Sept. 5, 2010
NASA rover finds active and ancient organic chemistry on Mars, Jet Propulsion laboratory, California Institute of Technology, News, Dec. 16, 2014.