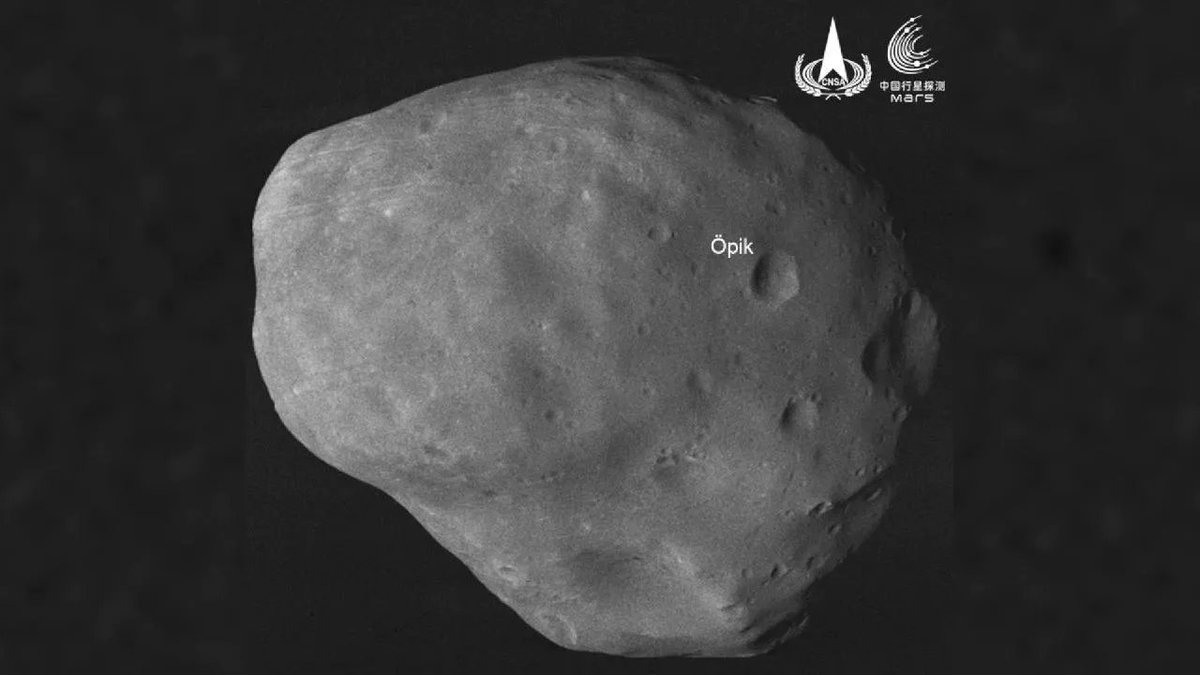
Two fundamental factors affect all astrophotography – timing and location. If a camera happens to be at the right place at the right time, it can capture images that have never been seen before. And with the proliferation of cameras throughout the solar system, more and more novel photos will be captured at an ever-increasing frequency. China’s Tianwen-1 probe added to that novel collection to celebrate its second anniversary by taking a shot of Mars’ moon Phobos.
Continue reading “New Pics of Phobos From China’s Tianwen-1 Orbiter”Not Just a Planet Hunter. TESS Found Over 25,000 Flaring Stars
One of the beauties of modern-day space telescopes is that the data they produce, which is eventually wholly released to the public, contains useful information about much more than their primary mission objective. Other astronomers can then sift through the data using their own ideas, and in many cases, their own algorithms. Recently, a team from Poland turned a flare-searching algorithm on TESS’s planet-hunting data, and found an astonishing 25,229 stars with solar flares in the data set.
Continue reading “Not Just a Planet Hunter. TESS Found Over 25,000 Flaring Stars”Falling Space Junk has a 10% Chance of Killing Someone in the Next Decade
The statistics of how people die offer a gruesome but informative way to understand both how humans perceive threats and how they react to fear. For example, you are more likely to be crushed by a falling vending machine (~13 people killed per year) than be eaten by a shark (~10 per year). However, there is one currently statistically unlikely cause of death that has a real risk of increasing dramatically in likelihood over the coming decades – falling space debris. According to a new study, there’s a 6-10% chance that someone will die from debris falling from space over the next ten years.
Continue reading “Falling Space Junk has a 10% Chance of Killing Someone in the Next Decade”A Satellite had to Dodge Space Junk as it was Raising its Orbit to Avoid Solar Activity
The phrase “when it rains, it pours” is commonly used in the US to denote that bad things usually happen simultaneously. And it doesn’t only have to apply to things that happen where it can physically rain. Recently an ESA satellite had a series of bad things happen that could potentially have happened to it, but quick action from the team responsible for the satellite avoided two what could have been catastrophic events.
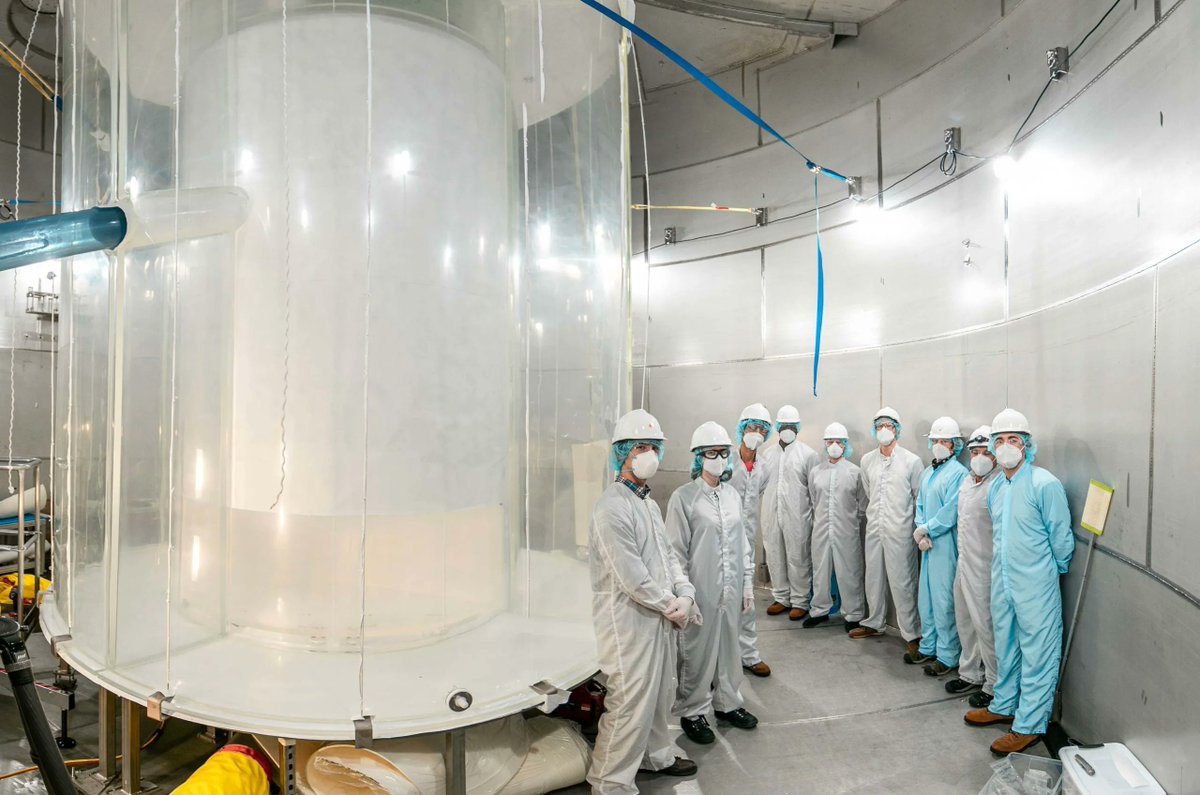
Continue reading “A Satellite had to Dodge Space Junk as it was Raising its Orbit to Avoid Solar Activity”The World’s Most Sensitive Dark Matter Detector has Come Online
Individual contributors have become less and less prominent in scientific fields as the discipline itself has matured. Some individuals still hold the public spotlight for their discoveries, such as Peter Higgs with the Higgs boson, which several other physicists also theorized around the same time he did. However, the actual data that eventually gave Dr. Higgs and François Englert their Nobel prize were collected by the Large Hadron Collider, arguably one of the largest technical projects that took thousands of scientists decades to design, build, and test.
Continue reading “The World’s Most Sensitive Dark Matter Detector has Come Online”Astronomers Have Digitized 94,000 Photographic Plates of the Night sky, Going Back 129 Years
Since the early days of the internet, and even computers more generally, there has been a push to collect all of the world’s information, built up over thousands of years, into a digital form so it can at least theoretically latest indefinitely. It also makes that information much more accessible to people interested in it. That was the motto of the original Google search engine, and specialists in various historical fields have been making slow but steady progress in doing just that over the past few decades. Now astronomy has gained one of its largest hauls of historical data as the Friedrich-Alexander University of Erlangen-Nuremberg has digitized 40,000 of its historical astronomical plates, along with 54,090 plates from other sources.
Continue reading “Astronomers Have Digitized 94,000 Photographic Plates of the Night sky, Going Back 129 Years”A Mission to Reach the Solar Gravitational Lens in 30 Years
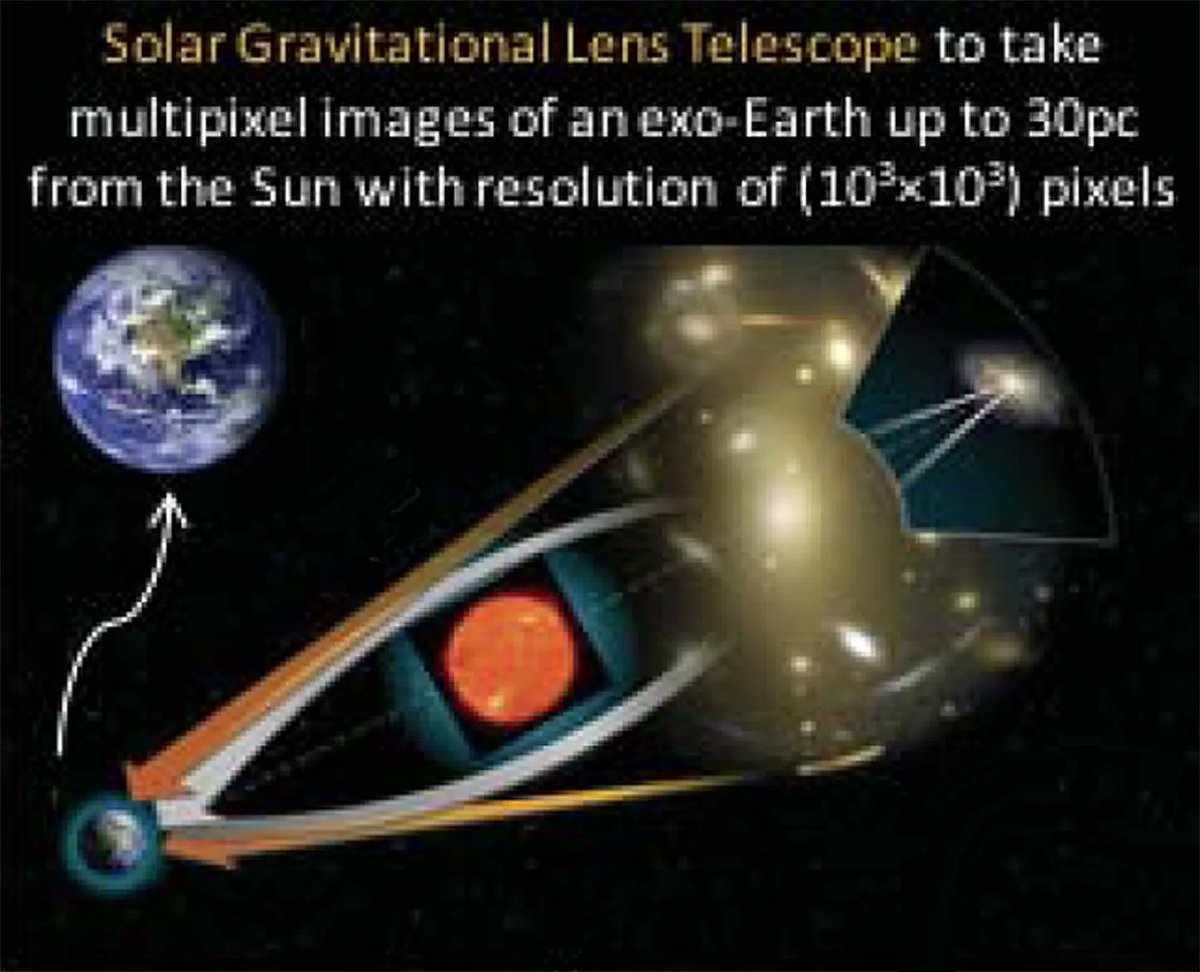
NASA’s Institute for Advanced Concepts is famous for supporting outlandish ideas in the astronomy and space exploration fields. Since being re-established in 2011, the institute has supported a wide variety of projects as part of its three-phase program. However, so far, only three projects have gone on to receive Phase III funding. And one of those just released a white paper describing a mission to get a telescope that could effectively see biosignatures on nearby exoplanets by utilizing the gravitational lens of our own Sun.
Continue reading “A Mission to Reach the Solar Gravitational Lens in 30 Years”Researchers Create a Plasma Bubble With Lasers That Could Provide Propulsion or an Artificial Magnetosphere
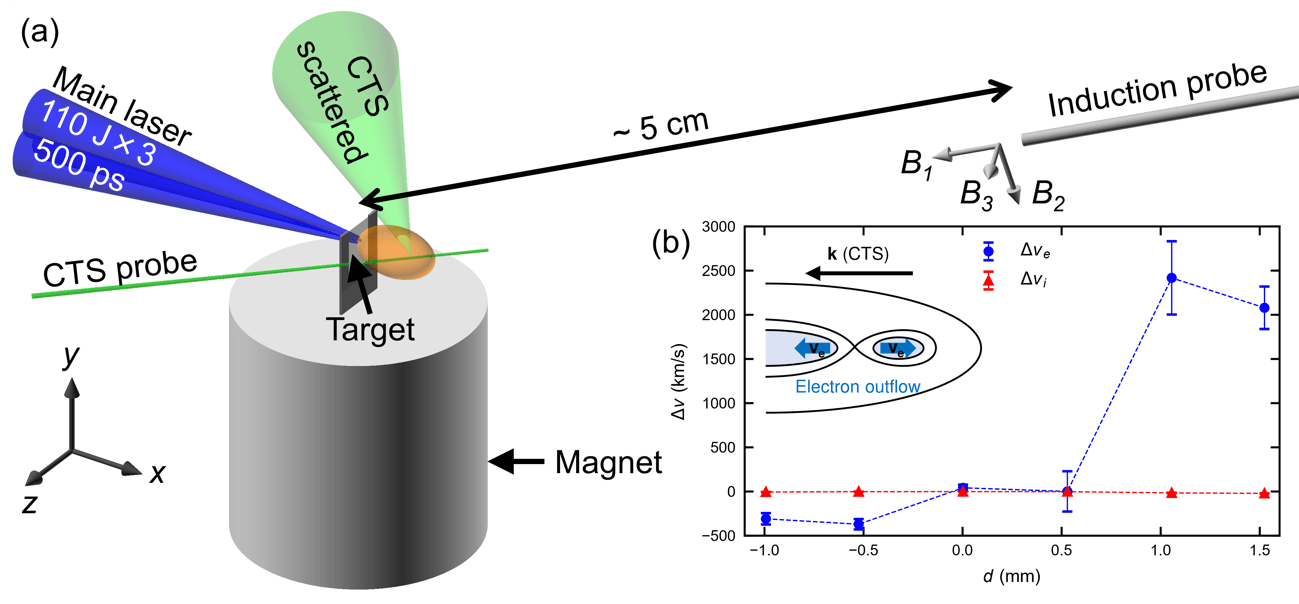
Lasers are useful for a lot of things. They made CDs work (when they were still a thing). They also provide hours of entertainment for cats (and their humans). But they can also create magnetic conditions similar to the surface of the Sun in a lab, according to new research by scientists at Osaka University. And that might help a wide range of other scientific disciplines, ranging from solar astronomy to fusion.
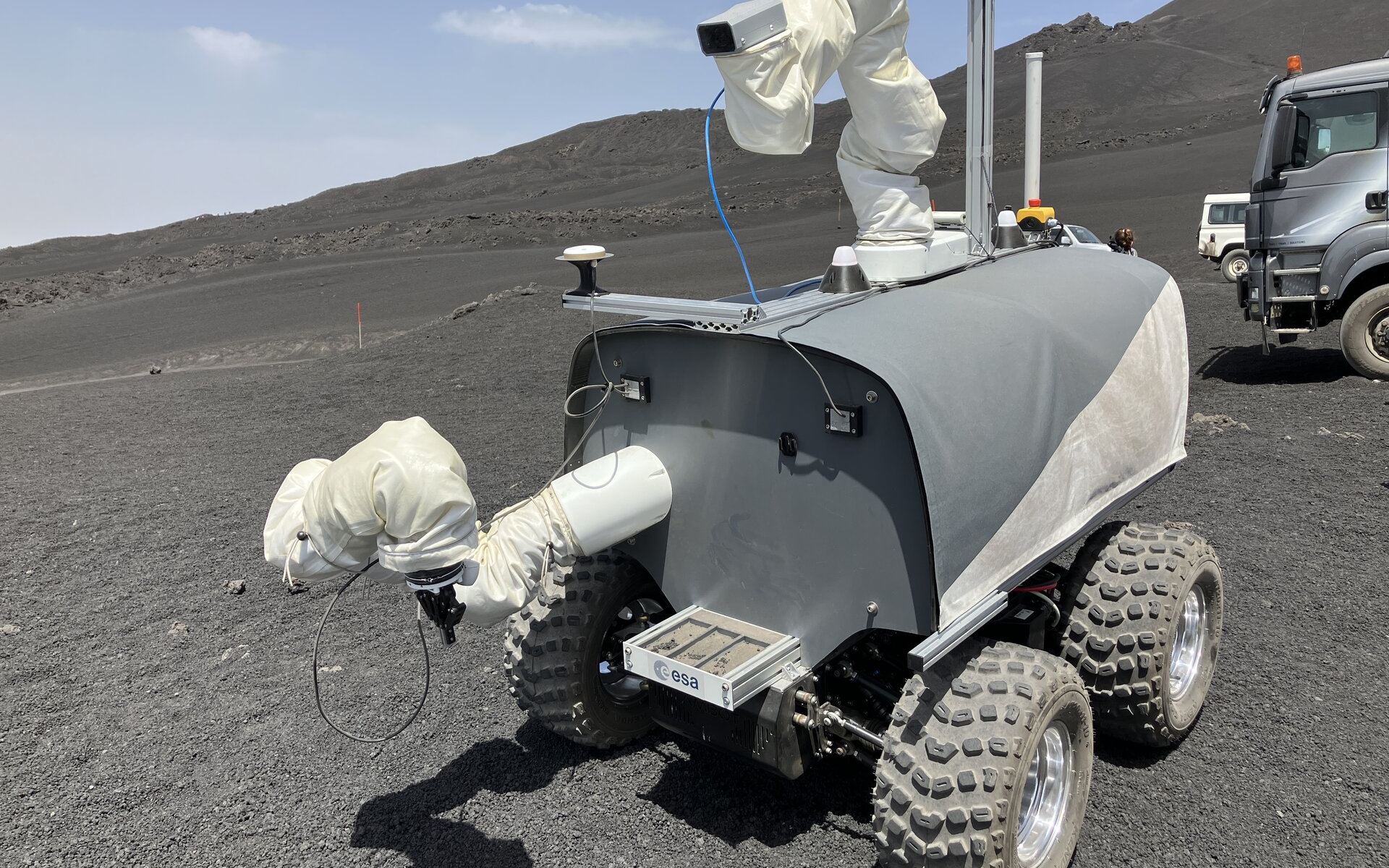
Continue reading “Researchers Create a Plasma Bubble With Lasers That Could Provide Propulsion or an Artificial Magnetosphere”An Astronaut Controlled a Rover as it Collected Samples on Mt Etna. In the Future, it’ll be on the Moon
Lunar exploration has been gaining more and more traction from various sources recently. Every step forward is another towards potentially having a permanent human presence on another solar system body. ESA took another step recently with the completion of its Analog-1 robotics test, which took place successfully on the slopes of Mt Etna earlier this month.
Continue reading “An Astronaut Controlled a Rover as it Collected Samples on Mt Etna. In the Future, it’ll be on the Moon”An Ambitious Plan to Find Earth 2.0
When it comes to astronomy, the more instruments watching the sky, the better. Which is why it has been so frustrating that the world’s rising superpower – China – has long lacked focus on space-science missions. In recent years, with some notable exceptions, China’s space agency has focused on lunar exploration and human spaceflight, as well as some remote monitoring capabilities, leaving the technical know-how of arguably the world’s second more capable country on the sidelines when it comes to collecting space science data. Now, a team led by Jian Ge of the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory has suggested the most ambitious Chinese-led space science mission to date. And it plans to search for one of the holy grails of current astronomy research – an exoplanet like Earth.
Continue reading “An Ambitious Plan to Find Earth 2.0”