[/caption]
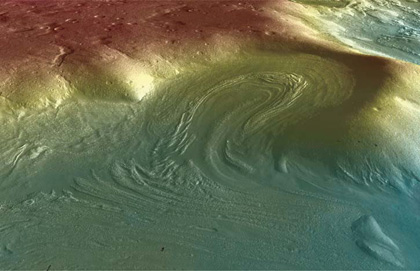
There’s more than just a little ice under Mars’ surface. According to data from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter radar system, vast Martian glaciers of water ice lie buried under rocky debris. And this ice is not just at the Arctic region where the Phoenix lander scratched the surface in searching for ice. MRO found evidence for a huge amount of underground ice at much lower latitudes than any ice previously identified on the Red Planet. “Altogether, these glaciers almost certainly represent the largest reservoir of water ice on Mars that is not in the polar caps,” said John W. Holt of the University of Texas at Austin, who is lead author of the report. “Just one of the features we examined is three times larger than the city of Los Angeles and up to half a mile thick. And there are many more. In addition to their scientific value, they could be a source of water to support future exploration of Mars.”
Scientists say buried glaciers extend for dozens of miles from the edges of mountains or cliffs. A layer of rocky debris blanketing the ice may have preserved the underground glaciers as remnants from an ice sheet that covered middle latitudes during a past ice age. This discovery is similar to massive ice glaciers that have been detected under rocky coverings in Antarctica.
Scientists have been puzzled by what are known as aprons — gently sloping areas containing rocky deposits at the bases of taller geographical features — since NASA’s Viking orbiters first observed them on the Martian surface in the1970s. One theory has been that the aprons are flows of rocky debris lubricated by a small amount ice. Now, the shallow radar instrument on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter has provided scientists an answer to this Martian puzzle.
“These results are the smoking gun pointing to the presence of large amounts of water ice at these latitudes,” said Ali Safaeinili, a shallow radar instruments team member with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif.
The buried glaciers lie in the Hellas Basin region of Mars’ southern hemisphere. The radar also has detected similar-appearing aprons extending from cliffs in the northern hemisphere.

Radar echoes received by the spacecraft indicated radio waves pass through the aprons and reflect off a deeper surface below without significant loss in strength. That is expected if the apron areas are composed of thick ice under a relatively thin covering. The radar does not detect reflections from the interior of these deposits as would occur if they contained significant rock debris. The apparent velocity of radio waves passing through the apron is consistent with a composition of water ice.
“There’s an even larger volume of water ice in the northern deposits,” said JPL geologist Jeffrey J. Plaut, who will be publishing results about these deposits in the American Geophysical Union’s Geophysical Research Letters. “The fact these features are in the same latitude bands, about 35 to 60 degrees in both hemispheres, points to a climate-driven mechanism for explaining how they got there.”
The rocky debris blanket topping the glaciers apparently has protected the ice from vaporizing, which would happen if it were exposed to the atmosphere at these latitudes.
“A key question is, how did the ice get there in the first place?” said James W. Head of Brown University in Providence, R.I. “The tilt of Mars’ spin axis sometimes gets much greater than it is now. Climate modeling tells us ice sheets could cover mid-latitude regions of Mars during those high-tilt periods. The buried glaciers make sense as preserved fragments from an ice age millions of years ago. On Earth, such buried glacial ice in Antarctica preserves the record of traces of ancient organisms and past climate history.”
Source: NASA

Source article?
http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/081120-martian-glaciers.html
Cool!
Now we just need Ahnuld to activate the ancient reactor to thaw the ice.
jasond- Nope. NASA.
Can anyone guess about how approximately much water there is in a city the size of Los Angeles and a half mile thick?
And where does that put Mars in relationship to the water of the Moon?
And can anyone explain what is the difference between Moon dust and Martian dust.
Thanks
Oh, man, this is awesome news.
Terraforming, here we come.
Though the amount does not yet seem sufficient.
Depends on how much of a terraform your out to do.
Find a nice cave, cap the entrances, shock-crete the walls, pump in the martian made atmosphere and you’ve got the makings for a good sized human city.
Thats already one hell of a goal.
Leave the details of a full terraform to the martians.
The more we discover about Mars, the more Kim Stanley’s Mars trilogy — Red Mars, Blue Mars, Green Mars — looks do-able. Now, if there were only a Mars where Deja Thoris ruled with John Carter . . .{sigh}
Don Alexander Says:
November 20th, 2008 at 3:35 pm
“Oh, man, this is awesome news.
Terraforming, here we come.”
>>>’Total Recall’ here we come!
“jasond Says:
November 20th, 2008 at 1:05 pm
Source article?”
>>>Notice the little line at the end of every single UT article in existence – >’source: ___’. Also notice that it says NASA on this particular article.
wow.
Assuming just land and according to wiki data and making some wild assumptions and relying on my dodgy maths ..
LA = 71000m x 41000m x 800m Deep ( 1/2 mile )
= 2669600000000 m3
less say 9% for water to ice
= 2429336000000 ltrs of water
= ~ 971735 Olympic sized swimming pools of water.
Of course, this could be wrong … 🙂
Alandee – You probably pulled the dimensions for L.A. county. 71km by 41km is pretty big. The City of Los Angeles would be quite a bit smaller.
We Freman are not pleased that you have found our water caches.
Shai-Hulud!!!
Mars looks to be a lot more amenable to human habitation than the Moon. Come on, Humankind, get there in my lifetime!
Sometimes when i think of the developments in understanding Mars and its history, it is very surprising…Just 4 yrs ago when the twins landed, we had only hopes and speculations…Now damn solid facts …. It is a huge advancement in understanding the Martian evolution….It is filled with breakthroughs after breakthroughs… Makes me feel damn proud of the little ones there and the team here…..Best Wishes for more interesting news…
maudyfih asks
“And can anyone explain what is the difference between Moon dust and Martian dust.”
Moon dust grains are sharp edged, like asbestos dust. Moon dust is a health hazard, similar to asbestos on Earth, or to “fresh” stone dust in a mine.
Mars dust has been tumble polished by being blown about in the wind. The grains are smooth, like miniature pebbles, like fine desert sand on Earth.
Thanks Alandee,
Even if the measurements of the city of LA. were half that size, that is a lot of water and that is only one spot? WOW………..
I wish NASA would talk more about
this finding and what it means to them.
“Just one of the features we examined is three times larger than the city of Los Angeles and up to half a mile thick”
The above comment is important to note. Three times the City of LA is a huge area!
The surface of Mars is 38.000 times the area of LA. The glaciers by far do not contain enough ice to create a wet Mars, and the atmospheric pressure on Mars is too low for liquid water: it boils away as soon as the melting ice releases it.
You need a whole lot more than just some water to make a place habitable. You need a complex living environment. This is not available on Mars. This place is deadly cold, the air is thin and free of oxygen, there is no water to drink, there is nothing to eat, no rainfall ever, no grass, no trees, no flowers, no animals, no smells except your own.
Mars is a planet, but that does not give it any virtues to become a home.
Even the top of Mount Everest is extremely better habitable than any place on Mars. Living on Mars means living in a space suit 24 hours a day every day for the rest of your life.
Compared to that, any life sentence is paradise.
Regards,
Günther
I wanted to correct your article. You said:
“This place [Mars] is deadly cold, the air is thin and free of oxygen, there is no water to drink, there is nothing to eat, no rainfall ever, no grass, no trees…”
No trees?
Then what is this log that the rover photographed on Mars and is on JPL’s website?
http://marsrovers.jpl.nasa.gov/gallery/all/1/n/115/1N138388241EFF2700P1994R0M1.HTML
Closeup. If you don’t believe this image, use your own software to zoom into JPL’s image.
http://img132.imageshack.us/img132/9321/moontworg4.jpg
There are 4 explanations for this.
1. A NASA employee photoshopped imagery coming from the rover and planted a tree log in the middle of Mars
2. A HACKER photoshopped imagery from JPL’s website, broke into NASA’s computers and pasted the photoshopped image over the original.
3. A TREE or railroad tie was jettisoned from Earth and landed in Mars completely in tact, while not disturbing the martian soil.
4. TREES exist or have existed on Mars and NASA is covering it up.
I have my own opinion. Anybody else want to theorize how a Martian piece of wood from a tree is photographed by the Mars rover and uploaded to NASA’s website?