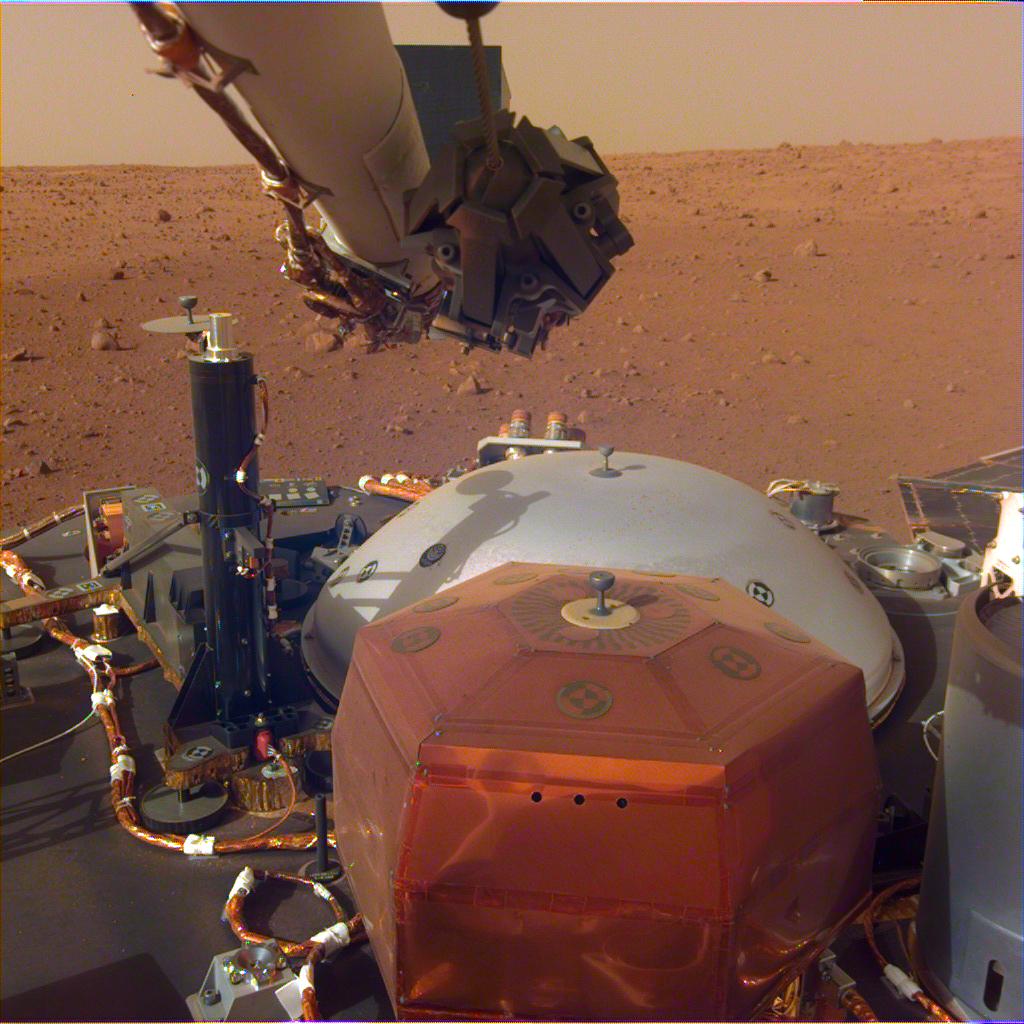
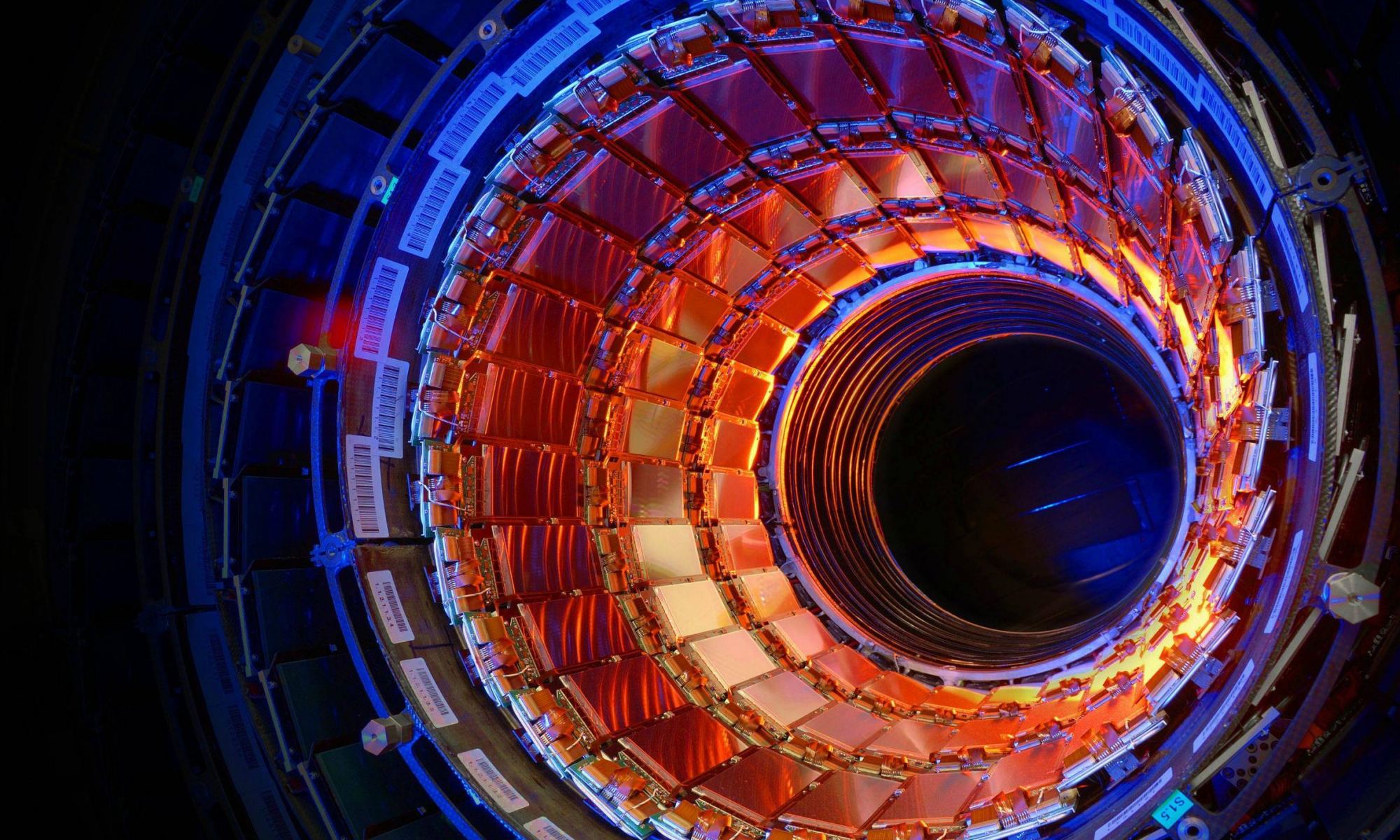
Scientists with the Deep Carbon Observatory (DCO) are transforming our understanding of life deep inside the Earth, and maybe on other worlds. Their discoveries suggest that abundant life could exist in the sub-surface of other planets and moons, even where temperatures are extreme, and energy and nutrients are scarce. They’ve also discovered that all of the life hidden in the deep Earth contains hundreds of times more carbon than all of humanity, and that the deep biosphere is almost twice the volume of all Earth’s oceans.
“Existing models of the carbon cycle … are still a work in progress.” – Dr. Mark Lever, DCO Deep Life Community Steering Committee.”
The DCO is not a facility, but a group of over 1,000 scientist from 52 countries, including geologists, chemists, physicists, and biologists. They’re nearing the end of a 10-year project to investigate how the Deep Carbon Cycle affects Earth. 90 % of Earth’s carbon is inside the planet, and the DCO is our first effort to really understand it.



![This illustration shows the percentage of marine animals that went extinct during Earth's worst extinction at the end of the Permian era by latitude, from the model (black line) and from the fossil record (blue dots).A greater percentage of marine animals survived in the tropics than at the poles. The color of the water shows the temperature change, with red being most severe warming and yellow less warming. At the top is the supercontinent Pangaea, with massive volcanic eruptions emitting carbon dioxide. The images below the line represent some of the 96 percent of marine species that died during the event. [Includes fossil drawings by Ernst Haeckel/Wikimedia; Blue crab photo by Wendy Kaveney/Flickr; Atlantic cod photo by Hans-Petter Fjeld/Wikimedia; Chambered nautilus photo by John White/CalPhotos.]Justin Penn and Curtis Deutsch/University of Washington](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Penn_sumfig_final.jpg)