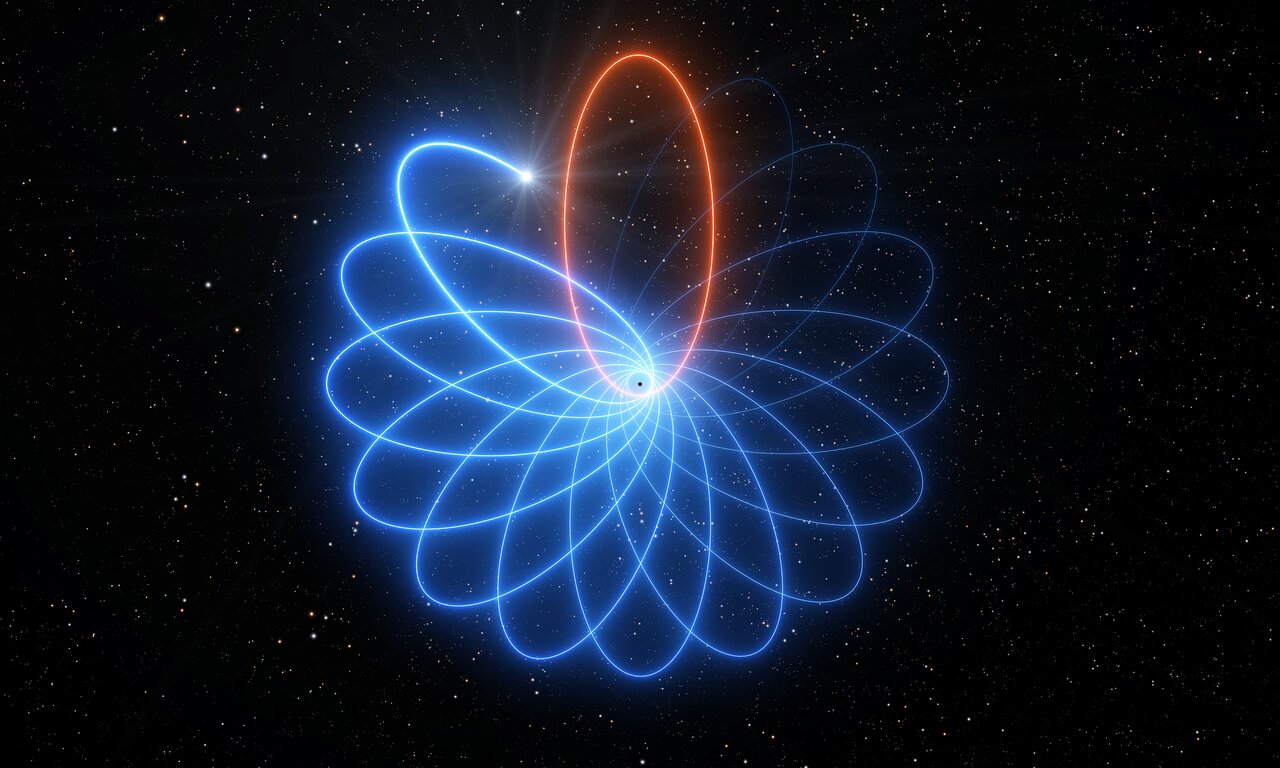
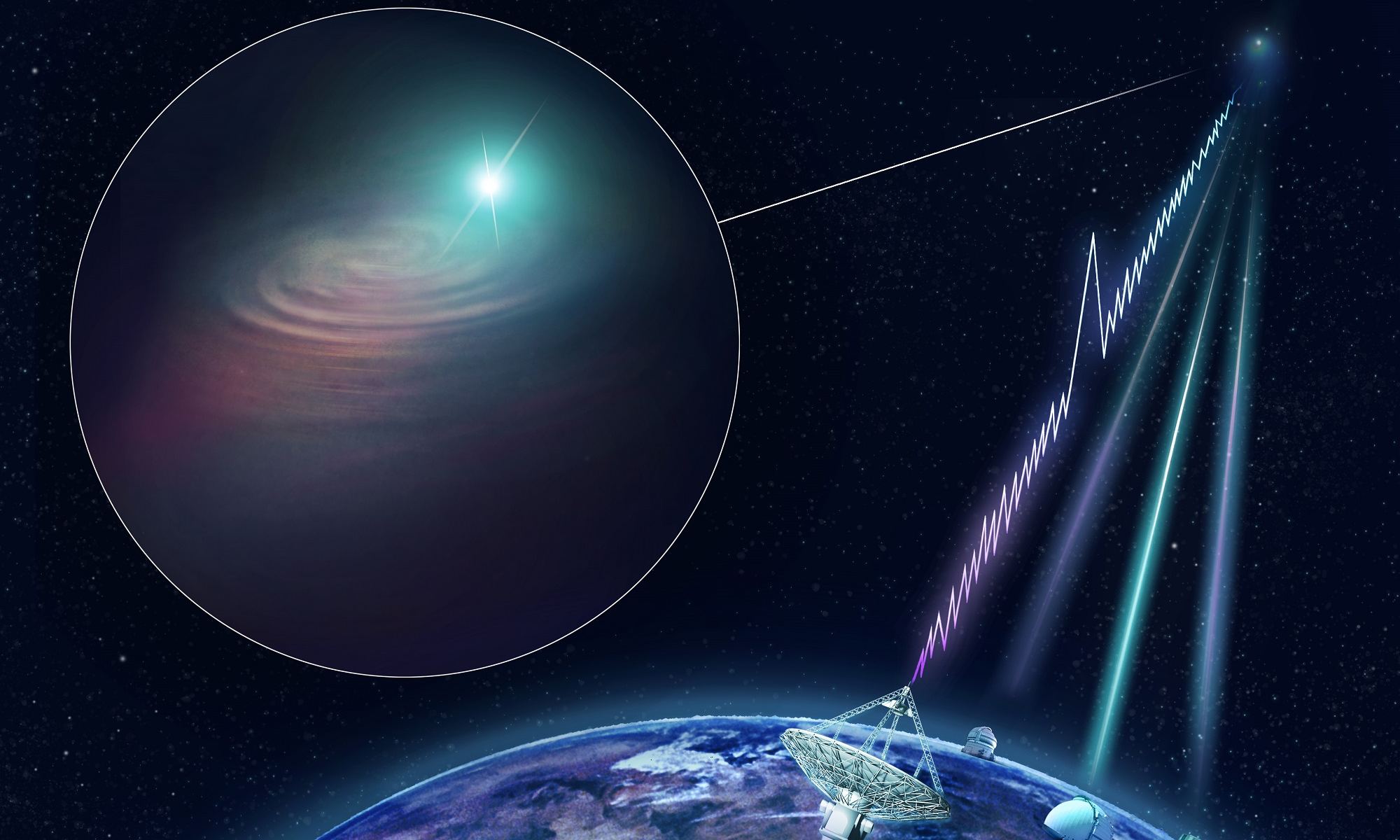
At the center of our galaxy, roughly 26,000 light-years from Earth, is the Supermassive Black Hole (SMBH) known as Sagittarius A*. The powerful gravity of this object and the dense cluster of stars around it provide astronomers with a unique environment for testing physics under the most extreme conditions. In particular, it offers them a chance to test Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity (GR).
For example, in the past thirty years, astronomers have been observing a star in the vicinity of Sagittarius A* (S2) to see if its orbit conforms to what is predicted by General Relativity. Recent observations made with the ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) have completed an observation campaign that confirmed that the star’s orbit is rosette-shaped, once again proving that Einstein theory was right on the money!
Continue reading “A Star is Orbiting the Milky Way’s Black Hole and Moving Exactly How Einstein Predicted it Should”